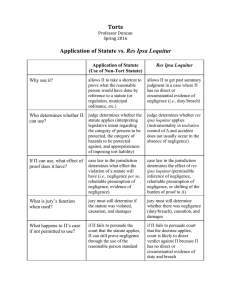
Common Law
advertisement

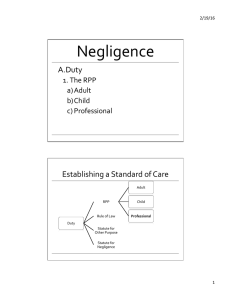
Managing Fire Safety Arguments For Fire Management • Moral: ethical and responsible behaviour • Financial: costs of injuries and illhealth • Legal: criminal and civil liability Fire Terminology • Primary fires – all fires in buildings, vehicles and outdoor structures or any fire involving casualties, rescues or fires attended by five or more appliances • Secondary fires – outdoor fires including grassland, refuse and derelict buildings • Chimney fires – occupied buildings where fire confined to chimney • False alarms – fire service called to fire and find there is no incident Cost Of Fire Incidents • Statistics published by the office of the Deputy Prime Minister: 2004 Fire Service Attended: – 900,000 fire and false alarms – Fires 442,700 – Dwellings 442,700 – Buildings 97,700 Casualties From Fire • 2004 – Fire related deaths 508 – Non fatal casualties (inc fire fighters) 14,600 • These figures are down 6% from previous year. Cost Of Inadequate Fire Risk Management • 2003 – Insured costs £672 million – Indirect cost £81 million – UK economy £6.6bn per year – Fire and Rescue Service £1.7bn – Average cost of commercial building £58,000 – Average cost domestic building £25,000 – Average cost of vehicle fire £4,700 Case Studies • • • • • • • • Primark Warehouse Buncefield Oil Termina Bradford Piper Alpha Kings Cross Sainsbury’s Bhopal Flixborough LAW Rules of human conduct, imposed upon and enforced among the members of a given state CIVIL LAW • Law concerning private and civil affairs without direct involvement of the state • Breaches usually remedied by compensation • Costs and damages normally covered by insurance Employers’ Liability (Compulsory Insurance) Act 1969 • Burden of proof: on a balance of probabilities SOURCE OF CIVIL LAW • Common Law Evolution of legal principles over time by decisions of courts and judges - system of rules or precedents which bind future similar cases Some common law offences are crimes, (e.g. murder, criminal libel) Common Law: Negligence • Negligence is a tort - A Civil wrong. • Three essential elements of proof on claimant: 1. Duty is owed 2. A breach of the duty 3. Damage/injury Employer’s Common Law Duty Of Care To Employees • • • • A safe place of work Safe appliances and equipment A safe system of work Competent and safety conscious personnel • A duty of care owed by the occupier of a building Vicarious liability • The principle that the employer is liable for the torts of their employees, provided that they are committed during the course of their employment to a third party. Breach of Statutory Duty • A common law action based on statute to protect employees - usually linked with a claim in negligence (the double barrelled approach) • Claimant will succeed in an action for negligence if a breach of statute law is shown to have caused the injury • Act or Regulations may prohibit right of action in civil proceedings, e.g. HASWA 1974 Negligence: Defences • • • • • • No duty owed No duty breached Volenti non fit injuria Contributory negligence Statute limitation Injury not as a direct result The Civil Courts • The County Court: hears most civil cases • The High Court: hears complex cases and those where damages expected to be in excess of £50000 • Employment Tribunals Criminal Law • Addresses public and moral wrong doing • No absolute definition and may change over time, e.g. drugs • Health and safety offences initiated by Fire Authority / HSE / EHO • Prescribes punishment: e.g., fines, imprisonment • Burden of proof: beyond reasonable doubt Source of Criminal Law • Statute Law • Law created by Parliament - rules of conduct to be observed by persons to whom statute is made applicable • May take form of an enabling Act • Sometimes enacted to remedy inconsistency in common law - e.g. Law Reform (Contributory Negligence) Act 1945 Duties • • • • Absolute Practicable Reasonably Practicable Reasonable Crown Court Magistrates Court HSE EHO CPS Punishment of Guilty Beyond all Reasonable Doubt Statute Law Burden Of Proof Source of Law CRIMINAL LAW Instigator of Action Remedy Sought Civil Law The Aggrieved person Compensation For Injury Loss Damage Caused Balance of Probabilities Small Claims Set By Precedence County Court High Court Created by Dave West for HSFB Common law