Sink
advertisement

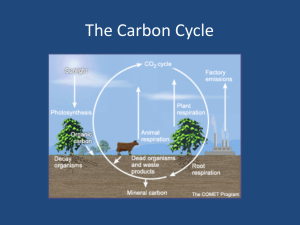
Global Carbon Cycling Where does it all go? Main Concepts Current CO2 levels: fluxes in and out What are C reservoirs? Natural CO2 sources and sinks: The land breathes. The ocean breathes. The rocks breathe. Carbon Residence time? Timescales of carbon removal from the atmosphere. Atmospheric CO2 What are the major sources of C emissions? How unique are modern CO2 levels? Where does it all go? How long will it stick around? Fossil fuel CO2 emissions: Burning buried sunshine Global C emissions map Atmospheric CO2:Last 50 years (1.5 ppm/year increase) Atmospheric CO2: Last 250 years Atmospheric CO2: last 400,000 years! Atmospheric CO2: Last 50 MILLION years How unusual are modern CO2 levels? Atmospheric CO2: Last 500 MILLION years Estimating Ancient CO2: Leaf Stomata Living Stomata density related to CO2 high CO2 = low stomatal density Fossil Carbon fluxes (in Gt/yr), reservoirs (bold, Gt), and residence times (years) as of 1990 Note: 2006 emissions were 7.7 Gt / year, How much is a gigaton (Gt)? • One billion metric tons (1015 g) • It is about 2750 Empire State Buildings. • Global C emissions are about 6 Gt. Carbon cycle fluxes These have significant errors and change year-to-year Cycling Ocean uptake Flux rate (Gt/year) -2.0 Photosynthesis -120.0 Respiration +120.0 Fossil Fuel Combustion Biomass burning +6.0 +1.0 ( “-” means removed from atmosphere; 1990 data) The atmosphere only contains about 2/3 of the total C emissions - why? Carbon “sinks” Source: Carbon Emissions: 6.0 Gt/year Sink: Obs. Atm increase: 3.2 Gt/year Ocean uptake: 2.0 Gt/year “missing sink”: 1.8 Gt/year 1990 estimates Ocean-Atmosphere gas exchange Air Sea CO2 + H2O H+ + HCO3- Vertical Sections through the oceans Air-Sea CO2 fluxes Gases are more soluble in COLD water Ocean uptake Net: -2 Gt/yr Ocean release Ocean uptake Ocean uptake Ocean release Ocean and Atmoshere C reservoirs Ocean C: 39,000 Gt (as HCO3-, CO32-) Atmosphere: 1580 Gt (as CO2) Ocean has 50x more carbon than the atmosphere. Carbon Fluxes Calculating Residence time Residence time is a “replacement time”: time required to affect a reservoir given a certain flux. (years) = reservoir / input rate Example: Residence time of a CU undergrad Reservoir: Size of Columbia’s UG Student Body? Input rate: Incoming 1st-year class size Calculating residence time of Carbon due to air-sea exchange Ocean uptake rate: -2.0 Gt / year Total Ocean C reservoir : 39,000 Gt Surface Ocean C reservoir : 600 Gt C residence time (whole ocean) = ? C residence time (surface only) = ? Q1: Carbon Cycle Budget At steady state: Sources = Sinks Sources: Respiration, FF, land use Sinks: Photosynthesis, ocean uptake But.. C is not at steady state… (CO2 is rising, right? Equivalent to +3.2 x1015g/ year So the following should be true: +3.2 Gt/year = (Sources) + (Sinks) The missing C sink (Gt/yr) +3.2 = (Sources) + (Sinks) + (other) +3.2 = (122+90+6+1) + (-120-92-2) + (other) +3.2 = (219 - 214) + (other) “other” = 5.0 - 3.2 “other” = missing sink of -1.8 Gt/year This “missing sink” has been removing C from atmosphere each year…(a good thing) The Missing Sink (history) Missing C sink: What is it? CO2 fertilization of high-latitude forests Plants grow faster/better at higher CO2 Plant C uptake Atm CO2 level Current state of the Missing Sink “Missing sink” was accelerated growth of northern forests under high CO2 (carbon uptake) This sink is now completely offset by tropical deforestation. (additional carbon emission) Bolivia (1984-1998) The future of fossil fuel CO2 How quickly would the planet take up our CO2? Fast: “solubility pump” Air-Sea CO2 exchange (centuries) Moderate: “Deep ocean acid neutralization” (tens of thousands of years) Really slow: “Weathering of continental rocks” (millions of years) Fast C cycling: Air-Sea Exchange Centuries Moderate C Cycling Neutralize deep ocean acidity by Dissolving ocean CaCO3 sediments 104 years Really Slow C cycling Continental weathering (dissolves mountains!) “Urey reaction” - millions of years CaSiO3 + CO2 --> CaCO3 + SiO2 Carbon Reservoirs (1Gt = 1015g) Reservoir Rocks Size 65,000,000 Oceans 39,000 Soils 1,580 Land Plants 610 75% in 300 years 25% “forever” Bottom Line Human C Emissions are large Nature can’t keep up Natural C sinks are diminishing Lifetime of CO2 from your tailpipe: “300 years, plus 25% that lasts forever”