SG_Odilon
advertisement

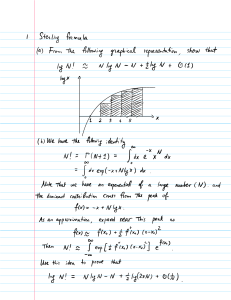
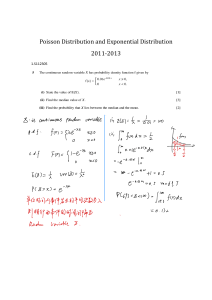
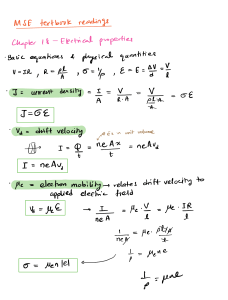
Integração de Tecnologias para viabilização da Smart Grid – SBSE 2010 DJALMA M. FALCÃO - COPPE/UFRJ Conceito Smart Grid: Utilização intensiva de tecnologia de informação e comunicações na rede elétrica. Convergência de tecnologias exigindo o desenvolvimento de novos métodos de controle, automação e otimização da operação do SE Características associadas • Auto-recuperação: detectar, analisar e restaurar falhas na rede automaticamente • Empoderamento do Consumidor: inclusão dos equipamentos e comportamentos dos consumidores no planejamento e operação do SE. • Viabilizar e beneficiar-se de mercados competitivos de energia: microgeração • Acomodar uma Grande Variedade de Fontes e Demandas de energia (plug and play) • Tolerância a Ataques Externos • Melhorar a Qualidade e eficiência do SE • Reduzir o impacto ambiental do sistema produtor de eletricidade Tecnologias Viabilizadoras • Automação e controle digital da rede elétrica • Medição eletrônica • Rede de sensores inteligentes • Dispositivos de eletrônica de potência • Geração distribuída, microgeração e armazenamento • Sistema integrado de comunicação (fibra ótica, PLC, wireless, etc.) Tópicos de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento: GERAÇÃO: integração de fontes de energia de pequeno porte e elementos armazenadores através do conceito de microredes TRANSMISSÃO: sistemas integrados de monitoração, controle e proteção (PMU, FACTS, ...) DISTRIBUIÇÃO: sistemas automáticos de medição, medidores eletrônicos, automação da distribuição USO FINAL: sistemas de gerenciamento de energia residencial, resposta pelo lado da demanda PADRÕES: padronização de redes de sensores e de comunicação de dados para troca de informação e interoperabilidade REGULAÇÃO: legislação para comercialização no varejo, precificação dinâmica. Exemplos de iniciativas no Brasil: • Microrede experimental – COPPE/UFRJ • Rede de PMUs para oscilografia e estimação de estado (ONS) • Monitoração e controle de segurança (ONS e Cepel) • Projeto piloto de medição fasorial: (MEDFASEE) - UFSC • Monitoração on-line da estabilidade de tensão: COPPE e CESI Distribuição • Medição eletrônica centralizada e automação: Ampla, Light, Eletropaulo, Cemig, etc. Conclusões • Alternativas reais para a otimização da qualidade de fornecimento de energia elétrica • Tecnologias necessárias à sua implantação estão disponíveis a custos razoáveis • Questão fundamental: avaliação do impacto dessas novas tecnologias no custo da energia para o consumidor final ISGT 2010 – Topics (Chamada de Trabalhos) 1. Standards for smart grid and grid codes 2. Regulatory aspects and market operations 3. Cyber and physical security systems and Information and Communication Technology 4. System and component reliability and diagnostics 5. Intelligent monitoring and outage management - self healing grids 6. AC and DC transmission and distribution systems - planning, operation and security 7. Protection and phasor measurement unit applications 8. Grid integration of renewable energy sources 9. Use and control of power electronic controllers and energy storage 10. Grid solutions for plug-in vehicles and low-carbon transportations 11. Sensors, communication and advanced metering infrastructure 12. Energy management and efficiency and end user benefits ISGT 2010 – Temas • Grid integration of renewable energy sources – 39 • “Evaluation of improved generation efficiency through residential PV voltage control of a clustered residential grid-interconnected PV” – Japão • “Voltage Stability Consequences of Decentralized Generation and Possibilities for Intelligent Control” Holanda • AC and DC transmission and distribution systems - 23 • “Linear Constraints for Remaining Transfer Capability Allocation” – Alemanha • “Optimal Placement of Fixed and Switched Shunt Capacitors for Large-Scale Distribution Systems using Genetic Algorithms” - India • Energy management and efficiency and end user benefits - 17 • “Experience on the Implementation of a Microgrid Project in Barcelona” – Espanha • “Making the Electricity Consumption Visible (pilot project)” - Suécia • Protection and phasor measurement unit applications – 13 • “Virtual Resistance Principle for the Overcurrent Protection of PWM Voltage Source Inverter” - França • “PMU-Based Multi-Area State Estimation with Low Data Exchange” - UK • Grid solutions for plug-in vehicles – 10 • “Impact of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) on the French Electric Grid” • “Vehicle to Grid — Reference Architectures for the Control Markets in Sweden and Germany” • System and component reliability and diagnostics – 10 • “Design and Analysis of Fuzzy Power System Stabilizer” • “A Hybrid Expert System Realization of Adaptive Autonomy for Smart Grid” • Intelligent monitoring and outage management – 9 • “Spectral Analysis Techniques with Kalman Filtering for Estimating Power Quality Indices” – Australia • “Islanding Operation of Active Distribution Grids using an Agent-based Architecture” - Portugal • Power electronic controllers and energy storage – 9 • “Design Study of a Converter Interface Interconnecting an Energy Storage with the dc-link of a VSC” – Suécia • “Experiences from a Back-to-Back Converter fed Village Microgrid” - Finlandia • Sensors, communication and advanced metering infrastructure – 7 • “Wireless Network Performance for Residential Demand-Side Participation” – Canadá • “Automated Meter Reading Using RF Technology” – Irã • “Simulation of Power Line Communication using ATP-EMTP and MATLAB” - UK • Regulatory aspects and market operations – 4 • “Software Evaluation of Smart Meters within a Legal Metrology Perspective: A Brazilian Case” • “Learning from Experiences of the prior Swedish Electrical Distribution System Regulation - Reference Material when Developing the Future Regulatory Incentives” - Suécia • Cyber and physical security systems – 3 • “Cyber Security for Smart Grid: A Human-Automation Interaction Framework” - Irã ISGT USA 2011 - Conference main topics • Impact of Smart Grid on Distributed Energy Resources (electric cars, demand response, distributed generation, storage) • Smart Sensors and Advanced Metering Infrastructure • Cyber Security Systems (intelligent monitoring and outage management) • Wide Area Protection, Communication, and Control in Energy Systems • Power and Energy System Applications (generation, transmission, distribution, markets, operations, planning) • Energy Management Systems (with applications to building and home automation) • Smart Grid Standards IEEE: http://smartgrid.ieee.org/smart-grid-framework-diagram/smart-grid-interactive-search-tool ONS: http://www.ons.org.br/newsletters/informativos/out2009/05-materia01.html