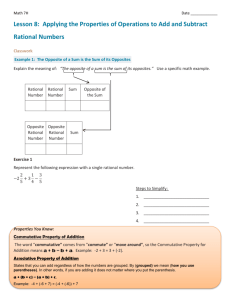
H.E Dr. Vathana Sann, Deputy Secretary
advertisement
Development and Implementation of an Integrated National Social Protection Strategy Vathana Sann (PhD) Deputy Secretary General Council for Agricultural and Rural Development South-South in Practice: Implementation of Sustainable Social Protection Floors September 2013 1 Country Overview Kingdom of Cambodia, Constitutional monarchy in Southeast Asia Landmass : 181,035 Km2 Population : 14.5 M Poverty : 25 % GDP : 915$ /capita SP Spending : 5.5% GDP 2 Rational SP, part of Cambodian life from reconciliation, rehabilitation, reconstruction and development phase Labour intensive and social assistances were the major national programs in post-war periods End-2008, DP and RGC committed to review the existing SSN to address food security during economic crises 3 Rational SP Program Social Security (NFV, NSSFC, NSSF) Health protection (supply, HEF, CBHI) Social assistance and relief School feeding and scholarship ODA-funded social assistance projects NGO-funded social assistance projects Public Works Programmes Vocational Training Total Expenditure (million $) % of GDP 46.1 0.4 390.4 3.35 78.7 0.68 12.4 0.11 41.9 0.36 25.8 0.22 20.7 0.18 24 0.21 640 5.55 The new era of Social Protection has begun !!! 4 Rational : gaps of existing SP programs Good morning, national ownership !!! MEF Fragmented programs at ministerial and project sites (> 53 programs, 8 social sector ministries) on limited budget 5 Rational : gaps of existing SP programs The national net is to catch the national issues The lack of Monitoring and Evaluation Framework and the use of different targeting systems (1 program, 1 system) 6 Rational : gaps of existing SP programs The burden of delegating implementation roles to the decentralized government with on institutional capacity 7 Rational : gaps of existing SP programs Let’s them do the job!!! the hole isn’t at our side The need for coordination mechanism for policy oversight and strategy development between RGC and DP 8 Strategy development: Development framework Priority Existing prog. Basic needs during emergency Food distribution Human capital development School feeding, scholarship Employment and food security Social health protection Special vulnerable groups Legal framework Emergency and crises Constitution National strategy Sectorial law Public works Health equity, insurance Social assistances Poverty profile MDG National Strategic Development Plan Constraints to human development Un and under employment Health issue International conventions Special vulnerability 9 Strategy development: Defining scope Social Protec on Labour market policy Social Insurance (Contributory) Other insurance schemes Community -based Health Insurance Social Safety Net (Non-Contributory) Public Work Programs (Cash or food for work) Condi onal or Noncondi onal Cash or InKind Transfer Complementary Social Welfare Services Social Subsidy (to facilitate accesses to public u li es, health, educa on, housing…) Social Protec on for the Poor and Vulnerable 10 Strategy development: Gradual process 11 Strategy development: Balancing economic and social Contribution to human development and economic growth with equity Provision Social Development Health policies Education policies HIV/AIDS policies Social welfare policies and action plans Social Protection Social protection instruments to enable access and utilization of basic social services and improvements in human development Social Safety Nets Social protection instruments to enable response to emergency Promotion Social protection instruments to support engagement of the poor in economic activity and income earning Economic Development Macro-economic and fiscal policies Agricultural and rural development policies Industrial policies Trade policies Disaster management National disaster management policies 12 Strategy Implementation: Regional policy Natural disaster and climate changes, and climatic risks remain the challenges to livelihood of the poor Economic progress lifted millions out of poverty, not all have benefitted from these gains Many people are still poor, deprived of basic amenities, and vulnerable to economic and climatic risks Growth alone can not achieve sustainable development with equity: social costs of integration must be assessed 13 Strategy Implementation: Regional policy With the opening of a regional job market, labor mobility will rise and broaden opportunities for employment Low skill workers from Cambodia, Laos and Myanmar, might be pushed out by competition 60% of the workforce is engaged in the informal sector, with little social protection With increased threats of unemployment, resulting these workers taking even more insecure and lowpaying jobs 14 Strategy Implementation: Regional policy Climatic risks There might be a negative impact on regional peace, security, and prosperity. Human development (focusing on children) and healthier, educated, and productive workforce It is people-centred and socially responsible with a view to achieving enduring solidarity and unity among nations 15 Strategy Implementation: Coordination CDCF IWG / SPCG Cambodian Development Collaboration Forum: the highest join-RGC-DP forum for reviewing development process: SP Core Group: Selected DP, invited for specific issue, WB, UN, EU, IFAD, ADB, AusAid … IWG 2008 SPTF Social Protection Task-Force: RGC Structure, CARD, MoP, MEF MoI and 8 members Policy oversight and high level coordination Interim Working SPCU Group on SP: join-RGC-DP forum, Social Protection Coordination Unit: A secretariat at CARD to facilitate the volunteer, open forum, 200 members network between RGC-DP 2015 2014 2013 2009 Program Program Program 2010 2011 NSPP Strategy development with 5 Objectives: Emergency situation, Human Development, Employment, Health, Special vulnerability 2012 Guiding principle (M&E, targeting, capacity development) Implementation by local administration (design, financing) 16 Strategy Implementation: Coordination 17 Strategy Implementation: Living document 2015 Backbone strategy 2013 SP Implementation and service delivery at Sub-national level 2012 Implementation modality (ISPP, SSD) Toward a more integrated and systematic approach of social protection and gradual process to comprehensive social security system Turning policy into action - NSDP Mid-term - ASEAN SP - Micro-insurance - SPER - NSPS Costing - Rate of Return - Policy brief - SP Research Fund - SP Training - Equity campaign Policy Support and Oversight 2011 2010 2008 Design and scaling up CT, PWP SNA Capacity building and Private Sector involvement Partnership and Capacity Dev. Making information available for all - SPCU Website - Communication - Reporting system Information Management Evidence-base monitoring - Database review - SP Indicators - SP Framework Monitoring and Evaluation Redefining coordination roles and institutional establishment Existing program implementations: Social security, HEF, CBHI, SF… National Social Protection Strategy development and endorsement Milestone 2 Strategy implementation Milestone 1 Strategy development Mapping and scoping exercise, SP background study, 18 Strategy Implementation: Social service delivery 19 Strategy Implementation: Social service delivery 20 Summary Strategy development Determining a clear analytical frameworks based on poverty profile, existing programmes, and legal framework Defining country-specific scope and definition of social protection Setting the gradual process of moving from safety-net based to expanded and comprehensive social security Balancing the national focus on economic development and investment for social development 21 Summary Strategy implementation: Determining the areas of priorities at regional level where the floor of social protection can be addressed Promoting the coordination mechanism for the engagement of policy support, M&E, partnership, and information sharing Enhancing the role of Sub-National Authority to deliver social service with responsibility and accountability 22 Challenges and way forwards SP dialogue is moving from DP agenda to a more harmonized and integrated strategic approach No intention to phase-out and programs nor institutions, or establishment of new institutions Moving toward capacity development for SNA for SP design and financing as part of local development plan Guiding principles on M&E, targeting system (ID-Poor), one-window service are in place for better coordination Developing human resources to cope effectively with the challenges of modernization and globalization Participation of the private/business sector and the nongovernmental/people's organizations. 23 sUmGrKuN 24