KETONE BODY METABOLISM - Qassim College of Medicine
advertisement

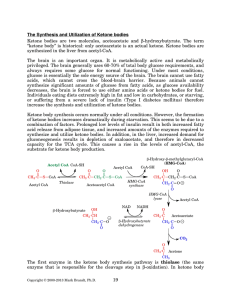
KETONE BODY METABOLISM Dr.Siddiqui Abdulmoeed Associate Professor of Biochemistry College of Medicine Al-jouf University OBJECTIVES • Define ketone bodies. List the functions of ketone bodies • Describe the synthesis of ketone bodies (Ketogenesis) • Describe the catabolism of ketone bodies (ketogenolysis) • Define Ketoacidosis, list its main metabolic causes & explain its mechanism of occurrence. Define ketone bodies. KETONE BODIES [KBs] are water soluble organic compounds generated in human body under certain metabolic conditions. The compounds acetone, acetoacetate and β–hydroxy butyrate are known as ketone bodies. Importance and functions • Ketone bodies being water soluble are easily transported from liver to various tissues. • The two ketone bodies acetoacetate and β–hydroxy butyrate serve as important sources of energy for peripheral tissues like skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, renal cortex etc. Importance ad functions-contd • The production and utilization of KBs becomes more significant when glucose is in short supply to tissues as observed in starvation and diabetes mellitus • During prolonged starvation KBs are the major source of fuel for brain and other parts of Central Nervous System. • RBCs lack mitochondria, hence cannot utilize KBs. Synthesis of Ketone bodies- ketogenesis • Site of Ketogenesis: • It occurs in liver and the enzymes responsible for it are located in mitochondrial matrix • Steps • • • • • Formation of Acetoacetyl CoA. Enzyme involved is β-Thiolase. Formation of HMG-CoA. Enzyme involved is HMG Co A Synthase which also regulates KB synthesis. Breakdown of HMG-CoA to acetoacetate and acetyl CoA by HMG-CoA lyase. spontaneous breakdown of Acetoacetate to Acetone. Formation of β-hydroxy butyrate by enzyme β–hydroxy butyrate dehydrogenase Catabolism of ketone bodies (ketolysis) • During prolonged starvation KBs are the major source of fuel for brain and other parts of Central Nervous System. • This an adaptation to survive during periods of food deprivation. Liver lacks Thiophorase enzyme hence cannot utilize KBs • . Ketone Bodies As Energy Sources In liver -Hydroxybutyrate Acetoacetate Acetoacetate is major energy source in cardiac muscle and renal cortex; also in brain in starvation and diabetes Succinyl CoA Thiophores Not found in liver Thiolase 2 Acetyl CoA Acetoacetyl CoA Succinate Combines with oxaloacetate TCA Cycle 8 Ketoacidosis • In normal humans there is a constant production of ketone bodies by liver and their utilization by extra hepatic tissues. • The blood level of KBs is about 1 mg/dl in a normal human adult. Their excretion in urine is very low and undetectable by routine tests. • When the rate of synthesis of ketone bodies exceeds the rate of utilization , their level increases in blood. This is known as ketonemia. • Ketonemia is produced due to increased production rather than decreased utilization. • In ketinemia , the excretion of KBs increases in urine, this is known as ketonuria. • The overall picture of ketnemia and ketonuraia is called as Ketosis. • Both acetoacetate and β–hydroxy butyrate are strong acids. They dissociate in blood and release H+ ions, which lowers the pH. This decrease in blood pH as a result of severe ketosis is called as Ketoacidosis. Metabolic causes of Ketoacidosis • Starvation: – In starvation the fatty acids [and amino acids] are used for energy needs of the body after the glucose reserves are finished. – This results in overproduction of Acetyl CoA which is not fully handled by TCA cycle . – TCA cycle is impaired due to deficiency of oxaloacetate which is diverted to gluconeogenesis. – The final result is overproduction of KBs from acetyl CoA. • Diabetes Mellitus – Uncontrolled DM is associated with impaired carbohydrate metabolism and increased lipolysis, both of which lead to accumulation of Acetyl CoA and its ultimate conversion to KBs. – In severe Diabetes the KB levels in blood may reach as high as 100 mg /dl and urinary excretion may be as high as 500 mg/day. – In diabetes loss of glucose and water in urine leads to decrease in blood volume and further complicate the condition. – Diabetic Ketoacidosis is dangerous and may result in coma and death if untreated. – Ketosis due to starvation is usually not accompanied by Ketoacidosis Thanks & Best Wishes