HoneyPot1 - Security Research
advertisement

DEFCON BANGALORE
17 Aug, 2013
Daniel Singh
Daniel@techngeeks.com
About the Presenter
• CISO @ TechNGeeks
• Security Researcher
• Cyber Security Evangelist
• C|EH, E|CSA
About the Presenter
DAY JOB: IM A PROGRAMMER.
(I GET 21 ERRORS IN A 20 LINE CODE)
My 1st successful program @S**t Inc.
do {!flush(commode);} //please
while (paperTowels.in(/*BOOL*/)==true);
throw(paperTowels); //in garbage collector
About the Presenter
BY NIGHTFALL: Transform into 1337 h4x0r
My
TO DO
LIST !!!
Agenda
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Introduction to Honeypots & Honeynets
Honeypot Background & History
Benefits & Downside of Honeypots
Classification & Implementation
Introduction to Honey Analysis
Legal aspects of Honeypots
Detection of Honeypots
Future of Honeypots
Anti-Honeypot Techniques
Summary
Further information
What is a Honeypot?
•
A pot, used to store honey
But as a Metaphor, a honeypot refers
to:
• Espionage Recruitment involving
Sexual Seduction (reality/fiction)
• Honeypot Site is a popular visitor
attraction for tourists
• A Sting Operation (like ‘Bait Car’)
What is a Honeypot?
•
Honeypot (noun), An esoteric slang
used
to
refer
to
Physically
attractive women under 30 years of
age who exude a measure of
restrained yet potent sexuality
Background
•
Term originated from the Military
•
Its a Fake target for ambush
•
Here it is used
in Network
Security
Environment
Some more definitions
Abstract definition:
“A honeypot is an information
system resource whose value lies in
unauthorized or illicit use of that
resource.” (Lance Spitzner)
Concrete definition:
“A
honeypot
is
a
fictitious
vulnerable IT system used for the
purpose of being attacked, probed,
exploited & compromised.”
What Honeypot actually is?
Definition
‘A honeypot is a resource which is
expected to be attacked or
compromised.’
•
•
•
Distraction of an attacker
To gain of information about
attacker
Attack Methods and Tools
Benefits of Honeypots
•
•
Risk Mitigation: A honeypot
deployed in a productive
environment may lure an attacker
away from the real production
systems
IDS-like functionality: since no
legitimate traffic takes place
to/from the honeypot, any traffic
appearing is malicious
Benefits of Honeypots
•Attack Strategies: find out reasons
and strategies why and how attacks
happen
•Attack Tools: detailed information of
attack tools
•Increased knowledge: knowing how to
respond & prevent future attacks
•Identification and Classification: Find
out who is attacking you and profile
them
Benefits of Honeypots
•Evidence: after identification of
attacker, all data captured can be
used in a legal procedure
•Research: reveal internal
communications of hackers,
infections, spreading techniques of
worms & viruses
Benefits of Honeypots
• Honeypot VS Antivirus
• Honeypot VS Sandboxes
• Honeypot VS IDS/IPS
• Honeypot VS Darknets
• Honeypot VS Secure Web Proxies
Downside of Honeypots
•Limited View: Honeypots cannot track
& capture activity directed towards
other systems
•Additional Risk: Deploying a honeypot
can create additional risks for whole
organization
•Legal risk: if honeypot is compromised
and joins a bot army, this could lead to
serious legal consequences
Classification of Honeypots
Server-side
Distributed
Physical
Production
Level
Client-side
Stand-alone
Virtual
Research
Level
High
Interaction
Medium
Interaction
Multifunction
Jails
General
Purpose
VOIP Pot
Specialized
Tarpits
Web
Applications
Bluetooth Pot
Hybrid Pots
SSH Pot
USB Pot
SCADA Pot
Sinkholes
Low
Interaction
Examples of Honeypots
Low Interaction Server Side:
General Purpose based
Amun, Dionaea, HoneyD, Tiny Honeypot
Web Application based
Glastopf, Google Hack Honeypot
SSH based
Kippo
SCADA based
Honeynet (Digital Bond), Conpot
VOIP based
Artemisa
Bluetooth based
Bluepot
Sinkhole
Honeysink
USB based
GhostUSB
European Network and Information Security Agency Report
Examples of Honeypots
High Interaction Server Side:
Argos, HiHAT, Sebek
Low Interaction Client Side:
PHoneyC, Thug
High Interaction Client Side:
Capture-HPC HG, Sheila
European Network and Information Security Agency Report
Examples of Honeypots*
•
•
•
•
•
HoneyMonkey
Canary Trap
Tarpits
Pseudoserver
Network
Telescope/Darknets
HoneyPot Sensors
Two types of Honeypot Sensors:
Fat Sensor: is a complete
system, processes, data from
the node and sends it to the
central
server
for
further
analysis and correlation.
HoneyPot Sensors
Two types of Honeypot Sensors:
Thin Sensor: is just a reflector –
it forwards all the connections
directly to the central server for
processing and data analysis
Honeynet
‘A honeynet is a network of honeypots
supplemented by Firewalls & IDS’
•
•
•
These are more relaistic
environments
Imporved Data Capture &
Analysis
Better Fingerprinting
Implementation of HoneyPot
INTERNET
Production Network
192.168.1.15
192.168.1.20
192.168.1.25
eth0
10.1.1.1
Honeywall
Gateway
eth2
192.168.1.254
Honeypot
192.168.1.101
eth1
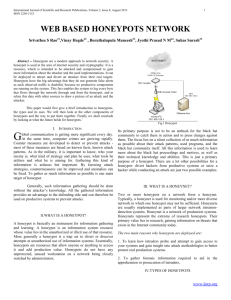
Implementation of HoneyNet
INTERNET
Production Network
192.168.1.15
192.168.1.20
192.168.1.25
eth0
10.1.1.1
Gateway
eth2
ROUTER
HoneyNet
192.168.1.101
192.168.1.102
eth1
192.168.1.103
192.168.1.254
Honey Analysis
Honey Analysis
Attacks over Time
Honey Analysis
Distriubution over Time Metric
Honey Analysis
Attack Origin over Time
Honey Analysis
Important Security Metrics:
• $Source IP
• $Source Port
• $Destination IP
• $Destination Port
Important Services and Ports:
Service
Port #
Description
FTP-Data
20
File Transfer [Default Data]
FTP
21
File Transfer [Control]
SSH
22
Secure Shell
Telnet
23
Telnet
SMTP
25
Simple Mail Transfer
DNS
53
Domain Name Server
Honey Analysis
Important Services and Ports:
Service
Port #
Description
BOOTPS
67
Bootstrap Protocol Sever
BOOTPC
68
Bootstrap Protocol Client
HTTP
80
Hyper Text Transmission Protocol
POP3
110
Post Office Protocol
NNTP
119
Network News Transfer
NTP
123
Network Time Protocol
NETBIOS-NS
137
NETBIOS Name Service
NETBIOS-DGM
138
NETBIOS Datagram
NETBIOS-SSN
139
NETBIOS Session Service
IMAP
143
Internet Message Access Protocol V4
Honey Analysis
Important Services and Ports:
Service
Port #
Description
SNMP
161
Simple Network Management
IRC
194
Internet Relay Chat
HTTPS
443
HTTP over TLS/SSL
MS-DS
445
Microsoft-DS
SMTPS
465
Secure SMTP
SMTP
SUBMISSION
587
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Submission
IMAPS
993
IMAP over TLS/SSL
IRCS
994
IRC over TLS/SSL
POP3S
995
POP3 over TLS/SSL
Honey Analysis
Important Services and Ports:
Service
Port #
Description
Astaro
1026
Astaro User Portal
Kazaa
1214
Kazaa Media
MS-SQL-S
1433
Microsoft SQL Server
MS-SQL-M
1434
Microsoft SQL Monitor
HP-SIM
2381
HP System Management
BES
3101
Blackberry Enterprise Server
MS-WBT-Server
3389
RDP Terminal Server
Kerio
4040
Kerio Connect Web Admin
Astaro
4444
Astaro Web Admin
ICQ
5190
ICQ.com
Legal Aspects of Honeypots
New Technology: The legal framework
& its adjudicators are going to take the
case in as-and-when circumstances
Varied Applications: Honeypots have
varied
applications
(simple
port
scanner to a virtual machine) which are
created on demand. Thus a common
law, cannot be internationalised &
hard to achieve
Legal Aspects of Honeypots
No Legal Cases: As of now, there
hasn’t been any legal case pertaining
to honeypots & their usage
Concepts legalised still debatable:
some issues relating to honeypots
themselves have debatable rulings in
difference scenarios
Legal Aspects of Honeypots
The basic legal themes related to
honeypots are:
1. Entrapment (including enticement)
2. Privacy
3. Downstream liability
Detection of Honeypots
Technical Attributes of Honeypot:
• Respond time & Banners
• Registry entries
• Inconsistent parameters
• “Social” properties of the System
• Usage Interaction & access logs
• Network Sniffing
• Packets going to/from the system
• Search for traces of VMware
Detection of Honeypots
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Sending invalid TCP packet (S+R)
Spotting System Anomalies
Spotting TTL, Window Size
Spotting IPID, DF-bit
Detect BIOS Version
Detect VMware tools extension
Detect VMware Magic Value
(0x564D5868)
Future of Honeypots
•
•
•
•
•
•
HoneyTokens
SCADA Honeypots
Wireless Honeypots
SPAM Honeypots
Search-Engine Honeypots
Honeypot Farms
Future of Honeypots
HoneyTokens are resources used for
detecting & tracking insider interaction
with legitimate resources.
Tokens are fake and crafted items,
counterparts of resources that should not
be
normally
accessed
(important
documents & research, source codes, MS
Word & Excel docs, SSNs & CC numbers,
confidential emails, login & password detail
files)
Future of Honeypots
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
HoneyTokens
SCADA Honeypots
Mobile Device based
Wireless Honeypots
SPAM Honeypots
Search-Engine Honeypots
Honeypot Farms
Anti-Honeypot Techniques
• Automated Honeypot
Scanners
• Honeypot Confusers
• Honeypot Exploits
• Honeypot Disablers
• Checking HTTPS & SOCKS
proxies
SUMMARY
Honeypots are a new field and
much is to be done:
•
•
•
•
Recommend Honeypot setups
Recommend Honeynet farms
Increase Honeypot accuracy
Invent Anti-Honeypot
techniques
Further Information
TH4NK5