File
advertisement

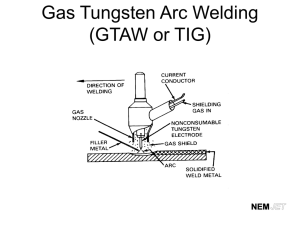
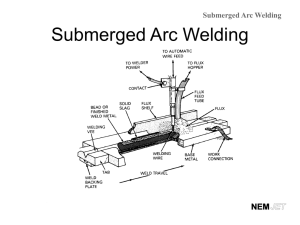
PowerPoint to accompany Welding Principles and Practices Third Edition Sacks and Bohnart History of Welding Chapter 1 1 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What is Welding? • Break into groups and discuss what you think welding is • Can you think of types of welding? 1-2 Overview • Welding is joining two pieces of metal by: – Heating to temperature high enough to cause softening or melting – With or without application of pressure – With or without use of filler metal • Usually best method to use when fastening metal 1-3 Uses of Welding • Constructing and manufacturing: 1-4 History of Metalworking • Welding began more than 3000 years ago – Hot or cold metals hammered to obtain forge weld 1-5 History of Metalworking • Bronze developed between 3000 and 2000 B.C. • Iron became known to Europe about 1000 B.C. – Several thousand years after use of copper – Replaced bronze as metal used in manufacture of utensils, armor and other applications after 800 B.C. 1-6 History of Metalworking • Working of metals followed one another in great ancient civilizations – From copper, to bronze, silver, gold, and iron 1-7 Early Developments in Welding • Edmund Davy discovered acetylene at beginning of nineteenth century = Oxy- Acetylene • Sir Humphrey Davy discovered the electric arc in 1801 = Arc Welding – Concerned with use of arc for illumination These inventions were forerunner of – Demonstrated possible to maintain high voltage arc present arc welding process. for varying periods of time by 1809 • Workable electrical generating devices invented and developed on practical basis by 1850 1-8 History of Metalworking • first commercial oxyacetylene welding torch at turn of the century • Electric arc welding method used in US until about 1920 – Handicapped because of welds produced by these bare electrodes not as strong as metal being welded • Welding arc very unstable • No Flux 1-9 History of Metalworking • Technology of welding progressed slowly until World War I – Demands of war called for improved methods of fabrication – End of war, welding widely accepted • Research on coated electrodes through 1920s resulted in electrode coatings and improved core wire 1 - 10 Multipass Welds Pass 1 Ability to make multipass welds such as this one, on plate and pipe, led to growth of industry. Welds are sound and have uniform appearance. Pass 2 Pass 3 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 - 11 History of Metalworking • Stick welding process – Advanced rapidly due to electrode coatings and improved core wire – Now called shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) – Uses 14” stick electrode that conducts current from holder to work – Arc melts electrode, creating weld Stick welding 1 - 12 Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Process An aluminum weld made using the TIG process. The welding of aluminum is no longer a problem and can be done with the same ease as that of steel. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 - 13 GMAW (metal inert gas: MIG) Process • Concentrates high heat at a focal point • Produces – – – – Small heat-affected zone Narrow bead width Deep penetration Faster welding speed Responsible for over 70 percent of welds being performed today. • Now used in all industries St Louis Car. Co. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 - 14 Industry Demand • Over 90 welding processes • Force new and improved developments in machines, gases, torches, electrodes, procedures, and technology • Constant research for new metals done by shipbuilding, space and nuclear industries – Needs Spur research in welding 1 - 15 Welding Associations • American National Standards Institute (ANSI) • American Petroleum Institute (API) • American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) • American Welding Society (AWS) • American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) Provide guidance and standards relating to the welding industry. 1 - 16 Resistance Welding • Includes spot welding, seam welding, and other similar processes performed on machines • Operators usually taught on job – Semiskilled workers do not need specific hands-onwelding skills 1 - 17 Arc and Gas Welding • Welders have almost complete control of the process – Must know properties of metals to weld; which weld process to use; and how to plan, measure, and fabricate 1 - 18 Welding Positions Overhead Vertical General Electric Corp. As well as flat and horizontal Miller Electric Mfg. Co. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 - 19 Weld Positions 1 - 20 Qualifications and Personal Characteristics • Welders certified for ability to do their work and have work pass inspection. • Required to pass periodic qualification tests • Certifications issued according to kind and gauge of metal and specific welding process • Can hold several different certifications simultaneously 1 - 21 Example of Magnetic-Particle Testing in Building Weld testing and inspection give proof of the soundness of welds. Circlesafe Aerosol/Circle Systems, Inc. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 - 22 Master Welder Job Examples Welds in these tanks must meet X-ray requirements and pass a dye penetrant test. Tanks are often lined with a very thin layer of pure silver. Nooter Corp Creating Art! Enrique Vega Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 - 23 Master Welder • Master craftsperson • Able to weld all steels and alloys – Plus nickel, aluminum, titanium, zirconium, and their alloys and claddings • Welds of highest quality • Welds meet requirement of job – Delicate welding of silver and gold – Heavy pressure vessels requiring 4-inch plate 1 - 24 Welding Occupations Requiring a High School Education • • • • • • • • Welding operator Welding fitter Combination welder Master welder Welding supervisor Welding analyst Inspector Welding foreman • • • • • • • Welding superintendent Equipment sales Sales demonstrator Sales troubleshooter Welding instructor Robotics welder operator Jog or fabrication shop owner 1 - 25 Welding Occupations Requiring a College Education • Welding engineer (metallurgical) • Welding development engineer • Welding research engineer • Technical editor • Welding professor • Certified welding inspector (AWS/CWI) • Corporation executive • Owner of welding business • Sales engineer 1 - 26 So... What is welding? • Alright so now what is welding? 1 - 27