Market Structures & Business Organizations By
advertisement

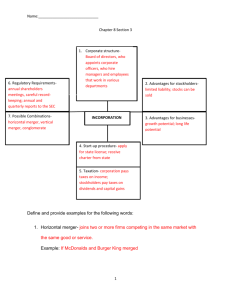
MARKET STRUCTURES & BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS By: Leanne Huynh & Tory Lynde Economics Alvarez (5) SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP • A business owned and managed by a single individual. That person earns all of the firm’s profits and is responsible for all of the firm’s debts. • Most popular in the United States. • ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES Ease of Start-Up Few Regulations Sole Receiver of Profit Full Control Easy to Discontinue Unlimited Personal Liability Limited Access to Resources Lack of Permanence PARTNERSHIPS • A business organization owned by two or more persons who agree on a specific division of responsibilities and profits. General Partnership – partners share equally in both responsibility and liability. • Limited Partnership – only one partner is required to be a general partner. • Limited Liability Partnerships – all partners are limited partners. • ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES Ease of Start-Up Shared Decision Making and Specialization Larger Pool of Capital Taxation Unlimited Liability Potential for Conflict CORPORATIONS • A legal entity owned by individual stockholders, each whom faces limited liability for the firm’s debts. Closely Held Corporations – issues stock to only a few people, often family members. • Publicly Held Corporations – sells stock on the open market. • ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES OF INCORPORATION Limited liability for owners Transferable ownership Ability to attract capital Long life Expense and difficulty of start-up Double taxation Potential loss of control by the founders More legal requirements and regulations PERFECT COMPETITION • • a large number of firms that all produce the same product. Four Conditions: Many buyers and sellers participate in the market • Sellers offer identical products • Buyers and sellers are well informed about products • Sellers are able to enter and exit the market freely • HORIZONTAL MERGERS Joining two or more firms competing in the same market with the same good or service. Combined yogurt company. VERTICAL MERGERS Combining two or more firms that are involved in different stages of producing the same good. FRANCHISES Large companies sell franchises, or contracts that give a single firm the right to sell their product in an exclusive area. Ex) NFL teams, fast food, restaurants in state parks, hotels. MULTINATIONAL CORPORATIONS Corporations that operate in more than one country at a time. Disadvantages Could negatively influence culture/politics Some MNCs have low wages and poor working conditions Advantages Provide jobs world wide. Spread new technologies COOPERATIVE ORGANIZATIONS Cooperative: Business organization owned and operated by a group of individuals for their shared benefit. Service Consumer Producer NON-PROFITS An institution that functions much like a business, but does not operate for the purpose of generating profits. MONOPOLY • A market structure with only one seller of a particular economic product that has no close substitutes. Natural Monopoly – costs are minimized by having a single firm produce the product. • Geographic Monopoly – no other business in the area offers competition. • Technological Monopoly – the special privileges given to those who invent a product or process. (i.e. copyright or patent) • OLIGOPOLY • A market structure in which a few large firms dominate a market. Few firms dominate • Some variety of goods • Some control over prices • High barriers to entry • MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION • • A market structure in which many companies sell products that are similar but not identical. Four Conditions: Many firms • Few artificial barriers to entry • Slight control over price • Differentiated Products •