Before during after vocabulary strategies
advertisement

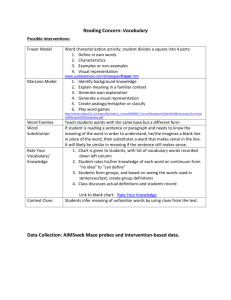
Monthlymeetings.wikispaces.com Why Vocabulary? Vocabulary knowledge is related to reading comprehension, intelligence, content knowledge, and reasoning. -Stahl, 1999 How confident do you feel about your vocabulary instruction? On a scale of 1 – 9, how confident are you about your vocabulary instruction? Place a post-it on the scale on the wall– 1 is the lowest & 9 is the highest. 1 5 9 Adapted from Dale, Rasband, Ross, Gardner, & Cunningham, 2004 How do you teach vocabulary? • Discuss within your group. • Record your responses. • Share out. Essential Questions: Why is vocabulary instruction so important? What are exemplary strategies for vocabulary instruction? What strategies do we want students to use during reading? 4 Components of an Effective Vocabulary Program 1. Wide or extensive reading to expand word knowledge, 2. Instruction in specific words to enhance comprehension of texts containing those words, 3. Instruction in independent word-learning strategies, and 4. Word consciousness and word play activities to motivate and enhance learning. Michael Graves, 2000 Components of Vocabulary Instruction The National Reading Panel (2000) concluded that there is no single research-based method for teaching vocabulary. From its analysis, the panel recommended using a variety of direct and indirect methods of vocabulary instruction. Direct or Intentional Vocabulary Instruction • Explicit instruction of vocabulary is highly effective. To develop vocabulary intentionally, students should be explicitly taught both specific words and word-learning strategies. • -National Reading Panel (2000) Research–based Strategies for Vocabulary Development • Wide and Extensive Reading • Morphemic Analysis • Contextual Analysis • Dictionary Use • Cognate Analysis (ELL) Word knowledge is much more than word identification or even definitional knowledge– “It takes more than definitional knowledge to know a word, and we have to know words in order to identify them in multiple reading and listening contexts and use them in our speaking and writing.” (Allen, 1999) Finding definitions and writing those words in sentences have had little apparent impact on their word knowledge and language use. Janet Allen, 1999 Dictionary Use! • When students have been provided dictionary definitions and asked to create sentences or answer brief questions about the words, research has shown: • 63 percent of the students’ sentences were judged to be “odd” (Miller & Gildea, 1985) • 60 percent of students’ responses were unacceptable (McKeown, 1991; 1993) When the horse you are riding dies, DISMOUNT! Some dead horses for vocabulary instruction… 1. Do not give students isolated words or weekly spelling words to look up in the dictionary and write sentences. This is a deadly useless activity that is boring, not good instruction, and only teaches student how boring it is to learn new words. 2. Move away from fill in the blank, or matching word definitions in isolation. Reading Aloud "The single most important activity for building the knowledge required for eventual success in reading is reading aloud to children." Becoming a Nation of Readers (1985) Wide Reading • Students learn more words than a year than we can teach • Best way for students to learn many words in conjunction with learning word parts Vocabulary Instruction Direct teaching of vocabulary can help improve comprehension when we follow these guidelines (Cooper, 1993): • A few critical words are taught. • The words are taught in a meaningful context. (including nonlinguistic representations) • Students relate the new words to their background knowledge. • Students are exposed to the words multiple times. Planning- Which Words to Choose? Fiction • Words that are important to the theme • Words necessary to understand the story Nonfiction • Words necessary to understand the text (usually in bold or italics) Words that are common across many contexts (tier 2 words) Planning- Instruction Routine • Students need repetition with the words that will be explicitly taught • Have a routine for explaining the words • Deep understanding of the words • Have a routine for practice with the words • Engage in activities with the words • Encourage students to discuss the words • Read the words in context What are exemplary strategies for vocabulary instruction? Explicit Vocabulary Instruction Vocabulary instruction is embedded within the instructional routine for reading and follows a before, during and after reading format. Before Reading Instruction Activities • Archer’s Instructional • Frayer Model Routine for Vocabulary • Marzano’s Building Academic VocabularySteps 1-3 • Beck’s Questioning Strategies • Semantic Mapping • Word and Concept Sorts During Reading Instruction Activities • Model strategy use • Vocabulary Tree Map • Monitor/support • Dictionary student strategy use • Providing affirmative and corrective feedback After Reading Instruction Activities • Marzano’s Building • Frayer Model Academic VocabularySteps 4-6 • Beck’s Questioning Strategies • Semantic Mapping • Word and Concept Sorts Background Knowledge The relationship between vocabulary knowledge and background knowledge is explicit in research. (Nagy & Herman, 1984; Marzano, 2004; Hart & Risley, 1995) “Our inner-city student might have little background knowledge related to camping trips but a lot related to getting around the city on the subway. Consequently, he would have difficulty learning and integrating new information about camping trips but would find it easy to learn new information about transportation via subway systems”. (Marzano, 2004) Marzano’s Six Step Process • Step 1- Provide a description, explanation or example of • • • • • the new term Step 2- Ask students to restate the description, explanation or example in their own words Step 3- Ask students to construct a picture, symbol, or graphic representation of the term Step 4- Engage students periodically in activities to help them add to their knowledge of the terms in their notebooks Step 5- Ask students to discuss the words with one another. Step 6- Involve students periodically in games that allow them to plan with terms Knowledge Rating Scale Word tyranny serendipity grapnel purport sensitive dubious Know it well, can explain it, use it Know some- Have seen thing about or heard it, can relate the word it to a situation Do not know the word Word Sorts- organizing words into categories hurricanes Why is this a good before reading strategy? Word Sorts hurricanes • Provide students with a set of vocabulary word cards (related to a specific concept or topic). • Work in groups to sort the words into categories. • Encourage students to find more than one category for the vocabulary words. • Students then discuss with teacher & peers their rationale for categorizing words. Let’s sort! Concept Circles Before Reading: Westward Movement Describe the meaning and relationships between and among the words in the sections of the concept circles. terrain disease Traveling west had many hardships. One of the many hardships were diseases that the people had without medical help. Wagons would need to hold many delicacies. For instance, food you’d need to eat and live on were carried in them. The trails could have bad terrain, or could be all flat. Hunting was important and learning how to hunt for buffalo, elk, deer, and birds was learned while on the trail and served as good food for all. Concept Circles Assessment: Circulatory System Describe the meaning and relationships between and among the words in the sections of the concept circles. (Which word does NOT belong? Write why below.) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Migrate • Sentence from text- Philpe’s family migrates from Virginia to Florida every year to pick oranges. Schwartz & Raphael, 1985 What is it? What is it like? To move regularly from one region to another moving around Part of speech relocating verb traveling migrate people working for seasonal jobs birds Nomads What are some examples? Word Map What is it? What is it like? Part of speech Scaffold What are some examples? Frayer Model Definition An extreme state of agitation. Characteristics Stress, anxiety, tension, hostility, Tears, physical symptoms SWIVET First, last week of school. Unexpected guests for dinner Four projects due Examples Sitting on the porch reading Bubble bath Lounging by the pool Non-Examples Frayer Model Definition Characteristics What is a Noun? Examples Non-Examples Fryer Model Visual Representation Term sphere Definition A round 3-D shape Personal Association My ball is the shape of a sphere. PRIME SCIENCE & PRIME SOCIAL STUDIES Which words would you pre-teach? Which words would you explain while you read? Frayer Model- Choose a word from the PRIME text Definition Examples Characteristics Non-Examples Contextual Redefinition Work with a group to make predictions for definitions of each of the following words. The words included here are found in Notes on the Space We Take. Remember that some words which look familiar will probably have new meanings in this context. WORD hiss exoskeleton Vulnerability Predicted Definition Definition Based on Context Context Clues Used Marzano’s Six Step Process • Step 1- Provide a description, explanation or example of • • • • • the new term Step 2- Ask students to restate the description, explanation or example in their own words Step 3- Ask students to construct a picture, symbol, or graphic representation of the term Step 4- Engage students periodically in activities to help them add to their knowledge of the terms in their notebooks Step 5- Ask students to discuss the words with one another. Step 6- Involve students periodically in games that allow them to plan with terms During Reading- Scaffolding • Brief explanation of words not important to concept or theme, but helpful to understanding the text • Moccasins- show a picture or provide a good explanation • Give synonyms, antonyms and examples • Point out word parts that the students are familiar During Reading- Scaffolding • Dictionary • How do you use the dictionary? • Only helpful when have context to help figure out the meaning • May need to revisit after reading to check for understanding Fryer Model- During Reading Visual Representation Term sphere Definition A round 3-D shape Personal Association My ball is the shape of a sphere. Contextual Redefinition Work with a group to make predictions for definitions of each of the following words. The words included here are found in Notes on the Space We Take. Remember that some words which look familiar will probably have new meanings in this context. WORD hiss exoskeleton Vulnerability Predicted Definition Definition Based on Context Context Clues Used Semantic Feature Analysis FDR JFK Nixon Reagan Clinton Democrat + + - - + War time President + - + - - Congress (same party) Re-elected Served in Congress Won majority of popular vote Semantic Feature Analysis Convex Equilateral Equiangular 4 sided Opposite sides parallel square x x x x x rectangle x x x x triangle x quadrilateral x Regular polygon x x rhombus x x trapezoid x x x x x PRIME SCIENCE & PRIME SOCIAL STUDIES Which words would you explain while you read? What type of explanation would you provide? Marzano’s Six Step Process • Step 1- Provide a description, explanation or example of • • • • • the new term Step 2- Ask students to restate the description, explanation or example in their own words Step 3- Ask students to construct a picture, symbol, or graphic representation of the term Step 4- Engage students periodically in activities to help them add to their knowledge of the terms in their notebooks Step 5- Ask students to discuss the words with one another. Step 6- Involve students periodically in games that allow them to plan with terms Interactive Notebooks • Students keep a log or journal to record what they are learning •Teacher provides a concept or word. •Students write quickly & spontaneously (free write/quick write) everything they know about the word. •Analyze word parts. •Draw a graphic representation. •Include graphic organizer and foldables used to learn the word. •Peer and/or teacher response. Concept Circles Which word does not belong? Rectangle Cone Hexagon Trapezoid Why? ___________________________________________________ Concept Circles Which word does not belong? Cuba England Hawaii Japan Why? ___________________________________________________ racism stereotyping Church bombing violence Concept: Civil Rights Movement Migrant Hobo Dust Bowl Hoovervilles Concept: The Depression Frayer Model (Frayer, Frederick, & Klausmeier, 1969) Definition Characteristics Best or greatest value Prime Examples Non-Examples Frayer Model (Frayer, Frederick, & Klausmeier, 1969) Content for this example taken from Baron & Heideima, (2002) Teaching Reading in the Content Areas (Supplement), McRel. Definition Characteristics • 2 is the only even prime number A whole number with exactly two divisors (factors) • 0 and 1 are not prime Prime Examples 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, ... •Every whole number can be written as a product of primes Non-Examples 1, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10. . . Frayer or Fryer Model Modifications • Many versions that can be used to expand on word knowledge Frayer or Fryer Model- another version Term sphere noun A round 3-D shape Verb- sphered, sphering To enclose into a sphere Adjective- spherical In the shape of a sphere Beck’s Questioning Strategies • Great sponge activities • A way to informally assess student’s knowledge of the words • Encourages students to truly understand the meaning of the words Questions, Reasons and Examples • Why might you walk around a dark room cautiously? • What is something that you could do to impress your teacher? Why? • Which of these things might be extraordinary? Making Choices • If any of the things I say might be examples of people clutching something say “Clutching”. If not, don’t say anything. Making Choices • I’ll say some things, if they sound leisurely, say “Leisurely.” If you’d need to be in a hurry say “Hurry.” Choices • Ask the children to choose between two words If you and your friends were watching a funny TV show together and began to laugh a lot, would you sound pounce or raucous? One Context for All of the Words • What would an immense plate of spaghetti look like? • Why might you feel miserable after eating all that spaghetti? • What would it look like to eat spaghetti in a leisurely way? Concept SortSort before, during and after vocabulary strategies Before During After + Concept SortSort before, during and after vocabulary strategies Before Knowledge rating scale Student friendly explanations During Dictionary After + Beck’s questioning strategies Student conversations about words Semantic Feature Analysis Synonym, antonyms, examples Games Word maps Frayer/Fryer Model Contextual redefinition Concept sorts Concept circles