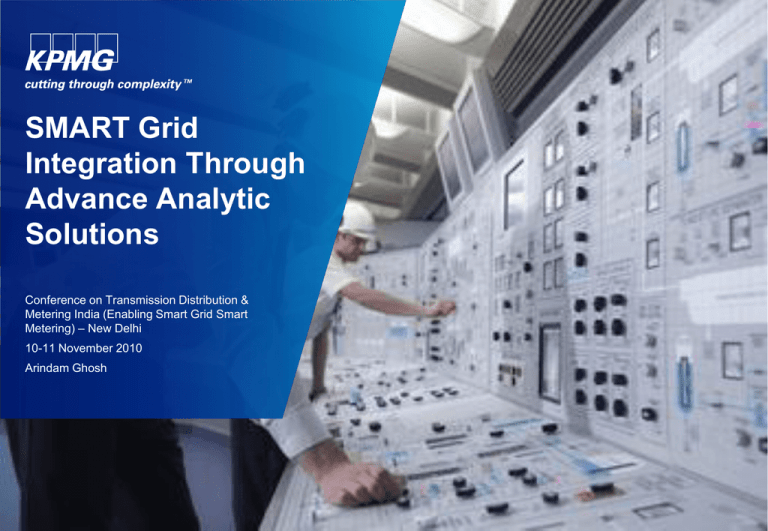
SMART Grid
Integration Through
Advance Analytic
Solutions
Conference on Transmission Distribution &
Metering India (Enabling Smart Grid Smart
Metering) – New Delhi
10-11 November 2010
Arindam Ghosh
Smart Grid Vision
To digitize a largely passive network into a two-way,
interactive information highway to support metering and grid
monitoring and control, from demand management to “selfhealing” circuits.
– Grid intelligence (collecting and analyzing data about grid
activities and behaviors) and the ability to act in real-time
are the defining capabilities.
– Smart Grid involves a large-scale investment in T&D
infrastructure aimed at enabling, and improving, advanced
metering, demand response, asset management, and
system reliability.
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Source: EEI
Uncertainties and obstacles
•
Little consensus on definition or direction
•
Lack of standards
•
Uncertain performance expectations,
benefits, and costs
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
•
Limited investment capacity
•
Uncertain regulatory treatment
Smart Grid Future Technology - the Driving Force
Characteristics of SMART GRID
Drivers of SMART GRID
Demand
• Rapid Growth in Overall
Electricity Demand
• Growing awareness for
Reliable and Quality
Electricity supply
Technology
• Network Operations
Optimization
• Dispersed Generation and
Grid coordination
• Renewable energy
Integration
Regulatory
• Increasing competition within
Industry due to deregulation
and restructuring
• Pressure on DISCOMS to
increase energy efficiency and
be self sufficient
Internal
• Theft and Fraud Detection
• Demand Management and
Volatility adjustment
• Meter based Billing rather than
estimated billing
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Smart Grid Represents a Major Enterprise Transformation
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
The Impact Is Broad and Pervasive
Smart Grid Business
Changes
Major Processes
Impacted
Benefit Categories
• Meter reading expense
Leveraging opportunities
to gain operational efficiency
• Asset management
• Meter to cash
• Field service and maintenance
• Preventable field labor accidents
• Back-office operating cost
• Revenue growth
• Field customer service costs
• Non-collectible expense
Leveraging opportunities
to gain operational efficiency
• Customer service
• Customer response
Enabling new capabilities for
advanced power management
• Network operations
• Generation capacity and planning
• Energy scheduling and dispatch
• Customer service field labor
• Service order response time
• Forecast accuracy
• Net billing
• Line loss revenue
• Fuel cost avoidance
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
A Broader Approach Recognizes the Role and Importance of Data
as a Transformation Driver
Technology
• Interoperability
• Systems integration Process
• Architecture
• There is tremendous value potential in
identifying ways in which data can
transform the business.
Organization
• Workforce rationalization
• Skill development
• Resource progression
• Data can be the source of new value as
well as being the “multiplier effect” to
leverage additional value from existing
Process
• Re-engineering
• Process optimization
• Quality and productivity
investments.
• Decision support
Data
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
• Optimized operation
• Automation
Data Becomes a Key to Driving Value
Optimizing the benefits of Smart Grid requires a data-driven transformation in addition to technology and process
New and Additional Data
• Interval consumption
• Interval demand
• Meter status/error reporting
• Event completion notification
• Condition alert (i.e. tampering)
• Grid node status
• Distributed generation data
• Feeder status/monitoring data
• Power quality incidents
• T&D line loss
• Grid voltage stability
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Meter Data Management Managing a Complex Environment
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Meter Data Management (MDM)
– Why it is critical for Smart Grid
•
New meter technologies capture significantly more data. Utilities need a central
repository for this data.
•
MDM is the foundation on which many AMI and Smart Grid programs will be built,
both as a technical prerequisite and as a foundation for improved business value.
•
While meter data was once viewed as simply an input to the billing process, its
strategic business value has grown considerably.
•
It provides the data required for regulatory reporting compliance as well as key
business metrics.
•
MDM is a central component to enabling and managing security and information
protection
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Some key data management considerations
• Data Volume & Management
• Data Collection & Collation
• Legal Consultation and Privacy Concerns
• Incident and Breach Management Planning
• Leverage Data Audits and Reviews
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
The Architecture of Smart Grid Creates a Paradigm Shift in the
Role of Data
At Present
Future
Bidirectional, real-time
communications
Time sensitivity in
milliseconds
Consolidated & Integrated
Applications
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
How to Extract Value from Data
Example – Distribution Management
Network Operation and
Maintenance
Schedule and Dispatch
Energy Management
Network Planning
Grid operations have historically been limited by unidirectional communication devices and a high degree of
manual involvement. Outage management is typically a reactive process based on trouble calls. A “Smart”
grid with numerous data collection and control points will provide the data to enable advanced distribution
and power management capabilities.
1. Identify
Available Data
• Condition-based monitoring
• Feeder segmentation
• Distributed generation
• Plug-in electric vehicle (PHEV)
• Demand-side demand response
• Home area network
• Grid voltage
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
2. Assess
Potential Value
• Enable “self-healing” and increase distribution
management automation
• Grid can proactively identify potential failure points
and react to prevent outage
• Reduce outage rate of occurrence and impact
• Make outage management more proactive vs.
reactive
• Increase grid management
“intelligence”
3. Develop the
Transformation
• Automate sensors and control nodes to react to specific
events
• Program outage alarms and notifications to automatically
initiate repair crew work orders and customer communication
• Establish a distribution management system to operate grid
• Assess potential redundancies with other systems (i.e. Outage
Management System (OMS)
Data Analytics - Life Cycle for a Power Distribution Utility
Data Point
Optimization
•
Demand Analysis
•
Market Insights
•
Dashboards
Business
Drivers to
Achieve
MDMS
•
Customer Data
Analytics
•
Load Data Analytics
•
Billing Data Analytics
•
Vendor Data
Management
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
•
Grid Optimization
•
Demand
Management
Revenue Protection
•
Outage
Management
Business
Benefits
after MDMS
MDMS
•
Abnormal
consumption report
•
Areas of High Loss
Report
•
Consumption
trends Report
MIS and Reporting
Key Concentration Areas
•
Roadmap after MDMS
Metered Data Management System
Intelligent Solutions
Business Analytics
Roadmap to MDMS
Advantages of Advance Analytics
“Customer Information
and Energy Use”
• Automation / effort reduction
• Restoration improvements
• Revenue protection
• Some demand reduction
“Grid Optimization “
• Asset life optimization
• System operational efficiency
• Improved reliability
• Predictive maintenance
Beyond the
Meter
“Strategic Consumer
Integration and
Empowerment”
• Consumer engagement
• Energy efficiency
• Incremental revenue
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Focus:
Change:
•
•
•
•
Infrastructure and meter install
Customer interaction
Usage and outage analytics
Meter to cash process
connectivity
• Governance
Focus:
Change:
• Network and asset management
• Advanced workflow
• Real-time data management and
analytics
• Operating model integration
Focus:
Change:
• Enhanced Business model
• Customer strategy and
behaviors
• Third party relationships
• Innovation and collaboration at
speed
14
Analytics Solution - Illustrative
Grid Optimization
Revenue
Protection
Customer Information and Energy Use
+
Active Load
Control
Performance
Outage
Management
Strategic Consumer Integration
and Empowerment
Sub-Metering
Abnormal consumption report
Demand Optimization
Price & Load Modeling
Load Forecasting
Load Profile
Solutions
_
Market profile
Customer profile
Peak clipping
Load shifting
Scheduling & Settlement
Tariff profiling
Theft Detection
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Integrated Voltage /VAR Control
Usage Analysis
Distribution Planning & Analysis
Areas of High Loss Report
Consumption trends Report
Real time
Decision
Making
Risk Analytics Solution - Illustrative
+
Rate Analysis &
Load Factor
Analysis
Usage and
Scenario Analysis
Energy
Performance
Accounting
Transformer &
cable load and
equipment load
analysis
Alarm and
Notifications
Energy Balance
Report
Transformer & cable
load and equipment load
analysis
Solutions
_
Last-Gasp, PowerUp Messages,
Carbon footprint
Analysis
Peak and Valley
Analysis
Demand violations
Abnormal power
factors
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Advanced switching
Modeling
Applications Utility
Modeling
Flexible Load building
Modeling
Reliability area
footprint modeling
Demand supply /
demand response
Modeling
Energy mix Analysis
Forecasting & Energy
Procurement
Baselines and Outlier Analysis
Identifying tampered meters
or zero readings
Customers who are billed but
never pay
Customers billed on average
or minimum
Customers with same name
and address
Same customer number with
different names and addresses
Customers with no name and
address
MIS and Reporting Solution - Illustrative
Continuous Monitoring and Vigilance Dashboard
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated
with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
•
Near real time energy accounting
•
Data Reconciliation Monitoring
•
Area / Office wise monitoring
•
Watching High Value Customers for fraud
Thank You
Presentation by Arindam Ghosh
Associate Director – Advisory
KPMG
DLF Corporate Park
DLF City, Phase III
Gurgaon 122002, India
Mobile: +91 9650666868
Email: arindamghosh@kpmg.com
© 2010 KPMG, an Indian Partnership and a member firm of the KPMG
network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International
Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
The KPMG name, logo and "cutting through complexity" are registered
trademarks or trademarks of KPMG International Cooperative ("KPMG
International").