01 GAR_revised
advertisement

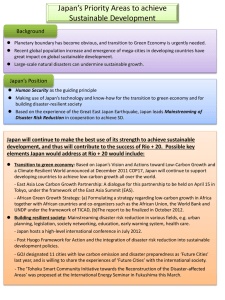
Global Assessment Report for Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 About ISDR and DRR ISDR: International Strategy for Disaster Reduction • Successor programme of the IDNDR (International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction, 1989-1999) • GA Res 54/219 and 56/195 establish the secretariat, under the authority of the USG for Humanitarian Affairs, and the IATF-DRR • GA Res A/RES/61/198 transforms the IATFDR into the Global Platform for DRR, thus including Governments What is Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR)? • A conceptual framework consisting of ways and means: – To minimize vulnerabilities and disaster risks. – To avoid (prevention) or to limit (mitigation and preparedness) the adverse impacts of hazards within the broad context of sustainable development. World Conference on Disaster Reduction Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 (HFA) - Building the resilience of nations and communities to disasters • 168 Governments, 78 regional and int’l orgs, and 161 NGOs attended • Integrate disaster risk reduction into policies, plans and programmes of sustainable development and poverty reduction • Recognize risk reduction as both a humanitarian and development issue – in the context of sustainable development • Focus on national and local implementation, with bilateral, multilateral, regional and international cooperation World Conference on Disaster Reduction Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 (HFA) • Three strategic goals: •The integration of disaster risk reduction into sustainable development policies and planning •The development and strengthening of institutions, mechanisms and capacities to build resilience to hazards •The systematic incorporation of risk reduction approaches into the implementation of emergency preparedness, response and recovery programmes World Conference on Disaster Reduction Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 (HFA) • Five priorities for action: •Governance: ensure that disaster risk reduction is a national and local priority with strong institutional basis for implementation •Risk identification: identify, assess and monitor disaster risks and enhance early warning •Knowledge: use knowledge, innovation and education to build a culture of safety and resilience at all levels •Reducing the underlying risk factors in various sectors (environment, health, construction, etc.) •Strengthen disaster preparedness for effective response Build a disaster risk reduction movement – ISDR system Our objective: To reduce disaster risk, worldwide, focussing on nations and communities The instrument: Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 The vehicle: ISDR system - ‘movement ’ About the GAR Global Assessment Reports (GAR) • Both a product and process – for evidence generation and policy engagement • Engaging partners from governments, UN agencies, international organisations, civil society organisation, academic institutions and many more since 2007 • Two iterations, in 2009 and 2011 • Both launched by UN Secretary General and received highest level of attention • Informed the 2nd and 3rd session of the Global Platform Global Assessment Report (GAR) • More than 500,000 chapter down loads • More than 10,000 copies distributed • More than 130 governments participated in reviewing their progress in DRR • More than 25 countries developed national disaster loss databases • More than 30 organizations participated in research and analysis GAR 2009: Risk and poverty in a changing climate • Focused on the identification of drivers of risk and what needs doing • Increase our understanding of the causal factors of risk and of it’s consequences for human and economic development • Propose policy initiatives to address gaps and challenges GAR 2011: Revealing Risk, Redefining Development • Focused on drivers of risk reduction and on how to address the challenges in doing so • Provided policy recommendations for governments to adapt and use public investment planning, social protection and other development instruments to upscale risk reduction • Revealed some new and key aspects of disaster risk and trends in risk reduction GAR 2009 Main Findings Disaster risk is intensively concentrated it’s unevenly distributed….. 22.5 million exposed per year GDPcap. US$31,267 HDI =0.953 Mortality ratio = 1 16 million exposed per year GDP cap. US$5,137 HDI = 0.771 Mortality ratio = 17 …… is increasing globally and….. hits small countries hardest. Global risk is driven by poverty and weak governance Risk is also extensively spread ….. ………….and increasing rapidly ….. feeds back into poverty driven by…….. deficient urban and local governance ...vulnerable rural livelihoods and ... declining ecosystem services ……magnified by climate change Mixed progress in reducing risk the key message In order to: Reduce disaster risk and achieving the Hyogo Framework of Action Adapt to climate change Achieve the Millennium Development Goals Goals Address the underlying risk drivers: poor urban governance; ecosystem decline; vulnerable rural livelihoods GAR 2011 Main Findings Growing losses – insignificant investment in disaster risk management Disaster losses by Presidential period Mexico 1982 – 2009 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Increased exposure of people and economic activities to weather-related hazards Population exposed to tropical cyclones, China coast section 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Falling mortality – rising economic loss risk Cyclone mortality risk Flood economic loss risk 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development A real-time window on investment in risk 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Risk – the future. Synchronic failures and sequential crisis ? Populations and economies exposed to tsunamis 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Mixed progress towards achieving the HFA 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Low investment in vulnerability reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Systematically account for disaster losses Number of education facilities damaged (1970-2009) Kilometers of road damaged (1970-2009) per province (Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Panama, Peru, Venezuela) 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development What is destroyed and by what type of disaster? Intense and strong but rare disasters Weak and extensive but common disasters 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Typhoon severity, and causes of disasters The stronger the typhoon, the less effective vulnerability reduction is Vulnerability Exposure Stronger typhoons 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Use public investment planning “Prevention is better than cure” Planning is better than relocation or retrofitting 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development … be selective in corrective investments Targeted investment in a few infrastructure projects yields more benefits 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Protect the most vulnerable Employment Guarantee Programmes Conditional Cash Transfers 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Reform risk governance 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2011 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction Revealing Risk, Redefining Development Revealing Risk, Redefining Development