Factory Built Housing
advertisement
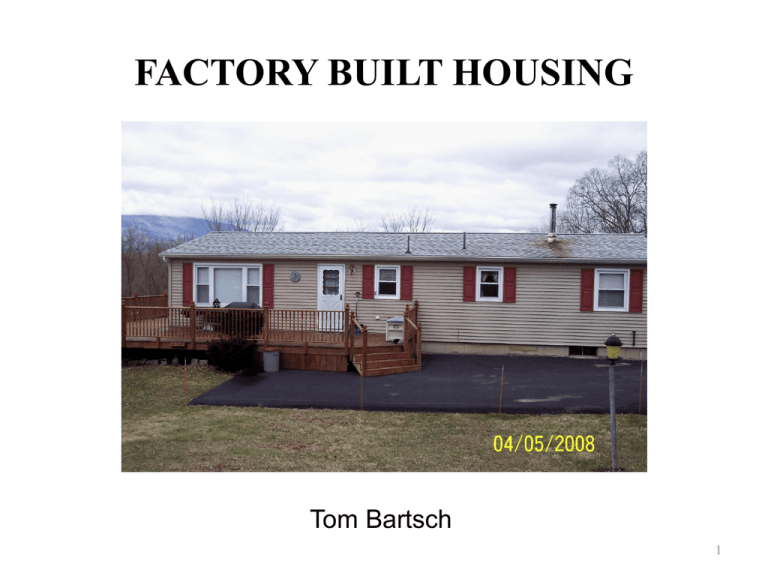
FACTORY BUILT HOUSING Tom Bartsch 1 Applicable Codes and Standards Building Code of NY Residential Code of NY Code of Federal Regulations, Title 24 (CFR 24), Part 3280 (HUD) NFPA 501-99 “Standard on Manufactured Housing” ANSI – 119.1 (American National Standards Institute) NCSBCS/ANSI – A225-1-1994 (National Conference of States on Building Codes and Standards, Inc.) 2 Factory Built Housing There are several types of factory-built housing structures; • Modular • Panelized • Pre-cut • and Manufactured All are transported to the site and assembled. 3 MODULAR, PANELIZED AND PRE-CUT HOMES 4 Factory Built Housing Definition of Modular Building; • A factory-manufactured dwelling unit, conforming to applicable provisions of the NYS code and bearing insignia of approval issued by the State Fire Prevention and Code Council, which is constructed by a method or system of construction whereby the structure or its components are wholly or in substantial part manufactured in a manufacturing facility, intended or designed for permanent installation, or assembly and permanent installation. 5 Factory Built Housing Modular Buildings; • built in different modules or sections. • meets state building and local codes. 6 Modular 7 Hard to believe, this is a Modular The roof is being installed 8 This a Modular Home!!!! 9 Factory Built Housing Panelized Building; • whole wall with windows, doors, wiring, etc., • meets state building and local codes. 10 Factory Built Housing Pre-cut Buildings; • kit, log, and concrete, • meets state building and local codes. 11 Factory Built Housing Modular Recognition; • very difficult to tell if factory or site built, • uses same framing, heating and cooling materials, • value the same as site built structures, • can be multi-storied. 12 Factory Built Housing Modular buildings have unique features; • there may be larger than expected, • concealed void spaces between each of the modules, • in multi-story modular buildings, there is typically a void space between each story and cavities in the walls, these voids are larger than site built structures. 13 Factory Built Housing Modular building are constructed using adhesives instead of nails or screws to attach drywall to the ceiling and wall studs. • possibility of adhesive failure due to fire behind the wall, • heat conducted through the drywall could cause adhesive to fail. 14 MANUFACTURED HOMES 15 Factory Built Housing Manufactured Building; • may be single or multi-section, • code requires that sections be built on a permanent chassis, • does not require a permanent foundation, • immune to local building codes, • may be governed by local Zoning laws, • must comply with “Code of Federal Regulations, Title 24 (CFR 24), Part 3280 – Manufactured Home Construction and Safety Standards” which supersedes local codes. (HUD) 16 Factory Built Housing Chassis and wheels Manufactured Homes used to be called “Mobile Homes” Skirt covering chassis and sometimes the wheels, if they haven’t been removed 17 Factory Built Housing Manufactured Homes aka “Prefabricated Homes” The term “Mobil Homes” was used prior to 1976 HUD Code Enactment; • strong trailer frames, axles, wheels & tow hitch. • Post 1976 units bear a label certifying compliance with HUD standards. 18 Factory Built Housing The Certification Label is permanently affixed to the exterior of each transportable section. The label is located one foot (1') up and away from the left rear corner (facing forward; the tow bar end indicates the front of the section). 19 Factory Built Housing Manufactured units come in two major home sizes; • Single-wide’s • Double-wide’s 20 Factory Built Housing Single-wides; • are 18 feet (5.5 m) or less in width and 90 feet (27 m) or less in length and can be towed to their site as a single unit. Double-wides; • are twenty feet or more wide and are 90 feet in length or less and are towed to their site in two separate units, which are then joined together. There are Triple-wides and even homes with four, five, or more units are also built, although not as common. 21 Factory Built Housing Zoning regulations usually restrict their placement. If you think your community is free of manufactured units, check around for construction trailers. Smaller units have a single egress and small windows. 22 Factory Built Housing May also be used for; • Temporary Office Space, • Education & Childcare, • Disaster Relief or Material storage. Not held to same code review and update as modular homes. New housing units now require; • Hard wired or 10 yr battery source, interconnected smoke alarms. • Provisions for special devices for hearing/visual impaired. 23 Factory Built Housing Frame Interior Walls Roof 24 Factory Built Housing 25 Factory Built Housing 26 Factory Built Housing Tornadoes and hurricanes often inflict their worst damage on trailer parks, usually because the structures were not secured to the ground and their construction is significantly less able to withstand high wind forces than regular houses. However, most modern manufactured homes are built to withstand high winds as well as a mainstream home, using hurricane straps and proper foundations. 27 Hazards Related to the “Manufactured” Home Can be extremely hazardous occupancies. Lightweight wood truss construction. Lightweight steel framing. Combustible finishes and furnishings. Electrical distribution equipment is the #1 cause of fires. Construction is typically less sturdy than other buildings of lightweight construction. 28 Hazards Related to the “Manufactured” Home Debris and combustible items under the unit. Older units have plywood wall paneling and wood based ceiling panels. “Mobile Homes” are extremely vulnerable during hurricanes and tornados. Most are found in rural areas and in areas with scarce water supply, insufficient FD manpower on the initial alarm and longer FD response times. 29 Firefighting Walls can be breached easy for victim access. Owner may have attached wood to the exterior. Some may have a brick veneer. Advancing hose lines can be difficult. Flammable liquids may be stored under the skirting. An additional roof may have been built above. Smaller space can hinder search and rescue ops. Propane usage. Exposures, especially in a mobile home park. Hard to save if heavy fire on arrival. 30 Summation Modular’s; difficult to tell if site or factory built. have concealed spaces. use of adhesives to install drywalls. Manufactured; extremely dangerous during hurricane or tornado events. lightweight construction. storage under skirting of flammable or combustible’s. 31 Prepared by Thomas Bartsch Chief Fire Inspector (ret) 32






![A Cell is like a Factory[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005446661_1-d01b8e928fa376b098eca9080626c037-300x300.png)