The BIG FIVE Components of Reading
advertisement

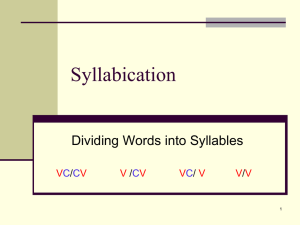
The BIG FIVE Components of Reading Phonics The Big Five Components of Reading Objectives At the end of this series of staff development, you will be able to – Identify the Big 5 of Reading and how you assess each – Discover where the Big 5 are present in your literacy instruction – Be intentional in planning so the Big 5 are present in all your lessons The Big 5 Components of Reading Comprehension Phonological Awareness Phonics Vocabulary Fluency Phonological Processing Phonological Processing Verbal short term memory Word Awareness Phonological Awareness Syllable Awareness Rapid serial naming Rhymin g Articulation speed Phonemic Awareness Phoneme Phoneme Phoneme Phoneme Isolation Categorization Segmentation Blending and Identity Phoneme Manipulation Phonics Objectives You will be able to – Define Phonics and its components – Learn how we assess Phonics – Discover where Phonics is present in your literacy instruction – Be intentional in teaching Phonics Vocabulary • Graphic awareness • Synthetic phonics • Analytic phonics • Structural analysis • Elkonin Boxes Common Core Standards Reading Standards: Foundational Skills (K-5) • Look over the standards for your grade level • Look over the standards to see the progression of phonics skills across the grade levels Writing Independent Reading Balanced Literacy Phonics The relationship between the sounds of a spoken language and the letters of a written language Phonics Graphic Awareness Letter identification Concepts about print Spaces between words Synthetic Phonics Blending Consonants Vowels Digraphs (th, sh, wh, ch) Dipthongs (au, aw, oi, oy) Analytic Phonics Patterns in words Word families Vowel Patterns Closed Open Silent ‘e’ Double vowels Bossy ‘r’ Structural Analysis Prefixes Suffixes Compound words Contractions Syllabication patterns Graphic Awareness Concepts About Print • • • • • • How a book works – front, back Title Where to begin reading, which way to go Punctuation 1:1 matching What is a word? Sentence? Letter? Page 20 in handout Teaching the Letters and Their Sounds Learning letters in English is a hard task because: Problems with Graphic Awareness Phonics: Letter-Sound Association • Letters are abstract shapes and convey no meaning A B C D E F G H Δ Φ Ψ έ Њ Ѓ Ђ ж Problems with Graphic Awareness Letter Names May Sound Alike B “bee” P “pee” D “dee” T “tee” Problems with Graphic Awareness Letter Shapes May Be Similar b d p q V W M h n u m l i j Problems with Graphic Awareness Letter Forms May Be Different A a a G g g D d E e Problems with Graphic Awareness Letter Sounds in Letter Names Letter names that begin with the letter sound: b = ‘bee’ k = ‘kay’ t = ‘tee’ Letter names that end with the letter sound: f = ‘eff’ l = ‘ell` x = ‘ex’ Letter names not containing the letter sound: c = ‘see’ h = ‘aich’ w = ‘double u’ Principles of Teaching Letter-Sound Association • Teach sequentially and systematically • Teach directly and explicitly • Teach to mastery and automaticity • Use multisensory strategies • Teach sound to letter and letter to sound Teaching the Sounds of Letters Multi-Sensory Use picture cues and motions: Pam the lamb cries when she is hungry. She says, “a a a” The bouncing ball bounces all over the floor. “b b b” e = Jen’s Hen i = Pickles the Pig o = Bob the Fox U = Tubby the Tugboat Page 21-22ff in handout Drills for Letter-Sound Association • Flash cards for letter names – both capital and lower case • Flash cards for letter sounds. Use both capital and lower case. • Work with 3-4 letters at a time: – Sand – Shaving cream • Do not allow guessing Letters Consonants: b c d f g h j k l m n p q r s t v w xyz Vowels: a e i o u Sometimes y w R-controlled: ar, or, er/ir/ur Digraphs: sh, ch, wh, th, th, ng n(k) Diphthongs: oo, oo, ow, ou, aw, au, oi, oy Analytic Phonics • Patterns in words (the mind is a pattern seeker) • Word families – Teach the 37 most common rimes that make up 500 primary grade words – Teach one at a time – When children start to see the things words have in common, they see the relationship among words. This makes it easier for them to recognize and spell the words See handout p. 23-24 Synthetic Phonics Moving to Blending of Sounds Begin with a small set of items Vowels: a (begin with short vowels) Consonants: b t s f m Words: at, am, bat, tab, sat, Sam, fat, mat As soon as the “story” and actions for each letter sound are taught, begin to blend the sounds into words. Synthetic Phonics Teaching Blending For “dog” 1. Write d, Point: Sound 2. Students: /d/ 3. Write o, Point: sound 4. Students: /o/ 5. Slide under do, Blend Blend through the vowel 6. Students: /do/ 7. Write g, Point: Sound 8. Students: /g/ 9. Slide under dog, Blend 10. Students: /dog/ 11. What’s the word? 12. Students: dog Synthetic Phonics Blending with long vowel Mile: Write m. Point. Sound? /m/ Write i_e. Point. Sound? /i/ Blend. Slide /mi/ Write l in blank. Point. Sound? /l/ Blend. Slide /mil/ What’s the word? mile Synthetic Phonics Blending 2 syllables Replace: Write r. Point. Sound? Write e. Point. Sound? Blend. Slide Cover re. Write p. Point. Sound? Write l. Point. Sound? Write a__e. Point. Sound? Blend. Slide. Write c. Point to ce. Sound? Blend. Slide Uncover first syllable. Blend. What’s the word? /r/ /e/ /re/ /p/ /l/ /a/ /pla/ /s/ /plas/ replace replace Synthetic Phonics You try it bad show make hi flour steal law nighttime Vowel Patterns Six Types of English Syllables CLOVER Closed: vc, vcv at, hen le: (consonant +le) lit/tle Open: v, cv I, he Vowel teams: v+v eat, see Vowel whiners: au, aw, oy, oi, etc. E: silent e, vowel-consonant e like R: r-controlled, v+r far, for, her, bird, fur HO 25 Vowel Patterns Closed Syllable/Open Syllable Closed (short vowel) rock ask club west Open (long vowel) go me flu hi HO 26-27 Vowel Patterns Silent e When a word or syllable ends in e, the e gives up all its power to make the vowel long. The ending e becomes silent. make Pete mike bone use a__e HO 28 Vowel Patterns Vowel Teams - Vowel Walkers When two vowels go walking, the first one does the talking and the second one is silent. team day feet toe aim flue foal pie fruit May include consonants: igh, eigh Can also be short sound: bread HO 29 Vowel Patterns Vowel Teams - Vowel Whiners (Diphthongs) 2 vowels go together to make a new sound: au, aw fault, hawk oi, oy coil, boy ou, ow shout, cow oo long: moon short: foot HO 30 Vowel Patterns R-controlled Vowel plus r. R changes the sound of the vowel. farm for /er/ spelling most to least common: er ir ur her bird fur HO 31 Structural Analysis Rules for Syllabication • Count syllables • Most common types of syllables: – Consonant + le – VC/CV – V/CV – VC/V HO 35 Structural Analysis Syllables: Consonant + le • -le grabs the consonant before it and makes a syllable; vowel sound is a schwa: e able a/ble handle han/dle True 100% of the time in English HO 36 Structural Analysis Syllables: VCCV • When there are 2 consonants between the vowels, divide between the 2 consonants (closed syllable) goblin gob/lin cotton cot/ton silver sil/ver complex com/plex hundred hun/dred instruct in/struct Vowel is short HO 36 Structural Analysis Syllables: V/CV • When there is only 1 consonant between the vowels, we usually divide before the consonant (open syllable) romance ro/mance rodent ro/dent famous fa/mous pecan pe/can dethrone de/throne Vowel is long HO 37 Structural Analysis Syllables: VC/V • Sometimes when there is one vowel between the consonants, we divide after the consonant (closed syllable) satire sa/tire socket sock/et desert des/ert sat/ire Vowel is short HO 37 Teaching Syllabication Spot and Dot 1. Count the number of syllables Random = 2 syllables = you will hear 2 vowels in this word. 2. Find the first two vowels you hear and put a dot above them. random 3. Draw a line between the 2 dots . . 4. 5. 6. 7. . . random There are 2 consonants between the dots. Divide between them. What kind of syllable is ran? Closed = short vowel What kind of syllable is dom? Closed = short vowel Pronounce word - random HO 40 Teaching Syllabication Spot and Dot 1. 2. Count the number of syllables hotel = 2 syllables = you will hear 2 vowels in this word. Find the first two vowels you hear and put a dot above them. hotel Draw a line between the 2 dots . 3. . 4. 5. 6. 7. . . hotel There is 1 consonant between the dots. Divide before it (usually). What kind of syllable is ho? Open = long vowel What kind of syllable is tel? Closed = short vowel Pronounce word - hotel Teaching Syllabication Spot and Dot 1. 2. Count the number of syllables lemon = 2 syllables = you will hear 2 vowels in this word. Find the first two vowels you hear and put a dot above them. lemon Draw a line between the 2 dots . 3. . 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. . . lemon There is 1 consonant between the dots. Divide before it (usually). What kind of syllable is le? Open = long vowel What kind of syllable is mon? Closed = short vowel Pronounce word – lemon Sometimes the division goes after a single vowel lem on lem=closed=short vowel on=closed=short vowel You try it! Copy Me Teaching: computer com pu ter You try it: fantastic destroy fan tas tic de stroy Structural Analysis • Prefixes • Suffixes • Compound words • Contractions HO 41-44 Segmenting Words (Writing Skill) Elkonin Boxes: 1. Say the word 2. Stretch the word 3. Stretch the word counting sounds 4. Make that number of boxes 5. Slide a marker into each box as you make the sound 6. Later: Ask what sounds are heard and put out letters for those sounds 7. Later: Write the letters that make the sounds in the boxes Elkonin Boxes - Introduction Elkonin Boxes – Sound/Spelling Connection h a t Elkonin Boxes – Independence m l l a a i n t t t e l e You Try Elkonin Boxes • Make boxes for spike lamb dream spoon You Try Elkonin Boxes • Make boxes for s p i k spike lamb dream spoon l e a m b d r e a m s p oo n Principles of Phonics Instruction • Provide explicit instruction • Model the skills • Connect the sounds and the letters • Use manipulatives • Teach simple to complex • Pronounce sounds correctly • Provide guided practice Assessing Phonics • Please turn and talk about the ways you assess phonics and if this is sufficient Phonics Graphic Awareness Letter identification Concepts about print Spaces between words Synthetic Phonics Blending Consonants Vowels Digraphs (th, sh, wh, ch) Dipthongs (au, aw, oi, oy) Analytic Phonics Patterns in words Word families Vowel Patterns Closed Open Silent ‘e’ Double vowels Bossy ‘r’ Structural Analysis Prefixes Suffixes Compound words Contractions Syllabication patterns Resources for Teaching Phonics • http://education.uncc.edu/bric/ reading resources.htm – Letter Naming Fluency Classroom Activities – Nonsense Word Classroom Activities • Handouts • Put Reading First • fcrr.org – Florida Center for Reading Research • Cool Tools • Words Their Way Imagine It and Phonics • Please take out your manual and find where your grade level standards for phonics are taught Phonics Objectives • You will be able to – Define Phonics and its components – Learn how we assess Phonics – Discover where Phonics is present in your literacy instruction – Be intentional in teaching Phonics Vocabulary • Graphic awareness • Synthetic phonics • Analytic phonics • Structural analysis • Elkonin Boxes Common Core Standards Reading Standards: Foundational Skills (K-5) • Look back over the standards for your grade level • Talk with your partner about how you will not only teach the standards for your grade level, but teach previous standards for students who need them Vowel Patterns Consonant + le The –le grabs the consonant before it and makes a syllable. The vowel sound is a schwa: e fid/dle peo/ple fa/ble You do it: trouble trou/ble wiggle wig/gle able a/ble