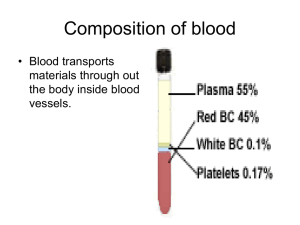
Blood components
Blood Components
Single blood bag:
Whole blood
Blood Bags
Double bags:
Packed red cells
plasma
Triple bags:
Backed cells
Plasma
platelets
Quarterly bags:
Backed cells
Plasma
Platelets
Plasma factors
Whole Blood (WB)
• Collected directly from donors into blood transfusion bag containing anticoagulant
• 500 ml transfusion bag is used (contains
63 ml of anticoagulant + 450 ml blood)
Anticoagulant ratio is 1.4 ml:10ml blood (63ml / 450ml)
Whole Blood (WB)
• Consists of RBCs, WBCs, platelets and plasma (with anticoagulant).
• 1 unit increases Hb 1 g/dl & Hct 3%
• When is it used?
– Patients who are actively bleeding and lost
> 25% of blood volume.
– Exchange transfusion
Blood Components
Separating WB into components of blood is necessary to avoid wasting of units.
Goals
• Decrease harmful effects of blood transfusion.
• Giving patients specific component needed.
• Allow a longer survival for components.
• More than one patient will use the unit.
What are the Blood Components?
►
Packed Red Blood Cells (PRBCs)
►
Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
►
Platelet Concentrates (PC)
►
Cryoprecipitate (CRYO)
►
Leukoreduced Red Blood Cells
Centrifugation Types
There are two types of centrifugation
• Light/soft spin ; (2000 rpm20 ºC )
• Heavy spin ; (3500 rpm20 ºC )
Centrifuged blood
Plasma
Buffy Coat (WBCs & Platelets)
Red Blood Cells
PRBCs
How to prepare (PRBCs)?
RBCs have higher specific gravity than plasma, it moves to lower portion of the bag by centrifugation.
Whole Blood :(Light spin): Two products:
1) PRBCs
2) Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP)
Whole Blood Unit
After centrifugation
WB separates into
PR Plasma &
PRBCs
PRBCs
A PRBC unit contains ~ 200 ml RBCs & 50 ml
Plasma.
– HCT of the unit should be ≤ 80%
– One unit increases hematocrit 3%
RBC units must by stored at 2-6 ºC
PRBC are indicated for:
Patients with anemia
Surgery
Newborn exchange transfusion
Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) centrifuged using (heavy spin), this will produce:
1) Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
2) Platelets Concentrate (PC)
FFP is the fluid portion of blood that is separated and frozen at -18 ºC within 8 hrs of WB donation.
Contains all the coagulation factors, including FVIII (factor 8) & Fibrinogen.
Whole blood unit
Centrifuge using LIGHT spin
Express Platelets Rich Plasma (PRP) into satellite bag
Take PRP and centrifuge again now using HEAVY spin
Express PPP into satellite bag & freeze at -18 ºC
Final products :PRBCs, Platelets concentrate & FFP
FFP
Freeze/store it at
- 18 ºC for 1 year from collection date.
• - 70ºC for up to 8 years
Cross match is not required, but should be ABO compatible.
Indications of FFP
• Liver disease
• Severe burns
• Provides coagulation factors for
– Bleeding
– Abnormal clotting due to massive transfusion
– Patients on warfarin who are bleeding
– Treatment of TTP
– Coagulation factors deficiency
– ATIII deficiency
– DIC when fibrinogen is < 100 mg/dl.
FFP
Platelets Concentrate (PC)
How to prepare PC?
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) centrifuged using (heavy spin), this will produce:
1) Platelets Poor Plasma (PPP)
2) Platelets concentrate (PC)
• PC are stored at room temperature on platelet agitator (prevent platelets clumping)
• PC stored for 5 days at 20-24 °C.
• Each unit should elevate the platelet count by
5000 /µL
P.C; Indications
1.To
prevent bleeding due to thrombocytopenia or platelet dysfunction.
2. For patients undergoing an operation, if the platelets count < 20,000 /µl.
Platelet concentrate
Pooling Platelets
6-10 units transferred into one bag
Expiration = 4 hours
Cryoprecipitate (Cryo.)
• Cryo-precipitated (Cryo.) or anti-hemophilic factor (AHF) is the precipitated protein portion that results after thawing FFP at cold.
• Contains
– von Willebrand’s Factor (vWF); (platelets adhesion factor).
– Fibrinogen
• 150 mg in each unit.
– Factor VIII
• About 80 IU in each unit.
Cryoprecipitate (Cryo.)
How to prepare Cryo.?
WB is centrifuged special heavy spin (3500 rpm at
4 ºC for 11 min.)
•
• PRBCs
Plasma store until frozen > -18 ºC (FFP)
FFP allowed to thaw at 4 ºC overnight.
Centrifuge plasma heavy spin to separate plasma from
Cryo ……..
Express supernatant plasma & Cryo. will remain in bag.
what the supernatant plasma is called?
The supernatant plasma is called cryoprecipitate
reduced or plasma cryo.
Good for Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
(TTP).
Cryo…..
Indications
Hemophilia-A von Willebrand Disease (vWD).
Congenital or
(dysfibrinogenemia).
acquired fibrinogen defects
Storage and Expiration of CRYO:
• Must be stored at -18ºC, preferably - 30ºC.
• Expires 1 year from original WB donation date, not from the date the Cryo., was prepared
.
Special Procedures
Aphaeresis
APHERESIS, Greek pheresis = ″ to take away ″ ; involves the selective removal of blood constituents from blood donors or patients.
Selective removal of a pathologic materials has a theoretical advantage over the removal of all plasma constituents.
In most aphaeresis instruments, centrifugal force separates blood into components on the basis of differences in density.
Apheresis
Plateletsphaeresis
To obtain platelets at least 3 × 10 11 platelets/unit from:
Random volunteer donors (5 Random donors=1 apharesis donor)
Patients’ family members
Donors with matched HLA or platelet antigen phenotypes.
-The most common platelets collection systems (Trima-right side &
Baxter-left side)
Irradiation of Blood Components
Cellular blood components are irradiated to destroy viable T- lymphocytes which may cause Graft Versus Host
Disease (GVHD).
GVHD is a disease that results when immunocompetent, viable lymphocytes in donor blood engraft in an immunocompromised host, recognize the patient tissues as foreign and produce antibodies against patient tissues, primarily skin, liver and GI tract. The resulting disease has serious consequences including death.
GVHD may be chronic or acute
Irradiation of Blood Components
Patients at greatest risk are:
severely immunosuppressed, immunocompromised, receive blood donated by relatives, or fetuses receiving intrauterine transfusions
Irradiation inactivates lymphocytes, leaving platelets, RBCs and granulocytes relatively undamaged.
Must be labeled "irradiated".
Expiration date of Red Blood Cell donor unit changes to 28 days.
May be transfused to "normal" patients if not used by intended recipient.