Week2
advertisement

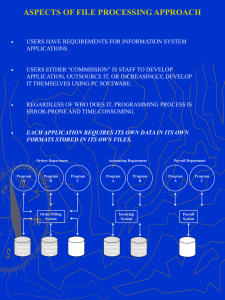
Business Intelligence/ Decision Models Week 2 IT Infrastructure & Marketing Database Design and Implementation Outline Issues with Mkt Databases DBMS Database Design and Schemas Data Integrity and Hygiene Demo and Lab: Table redundancy and Queries DB Marketing Problems Lack of a marketing strategy. Focus on promotions instead of relationships. Failure to have a 3600 picture of every customer. Failure to personalize your communications. Building a DB and sending e-mails in house. Getting the economics wrong. Failure to use tests and controls. Lack of a forceful leader. Bad DB architecture Corrupted data DB Environment Traditional Environment: Silo Approach Source: Laudon and Laudon 2012 Data Warehouse Technology Marketing Datamart Data Warehouse Architecture Data Warehouse Architecture Metadata Database Management Systems (DBMS) Flat Files Sequential A Name B C Address D A 1 Transactions 2 Fixed or variable length record 3 DBMS with VSAM Index TN NE NB IPE QC ON MB SK AB BC QC ON ON QC ON Hierarchical Indexed Direct Access DBMS Cust_id Name Purchases Top down Products Indexed Direct Access DBMS Key 107 110 145 167 234 267 Record 4 6 1 2 5 3 Records 1 145 2 167 3 267 4 107 5 234 6 110 ………. ………. ………. ………. ………. ………. Reversed Hierarchical DBMS Cust_id Name Psyte Code Lifestyle Purchases Bottom up/Top down Products Reversed Hierarchical DBMS NAME PSYTE Dubé Smith Bertrand White Harris Habib Jones 18 34 18 56 34 18 34 PURCHASES 120 130 150 200 50 300 430 PSYTE NAMES 18 Dubé; Bertrand; Habib 34 Smith; Harris; Jones 56 White Relational Database CUSTOMERS ORDERS 1 PRODUCTS Customer ID PK Order ID PK Product ID PK Cust First Name Customer ID FK Product Name Cust Last Name Product ID FK Product Description Street Order Date City Order Amount State Zip Relational DBMS Multiple Tables Source: Laudon and Laudon 2012 Relational DBMS with Query Source: Laudon and Laudon 2012 Relational Design An Unnormalized Relation For Order (flat file) An unnormalized relation contains repeating groups. For example, there can be many parts and suppliers for each order. There is only a one-to-one correspondence between Order Number and Order Date. Source: Laudon and Laudon 2012 Normalized Tables Created From Order Pros: Data integrity and updating Cons: Processing speed for large data sets Source: Laudon and Laudon 2012 Charitable Contributions The “Classic” Star Schema S to re D im e n sio n STORE KEY S to re D e sc rip tio n C ity S ta te D istric t ID D istric t D e sc . R e g io n _ID R e g io n D e sc . R e g io n a l M g r. Le v e l Fa c t Ta b le S TO R E K E Y PRO D UC T KEY P E R IO D K E Y D o lla rs U n its P ric e P ro d u c t D im e n sio n PRO D UC T KEY P ro d u c t D e sc . B ra n d C o lo r S ize M a n u fa c tu re r Le v e l Tim e D im e n sio n P E R IO D K E Y P e rio d D e sc Year Q u a rte r M o n th Day C u rre n t Fla g R e so lu tio n Sequence A single fact table, with detail and summary data Fact table primary key has only one key column per dimension Each key is generated Each dimension is a single table, highly de-normalized Tradeoff between data integrity, updating and speed Some alternatives: Star and Snowflake structure Benefits: Easy to understand, easy to define hierarchies, reduces # of physical joins, low maintenance, very simple metadata Source: Kishore-jaladi-DW.ppt Data Integrity and Hygiene Illustrating Data Hygiene Customers Undel. 15% Dup. 20% CPM = $500 Price = $60 GM 50% Quantities 2,000,000 1,700,000 15% 1,360,000 20% 2,000,000 1,700,000 1,360,000 2,000,000 1,700,000 1,360,000 Response 29,000 29,000 29,000 Cost $1,000,000 $850,000 $680,000 Revenue $870,000 $870,000 $870,000 BE = FC / (P-C) 1,000,000 / 30 $ BE = FC / (P-C) 850,000 / 30 $ BE = FC / (P-C) 680,000 / 30 $ 33,334 28,334 22,667 29,000 29,000 29,000 29,000 29,000 29,000 Response Rate 1.45% 1.71% 2.13% CPO $34.48 $29.31 $23.45 Profit -$130,000 $20,000 $190,000 ROI -13% 2% 28% Data Hygiene Processes (1) Standardize names Standardize addresses Address 1, Address 2, City, Province, Postal Code Abbreviations (apt., ave, p.o., province) Replace prestige names with postal addresses (i.e. Commerce Court) Scrubbing Title, First name, Initials, Family name, Suffix Ex. c/o, co, c/o Delivery FSA/LDU, Postal walk Address change database Data Hygiene Processes (2) Data Comparison Duplicate (cost, abuse) Householding • Hyphenated Names, Maiden Names, Spouse’s Name • Recomposed Families, Roommates Consolidation (merge/purge) • • • • Multiple Multiple Multiple Multiple Accounts (financial Services) policies (insurances) phone numbers (telco) divisions within firm Wrap-up Issues with Mkt Databases DBMS Database Design and Schemas Data Integrity and Hygiene Demo and Lab: Table redundancy and Queries Next Week Data Import Data Preparation Data Transformation