Quality Dimension Definition
advertisement

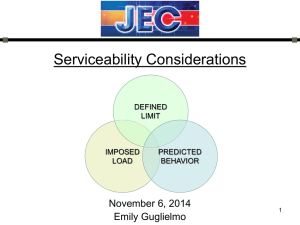
Towards Harmonized R & D Quality Dimensions (Indexes) The Kinneret College on the Sea of Galilee By: Raymond Austin under the guidance of Dr. Avigdor Zonnenshain. Agenda Introduction Eight Dimensions of Quality Quality Dimensions Exploration Questionnaire Questionnaire Data Analysis Conclusions Further Work Introduction • Growing importance of product quality. • Importance of quality dimensions in R&D process. • David A. Garvin’s eight quality dimensions for product as a principal basis for R&D. • Derivation of quality dimensions in R&D process using questionnaire. • Presentation of quality dimensions in R&D . Eight Dimensions of Quality Garvin’s Eight Dimensions Performance Features Reliability Conformance Durability Serviceability Aesthetics Perceived Quality of Product Quality Eight Dimensions of Quality # Quality Dimension Definition 1 Performance Primary operating characteristics of a product. 2 Features Characteristics that supplement basic product performance features. 3 Reliability Probability of a products success within a specific period of time. 4 Conformance Degree to which a product’s design & operating characteristics meet pre-established standards. 5 Durability Measure of product life: Amount of time of use one obtains from a product before it physically deteriorates. 6 Serviceability Speed, courtesy ease of use, maintenance and service. 7 Aesthetics The look, feel, sound, taste or smell of a product. 8 Perceived quality Relates to the customer’s subjective opinion of the product’s or company’s reputation. Quality Dimensions Exploration # Quality Dimension Definition 1 Performance • Primary operating characteristics of a product - basis for product development process. • R&D processes measured against performance standards and specifications. • Performance level benchmarked against competitive product/system in the market. • Product performance measured by conducting defined tests & experiments during R&D. 2 Features • Characteristics that supplement basic product performance features. • Feature criteria - Utilization in R&D process similar to Performance. • Features - Many a time never used; Additional complexity leading to decreased product reliability & serviceability. • Feature defined – Promote competitive marketing edge if provides value to customer. Quality Dimensions Exploration # Quality Dimension Definition 3 Reliability • Probability that a product will perform its intended function satisfactorily for a specific period of time under stated conditions. • Dimension important to customers. • Closely linked to Durability • Japanese emphasis on Reliability - Market Superiority. • Reliability close association to Serviceability, Safety. • Use of Modularity to increase Reliability. • Reliability involves measurable attributes. 4 Conformance • Degree to which a product’s design & operating characteristics meet pre-established standards. • Addresses “Tolerance stack-up” problem. • Positive Impact on products Aesthetics. • Japanese emphasis on Conformance - Market Superiority. • Product Conformance measured by simulations and experiments against design drawings and specifications. Quality Dimensions Exploration # Quality Dimension Definition 5 Durability • Measure of product life: Amount of time of use one obtains from a product before it physically deteriorates. • Durability - Economical & Technical Dimension. • Closely linked to Reliability. • Measured by assessing historical information concerning product life and controlled life testing. 6 Serviceability • Speed, courtesy ease of use, maintenance and service. • Dimension important to customers. • Requires strong customer service department & active field representatives. • Ease Of Repair - Objective Measure. • More Practical if included in Reliability. • Modularity - Positive/Negative Impact on Serviceability. Quality Dimensions Exploration # Quality Dimension Definition 7 Aesthetics • Inclusion of features which impact the customers subjective opinion of products look, feel, taste or smell. • Not limited to consumer products. • Important during Purchasing decision. • Good Design: Essential Measure. • Important part of design process: Adequate Alpha & Beta user testing. • Measured by allowing potential & actual end-users, professional designers to grade product/system. • Level of Aesthetics measured by comparing to International standards. 8 Perceived Quality • Relates to the customer’s subjective opinion of the product’s or company’s reputation. • Branding/Advertising - Key contributor. • Reputation - Primary contributor. • Requires to meet standard of quality higher than that established with preceding products. Questionnaire • • • • Includes a formal letter. Limited number of questions (Three). Limited in scope - Difficulty in obtaining response. Simple to avoid misunderstanding/misinterpretation of the questions. • Distributed to persons involved in product innovation, research, design and development. • Three questions asked: – Select THREE most important quality dimensions from the list of Garvin’s eight quality dimensions that apply to a majority of projects and explain why chosen. – Explain the impact of the chosen three quality dimensions on the R&D process. – Name and explain other quality dimensions having impact on R&D process based on previous experience. Questionnaire Data Analysis • ELEVEN responses received. • Quality dimensions in R&D processes applying to majority of projects: Reliability (11) Performance (8) Serviceability (5) Conformance (4) Features (4) Perceived Quality (2) • All recipients emphasized the importance of Reliability- Crucial having most impact on user. • Performance - Derivate of mandatory standards. Non-conformance leads to invalid product which is unacceptable. • Serviceability - Important requirement . • Conformance - Derivate of mandatory standards. • Features - most impact on customer. • Other quality dimensions/suggestions: – Durability - Crucial to the overall quality of the product. – Usability - Important from S/W development view. – Project schedule, time to market , Cost - Important considerations during project planning. (XX) – XX: Number of receipts Conclusions • ALL the Garvin’s eight quality dimensions were found relevant for quality in R&D. • Reliability, Performance, Serviceability ,Conformance and Features, with Reliability leading the list. • Usability was proposed as supplement to the above main quality dimensions. • Time to market and cost considerations Important in development process. • Other important relationship: – Reliability relation to Serviceability, Modularity and Safety. – Association of Conformance to Aesthetics.