第三章
advertisement
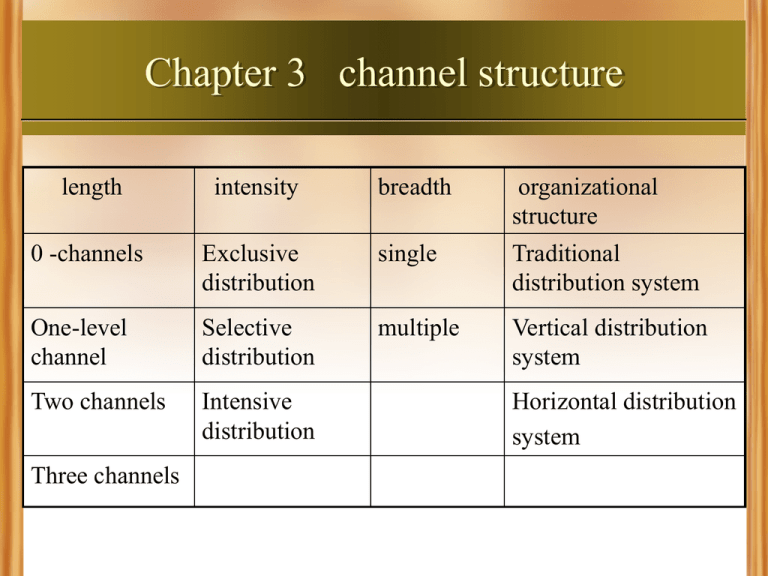
Chapter 3 channel structure length intensity breadth organizational structure 0 -channels Exclusive distribution single Traditional distribution system One-level channel Selective distribution multiple Vertical distribution system Two channels Intensive distribution Three channels Horizontal distribution system Section 1 length structure 一. zero-channel (direct channel, short channel) 1. meaning 2. characteristics In zero-Channels, there are only manufacturers and users, but no middleman. Commodities belong to manufactures before sale. Ownership of goods transfer from producers to users through only one time. Manufacturers Possess all of sales revenue and profits. 3. With regard to direct selling 1886年,雅芳公司在美国创造性地通过“雅芳小姐” 以单层次直销方式销售香水,展开了现代直销史的 篇章。1945年纽崔莱公司发展出多层次直销“团队 计酬”的奖金制度,多层次直销开始渐成风尚。上 世纪90年代初,直销模式引入中国 。(1990年11月, 美国雅芳公司经中国广州市人民政府批准,投资 2795万美元与广州化妆品厂合资成立广州雅芳有限 公司 ). Basic characteristics: 1:It is sale person to person or face to face, which distinguishes it from direct marketing. 2:Usually the sale is not accomplished in stores, which excludes direct selling in store. Conclusion Direct sale is the form of non-store selling, including direct selling、 direct marketing. The direct selling includes two schemes : the singlelevel and multi-level marketing; the latter is known as pyramid selling in our country . Discussion: Direct selling = Direct channels? There is a widely spread but not right opinion; that is putting direct marketing the same as direct channel. In fact, direct sale Does not mean direct channel. Direct channels are compared with the indirect channels, while direct sale is a form of non-store marketing; Direct sale can be in direct channels (such as personal selling), as well as indirect channels (such as a cosmetics firm commissioned a direct-sales company selling ). 4. emerging conditions 5. advantages analysis: Advantage: Realizing the integration of developmental strategy; easy to control; strengthen serves ; Shortcoming: Does not suit products widespread retailing; increasing expense ; decentralizing energy. case:Honda 、Amway、 DELL 二 indirect channels 1. The meaning ,pattern and characteristics 2. Advantage Analysis Focus on resources of production; simplify transactions, extensive distribution; Super services, risk-sharing. 3. Disadvantage analysis difficult to communicate information directly heavy burden on consumers ; market instability, difficult to control Examples: mobile, Wahaha 厂商----全国总代----二级代理---零售----用户 CDMA/GPRS: 厂商----运营商---自有代理体系----用户 GSM: 1987年 14万 4分冰棒; 1989年营养食品厂;1991年集团 分销的三个阶段 “联销体”的运行模式 价差、区域、品种和节奏 Section 2 breadth structure 1. Exclusive distribution Meaning: The manufacturer, at a certain place,selects only a intermediate institution(between the same type) to carry out the distribution of merchandise. Advantages: easy to control, low-cost promotion. Disadvantages : lack of competition, low market coverage, Over dependence. case:志高 维修到1998年 公司---省级总代理---批发---零售 成员分工:分销、促销、售后服务 2. Selective distribution Advantages: easier to control, greater market coverage. Problem: difficult to select brokers, fierce competition Case: Nike 3. Intensive distribution Advantages: great market coverage、 high rate of customer contacts, making full use of middlemen. problems: difficult to control、high-cost and intensive competition Coca cola's channel 一、target market 二、distribution goal 3A: 3P: Availability Pervasive Affordability Price to value Acceptability Preferred 三、distribution channel Head office---中国控股、嘉里、太古、中粮-----operation office---retailers( 22 channels) Breadth comparison category Distributor Market s amount coverag e compet control ition Suitable products exclusive single small weak strong Special or new products selective limited middle Relativ ely fierce Relative Selective goods ly strong intensiv multiple e broad fierce strong daily necessities Section 3 the breadth 1. meaning In addition to choosing which type of intermediary to use and how many of them to use, the channel manager must also decide whether to operate one or multiple channels in a market. Whenever more than one channel coexists in a market, that is dual distribution. Advantages: an increase of market coverage; lower channels cost; customers customized sales. Problem: more than two channels, easy to reach conflict. Conflict resolution 1: customer segmentation (P121) Conflict resolution 2: product segmentation Conflict resolution 3: integration Enterprise goal and channel selection length breadth direct indire ct concentricity Max sale √ Mix cost √ broadness selectivity intensit y Simplific -ation √ √ √ √ Best √ reputation √ √ √ √ √ Strongest control √ Highest stock ratio Mix conflicts √ √ √ diversificati on √ √ Section 4 organization (system) structure 1. Traditional channel system this structure is also called loose-type channel. The Channel is formed by various independent members; each member pursues the maximization of their profits; no member have full or adequate control over the other members. Commonly used by small and medium enterprises. 2. vertical channel system It is an unified coalition created by the producers wholesalers and retailers through property rights, contracts, etc. In this system ,each member is a part of the entire system. Includes three forms: Vertical system Corporate model Contract model Management model Franchised operating organization Wholesaler chain Retail cooperator 2.1 vertical marketing system of Company Also known as the “rigid” integration or vertical integration organizations. Refers to a company owning and controlling a number of manufacturing、wholesale and retail organizations; controlling a number of flows and even all the flows of the distribution; operating and unifying management of production, wholesale and retail business. There are property rights links. Case: Haier, Suning 2.2 Vertical marketing system of contract an integration organization of “flexibility”! Type: • Voluntary Chain • retail co-operation • Franchise 2.3 An vertical marketing system of Management integrated organization of “flexibility” refers to channel relations : big company or minority namely several strengths with the good brand prestige depending upon own influence, gather the numerous distributors through the powerful management. The characteristic is: A core、stable relation、 consistent goal、 social resource use. Case: P&G Wal-Mart 3. Horizontal marketing system Two or more non-associated companies integrate their resources or programs to develop a marketing opportunity. Adler said : it is symbiotic marketing.