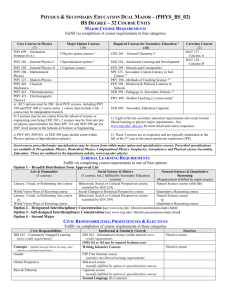
IEEE 802.20 Standard
advertisement

School of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Tehran Class Presentation for the Course: “Custom Implementation of DSP Systems” Mobile Broadband Wireless Access (MBWA) IEEE 802.20 Standard By: Reza Nakhjavani Instructor: Prof. S. M. Fakhraei May 2010 All Materials are Copyrights of Their Respective Authors as Listed in References Overview Introduction 802.16 802.20 802.20 PHY Layer 802.16e vs. 802.20 Intel® WiMAX Connection 2250 Summary References 2 Introduction [1] Importance of accessing data and information in today’s life. Network protocols such as Wi-Fi (802.11) and WiMAX (802.16) have been developed for such applications. Need for these information services under fully mobile conditions and in vehicular speeds has increased. IEEE 802.20 standard(Mobile-Fi), has been developed for mobile applications in speeds of up to 250 km/h. 3 Introduction [3] The Wireless Space 4 802.16: Fixed Broadband Wireless Access: Wi-Max [2] Frequencies from 10 to 66 GHz Time Division Duplex and Frequency Division Duplex configurations are supported Bandwidth 75 Mbps of bandwidth for 2 to 3 miles. Uplink : TDMA , DAMA Downlink: TDM 5 802.16: Fixed Broadband Wireless Access: Wi-Max [6] Architecture : 6 802.16: Fixed Broadband Wireless Access: Wi-Max IEEE 802.16e Providing true mobile broadband connectivity. Designed to support bands in the range 2 – 6GHz. Uses Scalable OFDMA to carry data Channel bandwidths :1.25 MHz~20MHz, with up to 2048 sub-carriers Adaptive modulation Good Signal : 64 QAM Intermediate Signal: 16 QAM & QPSK Poor Signal : BPSK [2] Good NLOS (Non-line-of-sight) characteristics 7 802.20 Development needed to 802.16 protocol. Aims basically at throughput than mobility. 802.20 is developed to cover the mobility part of the 802.16. allow the creation of low-cost, always-on, and truly mobile broadband wireless networks. Bandwidths of 5, 10, and 20 MHz Peak data rates of 80 Mbit/s. [7] 8 802.20 PHY Layer [2] PHY layer specs duplex modes : Time Division Duplex (TDD) , Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) multi-carrier modes: On , Off Modulation : OFDM with QPSK, 8PSK, 16QAM, and 64QAM 9 802.20 PHY Layer [4] Transmitter 10 802.20 PHY Layer Transmitter [1] OFDM Numerology 11 802.16e vs. 802.20 Standard 802.16e 802.20 Frequency Band 2-6 GHz 3.5 GHz Channel Bandwidth > 5 MHz < 20 MHz Transmission Rate 10 – 50 Mbps > 16 Mbps Parameter Mobility Mobile Speed MAC / PHY [2] High-data-rate fixed wireless user with adjunct mobility service Fully mobile, highthroughput data user 60 kmph up to 250 kmph Extensions to 802.16a MAC and PHY New PHY and MAC optimized for packet data and adaptive antennas 12 Intel® WiMAX Connection 2250 [8] The Intel WiMAX Connection 2250 is compliant with both IEEE 802.16-2004 and IEEE 802.16e-2005 specifications. 13 Intel® WiMAX Connection 2250 (Specs) OFDMA 512/1024 PHY mode Bandwidths: up to 10 MHz Support for TDD and H/FDD duplexing modes Concatenated Reed-Solomon and Convolutional Adaptive modulation (BPSK, QPSK, QAM16, QAM64) Highly optimized DSP engine with multiple parallel ALUs for concurrent complex operations per cycle, which enables efficient OFDM/OFDMA processing [8] 14 References 1- A. Jalili, S. M. Fakhraie, and S. Nader-Esfahani, “Performance Evaluation of IEEE 802.20 PHY Layer,” (ICCET 2009), Jan. 2009. 2- http://www.ucs.louisiana.edu/~vrb5959/final.pdf 3- https://www.ntt-review.jp/archive/ntttechnical.php?contents=ntr200805sf3.html 4- WALKER BOLTON, et al,” IEEE 802.20:MOBILE BROADBAND WIRELESS ACCESS”, IEEE Wireless Communications, February 2007 5- Local and Metropolitan Area Networks – Standard Air Interface for Mobile Broadband Wireless Access Systems Supporting Vehicular Mobility – Physical and Media Access Control Layer Specification, IEEE Standard 802.20, Aug. 2008. 6- http://www.mvt.co.th/images/upload/big/661.jpg 7- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.20 8- http://download.intel.com/network/connectivity/products/wireless 15 Questions? 16 Thank you 17