NOUH`s Projects in Egyptian Intermediate Cities
advertisement

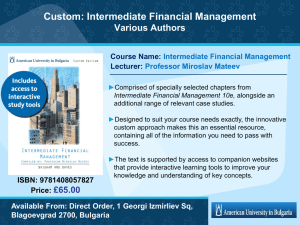
Egypt The National Organization for Urban Harmony (NOUH) and Intermediate Cities in Egypt Samir Gharib Presentation Structure: ▪ The Arabic version of ‘Looking at other urban spaces: intermediate cities’ ▪ Intermediate Cities: A prologue ▪ Characteristics of Intermediate Cities ▪ Proposals for Intermediate Cities ▪ National Organization for Urban Harmony (NOUH) ▪ NOUH’s Responsibilities ▪ NOUH’s Aims ▪ NOUH’s scope of work ▪ NOUH’s Work in Egyptian Intermediate Cities The Arabic version of ‘Looking at other urban spaces: intermediate cities’ The National Organization for Urban Harmony undertook the Arabic translation of ‘Looking at other urban spaces: intermediate cities’ , by our colleague and friend Josep Maria LLOP TORNÉ, Director, and Carmen BELLET SANFELIU, Technical secretary , of the CIMES program. We thereby highlighted the following aspects about intermediate cities. Intermediate Cities- A Prologue ● The adjective intermediate/intermediary was first registered in academic circles in the mid1980s, to replace medium-sized city ● The European Union defines intermediate cities as settlements that contain between 20,000 and 500,000 inhabitants, while the World Bank raises the upper limit to one million. Intermediate Cities- A Prologue Intermediate cities are not only defined in terms of their demographic size and according to specific dimensions , but, above all, on the basis of the functions that they perform: their role in the mediation of flows (goods, information, innovations, etc.) between the rural and urban territories within their areas of influence. Intermediate Cities- A Prologue The medium-sized/intermediate city cannot simply be defined on the basis of its physical or demographic size. As, or even more important, are: ● the role and the function that the city plays within its more or less immediate territory ● the influence and relations that it exerts and maintains with this territory ● the flows and relations that it generates towards the exterior. Characteristics of Intermediate Cities: ● more balanced and sustainable systems that can, in theory, maintain more open, harmonic, and balanced relationships with their regions ● easier to govern and control ● more human and effective scales, which makes them easier to understand and define, and hence also easier to physically plan and structure Characteristics of Intermediate cities: ● less environmental problems ● less socially conflictive and smaller associated social costs ● less socially and culturally diverse ● In parts of the Third World, intermediate cities act as centres that exploit large rural areas or exploit the natural and human resources of their areas of influence National Organization for Urban Harmony (NOUH) Location: Salah el Din Citadel – Cairo NOUH’s Responsibilities According to the law 119, for the year 2008,NOUH is responsible for: ● identifying heritage areas and buildings and setting principles for their restoration ● outlining policies, guidelines, and legislations for harmonious future urban development NOUH Saladin Citadel, Cairo NOUH’s Aims According to its establishment decree (no.37- 2001), NOUH aims at enhancing the urban environment and quality of life, through; 1. Restoring the cultural identity of Egyptian urban environments. 2. Fulfilling aesthetic values in existing and new settlements. NOUH’s scope of work ● Reforming the aesthetic image throughout the country ● Setting regulatory controls for existing and new urban development NOUH’s scope of work ● Formulating a comprehensive database for buildings of significant value The 19th c. Fire Brigade building - Ataba Square Continental Hotel - Opera Square Omar Affendi Department Store Sednaoui department store al Khazendar Square NOUH’s scope of work ● Restructuring guidelines for dealing with elements of the urban environment; advertisements and signs, open and green spaces, roads and sidewalks, street furniture,…etc. NOUH’s scope of work ● Revitalizing and restoring historic squares, public spaces and pathways Talaat Harb Square Talaat Harb Square NOUH’s scope of work ● Launching international competitions for the urban design and harmony, and historic conservation of major historic urban spaces, and the rehabilitation of major heritage buildings, including; - Ramsis Square - Khedive Cairo ( Results anounced 2009) - Opera and Ataba Squares - Khedive Cairo (ongoing) - ‘Sednaoui’ Building and the adjacent ‘al Khazendar Square’ (ongoing) International Competitions : 1- The International competition for the urban design and harmony of Ramsis Square-Khedive Cairo The first winner (Franco- Egyptian project)proposed a new underground tunnel to reduce traffic flow in the square International Competitions : 2- The International competition for the Urban Design and Harmony and Historic Conservation of Opera and Ataba Squares- Khedive Cairo Opera Square International Competitions : 3- Competition for the Rehabilitation of ‘Sednaoui’ Building and the Urban Design and Harmony of ‘al Khazendar Square’ NOUH’s Work in Egyptian Intermediate Cities Some of the priorities of urban plans and designs in intermediate cities are directly related to the objectives and scope of work of NOUH. These comprise; ● Protection and rehabilitation of heritage buildings and areas. Old quarters tend to be the original centres of contemporary cities. The histories, images and identities of these old quarters are inseparable from them. In the specific case of intermediate cities, their physical impact is very significant. ● Improving and revitalising existing squares, and the provision of new squares and parks. ● Treatment of waterfronts and water spaces. NOUH’s Projects in Egyptian Intermediate Cities Damanhour City, Capital of Beheira Governorate-Egyptian Delta Urban Design and Harmony of Opera Square before after NOUH’s Projects in Egyptian Intermediate Cities Assiut City, Upper Egypt Revitalizing and restoring the Nile Waterfront after before NOUH’s Projects in Egyptian Intermediate Cities Shebein el Kom City, Capital of Monoufia Governorate Development of Shebein el Kom City Centre: Urban Spaces before development after development NOUH’s Projects in Egyptian Intermediate Cities Shebein el Kom City, Capital of Monoufia Governorate Development of the Nile Waterfront after development NOUH’s Projects in Egyptian Intermediate Cities Damietta City Development of the Nile Waterfront NOUH’s Projects in Egyptian Intermediate Cities Damietta City Development of the Nile Waterfront NOUH’s Projects in Egyptian Intermediate Cities Damietta City Rehabilitation of Historic Bridge (1890) From outside From inside Intermediate cities can and should play a more active role in future urban development Thank you Samir Gharib chair@urbanharmony.org