Lecture One - Lcfalondon
advertisement

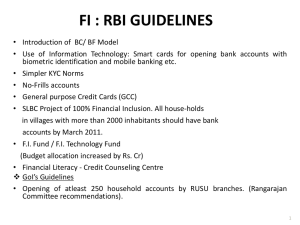
Lecture IT Service Management PROFESSIONAL INSTITUTIONS Aim of Lecture To enable students to show an understanding of the role of professional codes of conduct and apply them to specific situations Objective of Lecture To enable students to: Understand the role of professional institutions and their characteristics Understand the BCS Code of Conduct and its application in practice. Characteristics Shared by Most Profession A collective body with controlled entry - based on understanding of body of knowledge Self governing and self regulatory - has a code of conduct Established by royal charter or statute - defines extent of responsibilities and authority Examples of Professionals Doctors, Lawyers, Accountants, and Engineers The History and Present Membership Structure of the BCS The BCS was established in 1957, as a learned society It become a professional body in 1984 when it receive its Royal Charter. It is governed by a council. The BCS has two professional grades of membership, Member and Fellow. Members and Fellows with appropriate qualifications and experience are eligible for registration as Chartered IT Professionals. The History and Present Membership Structure of the BCS (2) There are a number of non-professional grades available for those who have not yet attained the professional membership status or who are not seeking it. BCS Activities that Support its Claim to be a Professional Institution. Professional development Specialist groups, Branches, Advice to government, Advancement of public knowledge and understanding. The BCS Code of Good Practice The BCS Code of Good Practice is a statement of good practices in a wide range of activities that members are likely to undertake. It is intended to set the standard for activities in each of the areas it covers. The Code of Conduct expects members to operate within the Code of Good Practice. The BCS Code of Conduct – Public Interest Section Due regard for public health, privacy, security and wellbeing of others and the environment. Due regard for the legitimate rights of Third Parties Conduct your professional activities without discrimination Promote equal access to the benefits of IT and seek to promote the inclusion of all sectors in society wherever opportunities arise. The BCS Code of Conduct - Professional Competence and Integrity Section Undertake to do work or provide a service that is within your professional competence. Do not claim any level of competence that you do not possess. Develop your professional knowledge, skills and competence on a continuing basis. Ensure that you have the knowledge and understanding of Legislation and that you comply with such Legislation, in carrying out your professional responsibilities. The BCS Code of Conduct - Professional Competence and Integrity Section Respect and value alternative viewpoints and, seek, accept and offer honest criticisms of work. Avoid injuring others, their property, reputation, or employment by false or malicious or negligent action or inaction. Reject and not make any offer of bribery or unethical inducement The BCS Code of Conduct - Duty to Relevant Authority Section Carry out your professional responsibilities with due care and diligence in accordance with the Relevant Authority’s requirements whilst exercising your professional judgement at all times. Avoid any situation that may give rise to a conflict of interest between you and your Relevant Authority. Accept professional responsibility for your work and for the work of colleagues who are defined in a given context as working under your supervision. The BCS Code of Conduct - Duty to Relevant Authority Section Do not disclose or authorise to be disclosed, or use for personal gain or to benefit a third party, confidential information except with the permission of your Relevant Authority, or as required by Legislation Do not misrepresent or withhold information on the performance of products, systems or services or take advantage of the lack of relevant knowledge or inexperience of others. The BCS Code of Conduct - Duty to the Profession Accept your personal duty to uphold the reputation of the profession and not take any action which could bring the profession into disrepute. Seek to improve professional standards through participation in their development, use and enforcement. Uphold the reputation and good standing of BCS, the Chartered Institute for IT. The BCS Code of Conduct - Duty to the Profession Act with integrity and respect in your professional relationships with all members of BCS and with members of other professions with whom you work in a professional capacity. Notify BCS if convicted of a criminal offence or upon becoming bankrupt or disqualified as a Company Director and in each case give details of the relevant jurisdiction. Encourage and support fellow members in their professional development Sections of The BCS Code of Conduct The BCS Code of Conduct (2004) has four sections: The public interest; Duty to the relevant authority; Duty to the profession; Professional competence and integrity Purpose and issues addressed by the Public Interest section Firstly this describes members’ responsibility to work with due care and to be aware of, and comply with, relevant aspects of the law and other forms of regulation and, more generally, to safeguard public health, protect the environment and have regard for human rights. This section also require members to avoid discrimination against clients or colleagues, on such grounds as race or ethnicity, and avoid various corrupt practices such as the giving or taking of bribes, misrepresentation or false claims of independent judgement. Purpose and issues addressed by the Duty to the relevant authority section Duty to relevant authority: this deals with avoidance of conflicts of interest, maintaining confidentiality, and a truthful representation about products. Purpose and Issues Addressed by the Duty to the Profession Section Generally acting in such a way as to uphold and enhance the standing of the profession, including advancing public knowledge, countering false or misleading statements and encouraging professional development, Purpose and Issues Addressed by the Professional Competence Section Keep up to date, conform to good practice, don’t claim competence that you haven’t got, accept full responsibility for your work. This requires members to undertake CPD again so that their personal status and that of the profession is maintained . Reservation of Title Reservation of title means that the title in question can only be used by holders of specific qualifications or by those whose names appear on specific registers. For example, in the UK only those registered with the Architects Registration Board can call themselves architects. Reservation of Function Reservation of function means that only holders of specific qualifications or those whose names appear on specific registers can undertake certain functions. For example, the function of giving medical treatment to animals is reserved for registered veterinary surgeons. SFIAplus Model (Skills Framework for the Information Age) SFIAplus is a matrix in which each row corresponds to a functional speciality (e.g. communications, databases, system development) and each column corresponds to a level of responsibility, from trainee up to senior manager or consultant. Associated with a cell, there is a description of the responsibilities that persons assigned to that cell are expected to undertake and a description of the qualifications or experience they are expected to have. The model covers the spectrum of roles within ICT. SFIAplus Model (Skills Framework for the Information Age) SFIAplus can be used to: Identify and benchmark skills to the industry standard Map current skills within an IT job role Identify career paths Plan training and development activities The Roles and Responsibilities of the British Computer Society Single institution responsible for the computing profession Advises UK Government on IT matters. Defines standards for professional conduct in IT; set related education standards. Maintains own member lists Disseminates knowledge and good practice in IT and runs the specialist groups & local branches Practice Questions 1 1. Briefly explain the purpose of a code of conduct. 2. Outline the benefits of adopting codes of conduct in the field of computing and information systems. 3. The BCS Code of Conduct is divided into four sections; one of these sections is ‘Duty to the Relevant Authority’. Members of the BCS are expected to behave professionally towards the relevant authority. Give THREE examples to explain what this means. Practice Questions 2 1. What are the characteristics shared by most professions? 2. Describe the BCS activities that support its claim to be a professional institution. 3. Discuss whether those working in the Information Systems field in general (i.e. not just members of the BCS) can be considered to constitute a profession. Practice Questions 3 For each of the following clauses in the BCS Code of Conduct, explain the purpose of the clause and discuss the issues members of the BCS face in trying to comply with the clause: 1. 2. Clause 6: You shall carry out work or study with due care and diligence in accordance with the relevant authority’s requirements, and the interests of system users. If your professional judgement is overruled, you shall indicate the likely risks and consequences. Clause 3: You shall ensure that within your professional field/s you have knowledge and understanding of relevant legislation, regulations and standards, and that you comply with such requirements. Practice Questions 3 3. Clause 8: You shall not disclose or authorise to be disclosed, or use for personal gain or to benefit a third party, confidential information except with the permission of your relevant authority, or at the direction of a court of law. 4. Clause 15: You shall not claim any level of competence that you do not possess. You shall only offer to do work or provide a service that is within your professional competence. 5. Clause 16: You shall observe the relevant BCS Codes of Practice and any other standards which, in your judgement, are relevant, and you shall encourage your colleagues to do likewise. Practice Questions 4 1. The BCS Code of Conduct (2004) has four sections: i) the public interest; ii) duty to the relevant authority; iii) duty to the profession; iv) professional competence and integrity. Summarise the purpose of, and the issues addressed by, each section. (Do not try to write out the code in full.) Practice Questions 4 2. It can happen that an employee finds that his or her employer is behaving in an illegal fashion and wishes to draw the attention of regulatory bodies or other authorities to this behaviour When is it appropriate for the employee to breach the confidentiality provisions of his or her contract of employment? What guidance can you draw from the BCS Code of Conduct, employment law, the Public Interest Disclosure Act or other appropriate legal and ethical sources? Practice Questions 5 Write brief notes on the following, and explain their meaning in the BCS context: 1. Code of Good Practice 2. Reservation of title and function 3. SFIAplus model 4. Continuing Professional Development