File
advertisement
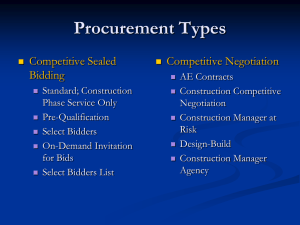
Lecture # 7 Civil Engineering Practice Works and Tenders. Instructor: Engr. Dr. Attaullah Shah Department of Civil Engineering Swedish College of Engineering and Technology-Wah Cantt. 2 What is a Project? • An adhoc endeavor to create a Unique Product or Service. • A unique one time effort bound by cost, time and resources/technical performance ( CST) and has defined objectives to satisfy the customer needs. • Project is an undertaking having definite objectives, and specific beginning and ending points, limited budgets, defined scope. • Sum of certain activities and tasks required to be performed in a specified period of time with human and non-human resources for specified objectives. ( Is your training a project? ) • Project is a one time non-routine opportunity to develop a new product. To satisfy the customer to achieve the organizational objectives. To be completed with in – Allocated budget. – Scheduled Time. – Approved Technical Performance. – Approved and agreed Scope of Work. – Without any change in the existing culture. 4 Triple constraints 5 What is management? The process of Planning, Organizing, Staffing, controlling and leading. Project management: The art of Directing and coordinating the human and non human Resources throughout the life of project by using modern Management techniques to achieve pre-determined objectives of scope, cost, time, quality and participants satisfaction. ( Project Management Institute America) • Project management includes: - Project Appraisal ( Before Commencement of Project PC-I, PC-II). - Project monitoring. ( During Execution of the Projects PC-III) - Project Evaluation ( After Completion of the projects. PC-IV,PC-V) Project Life-Cycle Project Planning( Pre-Investment Studies): – Project Opportunity Analysis ( Identification) – Project Selection & Problem analysis. – Project Pre-feasibility studies. – Project Feasibility Studies – Preliminary Design – Cost Estimation. Implementation ( Investment Phase) – – – – – – – – Detailed Design. Pre-qualification of bidders Tendering & Negotiation Construction and developing the facility Test Deployment Operation Commissioning Maintenance. – – – – Up-keeping ( Preventive) Adoptive Maintenance ( Project Integration). Enhancement Decommission What is management? The process of Planning, Organizing, Staffing, controlling and leading. Project management: The art of Directing and coordinating the human and non human Resources throughout the life of project by using modern Management techniques to achieve pre-determined objectives of scope, cost, time, quality and participants satisfaction. ( Project Management Institute America) • Project management includes: - Project Appraisal ( Before Commencement of Project PC-I, PC-II). - Project monitoring. ( During Execution of the Projects PC-III) - Project Evaluation ( After Completion of the projects. PC-IV,PC-V) Different Forms used by Planning Commission of Pakistan. PC-I Forms - Production Sectors - Infrastructure Sectors - Social Sectors. PC-II Form Survey and Feasibility Studies. PC-III Form PC-III (A) form for Physical Targets based on PSDP Allocations & Activity Chart. PC-III(B) Monthly Progress Reporting. PC-IV Form Project Completion Report. PC-V Form Annual Performance Report After Completion of Project Procurement Management • Procurement is acquisition of goods and services. • Project Procurement Management includes the contract management and change control processes required to administer contracts or purchase orders issued by authorized project team members. Procurement Cycle • Plan Purchases and Acquisitions. Determining what to purchase or acquire and determining when and how. – Purchase of equipment – Procurement of works – Procurement of supplies etc • Plan Contracting – documenting products, services, and results requirements and identifying potential sellers. – Developing the requisite documents – Specification – No and make etc. • Request Seller Responses. – obtaining information, quotations, bids, offers ,or proposals, as appropriate. – – – – Inviting bids Inviting quotations Request for Proposals ( RPFs) Expression of Interest ( EOI) etc. • Select Sellers. – Reviewing offers, choosing among potential sellers, and negotiating a written contract with each seller. – Tender/bids opening – Evaluation and Assessment of bids – Negotiation if required and allowed – Selection of the seller/contractor • Contract Administration – – Managing the contract and relationship between the buyer and seller. – Reviewing and documenting how a seller is performing or has performed to establish required corrective actions – Provide a basis for future relationships with the seller, – Managing contract-related changes and, when appropriate, – Managing the contractual relationship with the outside buyer. – Contract Agreement • Contract Closure – – completing and settling each contract, including the resolution of any open items, – Closing each contract applicable to the project or a project phase. Procurement Planning – Make-or-Buy Analysis – Whether a particular product or service can be produced by the project team or can be purchased. – Expert Judgment – Expert purchasing judgment can also be used to develop or modify the criteria that will be used to evaluate offers or proposals made by sellers. – Contract Types – Different types of contracts are more or less appropriate for Different types of purchases. • Fixed-price or lump-sum contracts. • Cost-reimbursable contracts.( cost Plus) • Time and Material (T&M) contracts. • Fixed Price contracts • • • • • • • Fixed price or lump sum Cost price with re-determination Fixed price plus incentive fee. Fixed price plus economic price adjustment Fixed price with successive targets incentives Fixed price for service material and labor at cost. Time and material labor hours only. • Others methods: • • • • • • • Turnkey Bonus - Penalty Joint venture Combination of the above BOOT ( Build Operate Own and Transfer BOT ( Build Operate and Transfer) Build Lease and Transfer ( BLT) Plan Contracting: Outputs • Procurement Documents – Procurement documents are used to seek proposals from prospective sellers. – A term such as bid, tender, or quotation is generally used when the seller selection decision will be based on price (as when buying commercial or standard items), – A term such as proposal is generally used when other considerations, such as technical skills or technical approach, are paramount. • Evaluation Criteria – Evaluation criteria are developed and used to rate or score proposals. They can be objective or subjective Evaluation criteria are often included as part of the procurement documents. • Other Selection criteria Understanding of need. How well does the seller’s proposal address the contract statement of work? – Overall or life-cycle cost. Will the selected seller produce the lowest total cost (purchase cost plus operating cost)? – Technical capability. – Management approach. • Technical approach. – Financial capacity. Does the seller have, or can the seller reasonably be expected to obtain, the necessary financial resources? – Production capacity and interest. Does the seller have the capacity and interest to meet potential future requirements? • Business size and type. • References. Can the seller provide references from prior customers verifying the seller’s work experience and compliance with contractual requirements? • Intellectual property rights. Does the seller assert intellectual property rights in the work processes or services they will use or in the products they will produce for the project? • Proprietary rights. Does the seller assert proprietary rights in the work processes or services they will use or in the products they will produce for the project? Request Seller Responses: Tools and Techniques • Bidder Conferences – Meetings with prospective sellers prior to preparation of a bid or proposal. – To have a clear, common understanding of the procurement – All potential sellers are given equal standing during this initial buyer and seller interaction to produce the best bid. – Advertising – Develop Qualified Sellers List – Qualified sellers lists can be developed from the organizational assets if such lists or information are readily available. Whether or not that data is available, the project team can also develop its own sources. Select Sellers • Selection decision process: – cost can be the primary determinant for an off-the-shelf item, – Proposals are often separated into technical (approach) and commercial (price) sections, with each evaluated separately. – Multiple sources could be required for critical products, services, and results to mitigate risks that can be associated with issues such as delivery schedules and quality requirements. – Select a single seller that will be asked to sign a standard contract. – Establish a negotiating sequence by ranking all proposals by the weighed evaluation scores assigned to each proposal. – On major procurement items, the overall process of requesting responses from sellers and evaluating sellers’ responses can be repeated. – A short list of qualified sellers can be established based on a preliminary proposal. A more detailed evaluation can then be conducted based on a more detailed and comprehensive proposal that is requested from the sellers on the short list. Select Seller Techniques • • • • • • Weighting System Independent Estimates Screening System Contract Negotiation Seller Rating Systems Expert Judgment Contract • A contract is awarded to each selected seller. •The contract can be in the form of a complex document or a simple purchase order. • Regardless of the document’s complexity, a contract is a mutually binding legal agreement that obligates the seller to provide the specified products, services, or results, and obligates the buyer to pay the seller. Contract Administration: Tools and Techniques • Contract Change Control System • A contract change control system defines the process by which the contract can be modified. • Buyer-Conducted Performance Review • Inspections and Audits • Performance Reporting Contract Closure • The Contract Closure process supports the Close procurement process since it involves verification that all work and deliverables were acceptable. • Contract Closure: Tools and Techniques – Procurement Audits – A procurement audit is a structured review of the procurement process from the Plan Purchases and Acquisitions process – Records Management System Procedures of Open competitive Bidding under PPRA Rules 2004. One Envelope Procedure • Each bid shall comprise one single envelopes containing, separately, financial proposal and technical proposal (if any) – Open competitive bidding procedure used for most of the procurement. – where the scope and technical specification of the procurements are very clear and unambiguous. – For projects of repetitive nature and where a pool of registered contractors with the departments is available sometimes. – In this procurement mode, the financially lowest bid is generally selected. – Such procurements become victim of low bidder dilemma as the bidding firms. – Poor history of successful procurements by this method. – Preferred for small and clear procurements. Two Envelops Procedure i) The bid shall comprise a single package containing two separate envelopes. Each envelope shall contain separately the financial proposal and the technical proposal: ii) The envelopes shall be marked as “FINANCIAL PROPOSAL” and “TECHNICLA PROPOSAL” in bold and legible letters to avoid confusion. Two Stage Bidding Procedure First Stage (Tech Proposal ) i) The bidders shall submit, according to the required specifications, a technical proposal without price, i) The technical proposal shall be evaluated in accordance with the specified evaluation criteria and may be discussed with the bidders regarding any deficiencies and unsatisfactory technical features. Continued iii) After such discussions, all the bidders shall be permitted to revise their respective technical proposals to meet the requirements of the procuring agency; iii) The procuring agency may delete, modify or add any aspect of the technical requirements or evaluation criteria, or it may add new requirements or criteria not inconsistent with these rules. Continued • Such revisions, deletions, modifications or additions are communicated to all the bidders equally at the time of invitation to submit final bids, and that sufficient time is allowed to the bidders to prepare their revised bids: • Such allowance of time shall not be less than fifteen days in the case of national competitive bidding and thirty days in the case of international competitive bidding; Continued v) Those bidders not willing to conform their respective bids to the procuring agency’s technical requirements may be allowed to withdraw from the bidding without forfeiture of their bid security. Second stage (Revised Tech Proposal) i) The bidders, whose technical proposals or bids have not been rejected and who are willing, to conform their bids to the revised technical requirements shall be invited to submit a revised technical proposal along with the financial proposal. Continued ii) The revised technical proposal and the financial proposal shall be opened at a time date and venue announced and communicated to the bidders in advance; and iii) The revised technical proposal and the financial proposal shall be evaluated in the manner prescribed above. The bid found to be the lowest evaluated bid shall be accepted. Best for projects of technical nature. Where the firm’s capacity to deal with the complexity of the project is critical to the successful implementation of the project The scaling of technical and financial score depends on the nature of the project and relevant importance of the of each major criteria Typical range from 50:50 to 70:30 for technical: financial respectively. For mega IT projects, where the technical expertise, global partnership and relevant experience of the firm are of paramount importance, the technical part can be given a score of 70 or even 80. Technical Evaluation for ICT project at AIOU Criteria Marks Nature of Firm ( 10) Max Individual firm: 02 03 Partnership: 05 Company: Add 1 mark per year since establishment Max 5 marks and Offices Outreach ( 10) Islamabad office: 05 01 Other: per marks office max: 05 Methodology and approach ( 20) Experience of similar works In hand (25) Min For two similar works: 10 2 Add marks per work. Completed ( 15) For Min four works: 05 Add 01 marks for add work References. ( 10) National: 05 Intn’l; 5 Financial soundness and bank references ( 10) Balance sheets: 05 Income Stat:03 Bank reference: 02 Key personnel for the project ( 10) Total Marks ( 100) Team leader: 05 team Core members: 10 Obtained. One Stage Two envelope bidding procedure:i) The bid shall comprise a single package containing two separate envelopes containing separately the financial proposal and the technical proposal; i) The envelopes shall be marked as “FINANCIAL PROPOSAL” and TECHNICAL PROPOSAL” in bold and legible letters to avoid confusion; Continued initially, only the envelope marked “TECHNICAL PROPOSAL” shall be opened; iv) The envelope marked as “FINANCIAL PROPOSAL” shall be retained in the custody of the procuring agency without being opened. v) The technical proposal shall be evaluated on the laid down criteria. vi) The financial bids of the firm fulfilling the criteria are opened and remaining are returned un-opened. vii) The lowest evaluated bid based on the technical and financial bids is approved. iii) Performance Guarantee • Where needed and clearly expressed in the bidding documents, the procuring agency shall require the successful bidder to furnish a performance guarantee which shall not exceed ten per cent of the contract amount. Two Stage Bidding Procedure • First Stage (Tech Proposal) – – – – The bidders shall submit, according to the required specifications, a technical proposal without price, The technical proposal shall be evaluated in accordance with the specified evaluation criteria and may be discussed with the bidders regarding any deficiencies and unsatisfactory technical features, After such discussions, all the bidders shall be permitted to revise their respective technical proposals to meet the requirements of the procuring agency; The procuring agency may delete, modify or add any aspect of the – technical requirements or evaluation criteria, or it may add new requirements or criteria not inconsistent with these rules. – Such revisions, deletions, modifications or additions are communicated to all the bidders equally at the time of invitation to submit final bids, and that sufficient time is allowed to the bidders to prepare their revised bids: – Such allowance of time shall not be less than fifteen days in the case of national competitive bidding and thirty days in the case of international competitive bidding; – Those bidders not willing to conform their respective bids to the procuring agency’s technical requirements may be allowed to withdraw from the bidding without forfeiture of their bid security. Second Stage: • The bidders, whose technical proposals or bids have not been rejected and who are willing, to conform their bids to the revised technical requirements shall be invited to submit a revised technical proposal along with the financial proposal. • The revised technical proposal and the financial proposal shall be opened at a time date and venue announced and communicated to the bidders in advance; and • The revised technical proposal and the financial proposal shall be evaluated in the manner prescribed above. The bid found to be the lowest evaluated bid shall be accepted. • Best for – Best suited for Large Civil Works projects, heavy equipment and complex projects – Where the available information and in-house expertise of the procuring agency is not enough to deal with. – The feedback of the firm may provide some additional information on the procurement. Thank You