Document
advertisement

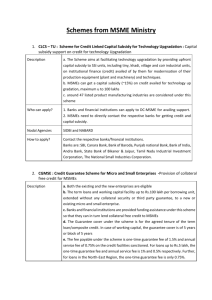
Welcome Participants and Delegates Dr. D.S. Mandloi, Director MSM E Development Institute MINISTRY OF MSME Govt. Of India Indore 24.2.2013 INDIA STATSTICS GDP • • • • $1.847 trillion (nominal: 10th; 2011) $4.530 trillion (PPP: 3rd; 2011) Contribution of sectors: agriculture: 17.2%, industry: 26.4%, services: 56.4% (2011 est.) Labour fource – 48.76 crores Labour distribution -agriculture: 52%, industry: 14%, services: 34% MSME Contribution ; Manufacturing - 40 %, Export - 45 %, GDP including all – 17 % MSME SCENERIO IN INDIA ACTIVITY – WISE MSMEs SERVICE WISE MSMEs FIXED INVESTMENT EMPLOYMENT Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises MSME SCHEMES Implemented by Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Government of India New Delhi 9 MINISTRY OF MSME IS HAVING FOLLOWING IMPORTANT SCHEMES 1. Skill Development 2. Cluster Development 3. National Manufacturing Competitiveness Programme( NMCP) 4. CLCSS 5. CGTMSE 6. Vendor development 10 Cluster : Definition & Principle DEFINITION : GEOGRAPHICAL CONCENTRATION OF UNITS PRODUCING SIMILAR PRODUCTS AND FACING SIMILAR THREATS AND OPPORTUNITIES PRINCIPLE : COLLABORATING WHILE COMPETING 11 Why Cluster Based Approach ? Offers critical mass for customization of interventions. Economies of Scale Better Access to Technology, information Greater access to customers, channels Cheaper access to inputs, raw materials “ Cluster approach should be preferred route for improving the manufacturing competitiveness. New and innovative approaches to cluster development should pe adopted “- NMCC 12 Not forgetting the Social Capital which is a prerequisite for SME common infrastructure Awareness Creation Sensitization Trust Organisation Capacity Building Competitive reliance on one another 13 Some Benefits of Clustering Ff1.Commercial Benefits 1.Enchaned chances of securing larger contracts 2.Greater Barganing power with customers 3 Greater presence in market place 4 Guidance from experienced larger companies with shared risk 2.Economic Benefits 1. Sharing & Pooling of resources 2. Sharing Business Development & operating cost 3. Access to New Technology 1.Commercial Benefits 1.Commercial Benefits 1 Aids in decongesting 1. Employmunits from urban areas -ent 2. Ensures that generation Enviroinmental 2. Compliance safety standards to trade are maintained related 3 Various forms of brriers. pollution always 3 Ensures under check enhanced security during the startup Why are Cluster Parks different- a Comparative analogy 1. CLUSTER PARKS 1.Focus on enterprises and their needs 2. Owned and managed by user enterprises 3. Pre- marketed 4. Customised infrastructure 5. Homogeneous units with strong linkages and collaborative behavior 2. INDUSTRIAL ESTATES 1. Focus on real estate 2. No involvement of user enterprises 3. Post marketed 4. Standard infrastructure 5. Absence of collaborative behavior. Integrated Infrastructural Development (IID) Scheme (Subsumed in MSE-CDP) To provide developed sites with basic infrastructural facilities like power, water, telecommunication, drainage,& pollution control facilities roads, Banks, Raw Material Storage, Marketing Outlets, common facilities services,& Technological Backup Services etc. The GOI grant will be 60 % of the cost of project of Rs 10 Cr.(excluding cost of land). Fund will be released on reimbursement basis or on matching share basis. Breakup of Fund :1. Land Development & Other Overhead infrastructure : Rs 7.50 Cr. 2. Administrative & Other services complex – Rs 1.50 Cr. 3.Effluent treatment facilities – Rs 0.80 Cr. 4. Contingencies and pre-operative expenses – 0.20 Cr. FUNDING PATTERN: CFC Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), i.e., Society/ Trust/ Co. to be formed by cluster beneficiaries before seeking funds for Common Facility Centre (CFC), For CFC, GoI support is 70 % of the cost of project of maximum 15 Cr. Cluster beneficiaries’ share should not be less than 10% of the total cost of CFC, the cost of project includes Cost of Land( subject to maximum 25 % of project cost), Building, Pre- Operative expenses, Machinery & equipment etc. State Government contribution will be considered as the viability gap funding. National Manufacturing Competitiveness Programme (NMCP) for MSME Sector Challenges faced by Indian MSMEs Access to Technology I.P.R. related issues, Design as market driver Wasteful usage of resources / manpower Energy in-efficiency and associated high cost Low ICT usage Low Market penetration Quality Assurance / certification. National Manufacturing Competitiveness Programme (NMCP) for MSME Sector Objectives Focus on increasing competitiveness of MSME sector Key initiative for survival of MSMEs in domestic / international markets A catalyst approach / create role models Implementation with Public Private Partnership Challenges for implementation Basically a Supply side initiative Fear of MSMEs in disclosing data. MSMEs are hesitant in investing their contribution. NATIONAL MANUFACTURING COMPETITIVENESS PROGRAMME (NMCP) 1. Lean Manufacturing Competitiveness Scheme for MSMEs 2. Design Clinic Scheme for design expertise to MSMEs Manufacturing sector (DESIGN) 3. Marketing Assistance & Technology Up-gradation Scheme in MSMEs. 4. Technology and Quality Upgradation Support to MSMEs 5. Mini Tool Rooms proposed to be set up by Ministry of MSME (MTR) 6. Quality Management Standard & Quality Tech. Tools (QMS/QTT) 20 • 7. DEVELOPMENT OF SMES THROUGH INCUBATORS 8. MARKETING SUPPORT/ASSISTANCE TO MSMES(BAR CODE) 9. BUILDING AWARENESS ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS (IPR) FOR MSME 10. PROMOTION OF ICT IN INDIAN MANUFACTURING SECTOR (ICT) 21 1. Lean Manufacturing Scheme Objective: To minimize wastages in manufacturing Lean Manufacturing (LM) is Better Production of Goods by Eliminating Non-value Added Activities / Wastes Helping to Produce More with Same Resources Scheme is under operation on pilot basis for 100 mini clusters NPC is working as Monitoring & Implementing Agency Evaluation completed for current scheme and further up- scaling EFC note being processed. 22 Lean Manufacturing Scheme Implementation approach Initially cluster units to be made aware regarding lean techniques ‘Mini Clusters’ of 10 units (appx.) to be created SPV to be formed by ‘Mini Cluster’. GOI : Private Share – 80:20 Max. cost of LMC to be Rs. 23.5 lakh Monitoring of milestones by NMIU. 23 1S implementation - scrap yard Before After Removed the scrap in scrap yard. & create the space for die storage 2S implementation - Packing & dispatch area Before After Packing & dispatch area – unwanted material removed Shining Example for Shadow Board Before After SPVs formed (Zone wise) 24% Zone SPVs formed 1 North 37 2 East 16 3 West 25 4 South 26 Total 104 36% 24% 16% North Sr. No. East West South SPVs formed (State wise) S.No. State No. SPVs formed S.No. State No. SPVs formed 1 Andhra Pradesh 3 11 Madhya Pradesh 2 2 3 4 5 6 Assam Bihar Delhi Gujarat Haryana 12 13 14 15 16 Maharashtra Orissa Punjab Puducherry Rajasthan 7 Himachal Pradesh 2 1 11 8 3 2 17 Tamil Nadu 15 5 11 1 2 13 8 Jharkhand 3 18 Uttar Pradesh 7 9 Karnataka 5 19 West Bengal 5 10 Kerala 4 20 Uttarakhand Total 1 104 SPVs formed (Sector wise) No. of SPVs formed Auto & Engg. Components 18 S.No. Sector/Sub Sector 1 S.No. Sector/Sub Sector 14 Light Engineering No. of SPVs formed 7 2 Ball Bearing 3 15 Machine Tools 3 3 Diamond Processing 1 16 Metal Work 1 Diesel Engines/Motor&Pump sets Electrical/Electric Fans 2 Oil expellers 1 Packaging 2 Engg. & Fabrication 19 1 7 Food Processing 6 20 Chemical & Die Units. Pharma 8 Foundry 4 21 Plastic 4 Granite 1 1 Hand Tool 4 IT Hardware & Electronics Rice Milling Handicrafts 2 24 Scientific Instruments 2 Apparels and Garments 8 25 White Goods 3 Leather 3 4 5 6 9 10 11 12 13 3 17 18 19 22 23 Total 2 3 104 Lean Manufacturing Scheme (Constraints) Lean Manufacturing is a comparatively new initiative (on such a large scale) hence MSMEs are initially hesitant Reluctance in data sharing SPV formation is time consuming NPC has limited resources for monitoring on large scale, hence some more agencies are required Good LMCs not inclined to work with MSMEs Pvt. Share is not being contributed as per schedule Difficulty in co-ordination among 10 units 30 2. Design Clinics Scheme Objective: To Bring the industrial design fraternity closure to the MSME sector Increase the competitiveness of local products / services through design Develop an institutional base for the industry’s design requirement Major activities : Setting up of design clinic centre - HQ Regional Centres – 4 Nos. Awareness seminars and workshops – 200 Clusters. Design projects for individual MSME or a group of MSMEs Students Projects Orientation Programme for Designers NID & IISc. Are the nodal agency 31 Design Clinics Scheme – New Products developed by MSMEs (1) Visitor Management System, (2) Improved light weight pump (3) Bottle vision equipment 32 Design Clinics Scheme – New Products (1) Portable Hydraulic (2) ENT multi scope (3) Syringe (precision type) 33 33 Design Clinics Scheme (Constraints) Lack of inclination of Industrial Design professionals towards MSMEs MSMEs hesitant to contribute their share Sector specific design institutes not yet actively involved MSMEs still believe in copy – paste rather then innovation 34 3. Technology and Quality Upgradation Support (TEQUP) Objective: Focuses on Energy Conservation, CDM & Product Certification Activities Proposed: 1) Awareness Generation for Energy Efficient Technology 2) Credit Linked subsidy for EET Projects (25 %) 3) Encourage MSMEs through subsidy to acquire National as well as International Certification of Products 35 ENERGY EFFICIENT TECHNOLOGY FOR MSME SECTOR Roller kiln - Morbi ceramic cluster Boiler - Plywood unit, Ernakulum Re-cupeater – pot furnace Firozabad 4. Promotion of ICT in MSME sector The modified ICT Scheme with cloud computing approach has been concurred by Planning Commission meeting will be held. and Shortly SFC Advantage of Cloud Computing • Capital Expenditure(CAPEX) is getting • • • • converted into operational expenditure (OPEX). Device and Local independent Centralized meeting system. Pay as you use model facility MSMEs does not have to invest in IT personnel for maintenance purpose. 38 Components of Cloud Computing • Software as Service • Portal as Service • Infrastructure as Service 39 5. Quality Mgt. Systems/Tools (QMS/QTT) Objectives: Scheme to support awareness generation as well as implementation of Quality System Tools in MSME sector Conforming to International Standards, 5S, Six-sigma, TQM, TPM ISO 9000, ISO 14000, ISO18000, ISO 22000 etc. Major activities to propagate Quality Management in MSMEs are: 1) Compulsory Courses in Govt . ITIs / Polytechnics 2) Awareness Programmes in Clusters on QMS / QTT topics 3) Implement Quality Mgt Techniques among MSMEs 4) Special Studies for Threatened Products 5) Assist International Study Missions for SME groups 6) Organize National level workshop on QMS/QTT 40 Quality Mgt. Systems/Tools (QMS/QTT) ….Contd. Progress: 1) Course materials for 1800 ITIs prepared and 1745 teachers trained, 2) Course details for Polytechnics is taken up this year. 3) More than 364 awareness programmes in MSME clusters completed on QMS / QTT topics by expert agencies, 4) Implementation of Quality Mgt .Techniques among MSMEs – 10 clusters has been initiated. 5) Assist International Study Missions for SME groups – 1 mission to Japan (with 20 SMEs) completed last year. 41 QMS/QTT (Constraints) QMS/QTT implementation not yet sanctioned due to IFW insisting on competitive bidding for engaging expert agency Limitation to use only clusters from Threatened product catagory QMS/QTT courses yet to be prepared for Polytechnics State Govt not sparing ITI teachers for training MSMEs / Associations Hesitant to give contribution Medium units not included 42 6. I P R Campaign Objectives: IPR Tools : – Patents Trademark Indl. Design – Copyrights G.I. Trade Secret Most MSMEs are unaware of IPR Benefits / Norms Focused Activities 1) Awareness & Sensitization Programmes 2) Pilot Study 3) Interactive Seminars / Workshops 4) Short / Long Term Training 5) IP Facilitation Centre 6) Assistance for Grant on Patent / GI Registration 43 IPR Campaign (Constraints) 1) Lack of Awareness, Knowledge & Expertise 2) Lack of confidence in Enforcement mechanism and perception of higher cost of Monitoring & litigation. 3) Majority of MSMEs do not have IP Strategy in place. 4) Shortage of Trained Human Resources 44 7. Incubators Objectives: Assist Incubation of Innovative Ideas Promote Emerging Technological Innovative Ventures Encourage Ideas to Become MSMEs & Knowledge-based 100 BIs to be Located in engineering colleges, management institutions and R&D Institutes @ 25 p.a in 4 yrs. Govt. Grant (Max. 85%) = Rs.4 - 8 lakh per Idea Each BI to Assist 10 Ideas / Units – Max. Rs.62.5 lakh + Rs.3.78 for Infrastructure & Training. BIs to support and Nurture ideas for commercialization in a year 45 8. Marketing Assistance and Technology Upgradation Scheme for MSMEs Objectives: To enhance MSMEs competitiveness in the National as well as International market through following activities; Major activities: Technology up gradation in packaging Skill up gradation /development for Modern marketing techniques Special component for NER clusters State/District level local exhibitions Corporate governance practices Marketing hubs Reimbursement to ISO 18000/22000/27000 certification 46 9. Bar Code Objectives: Bar Coding assist in popularizing MSME Products, especially for Exports & Retail Bar Coding an effective Tool to improve marketability Reimbursement allowed : 75% of Annual Fee for first 3 years (Bar Code Certificate) 47 10. Mini Tool Rooms on PPP Mode Objectives: Scheme to Develop 15 new Mini Tool Rooms For Technological Support to MSMEs By Creating Capacities in the Private Sector ‘Mini Tool Rooms’ can be set up, : With GOI assistance restricted to Rs.9.00 cr. PPP is the Preferred Option (Model – I), - Private partner as promoter - VGF of 40% restricted to Rs. 9.00 cr. - Remaining resources by promoters - O & M by promoter OR 48 Model- II (State PPP Model): - SPV (State Govt. with private partner) - 90% of cost of machinery, restricted to Rs. 9.00 cr. - Remaining cost of M/c, L & B, recurring exp. by SPV. - State Govt. share > 26%. - O & M by SPV OR Model- III (Centre / State Model): - State Govt. / State Govt. agency to identify Implementing Agency (IA) - 90% of cost of machinery, restricted to Rs. 9.00 cr. - Remaining cost of M/c, L & B, recurring exp. by IA - O & M by IA Thank You 50