C3_chemicals_in_our_lives_revision_map
advertisement
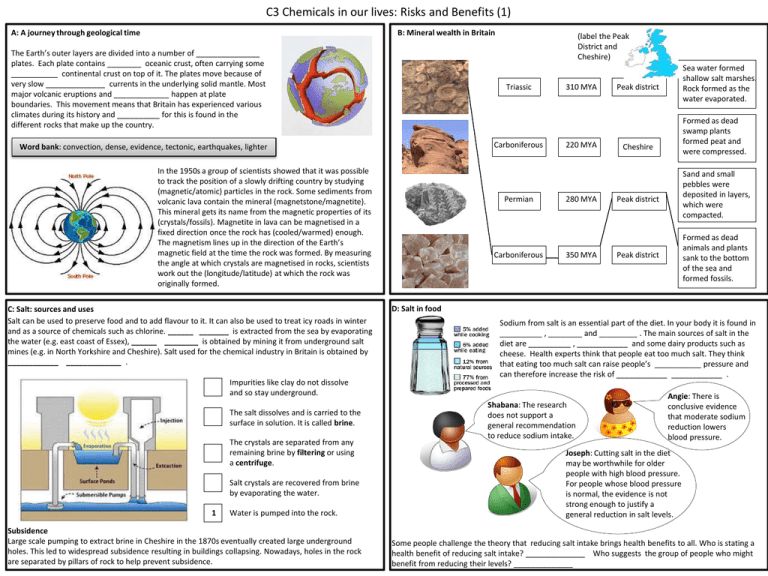
C3 Chemicals in our lives: Risks and Benefits (1) B: Mineral wealth in Britain A: A journey through geological time The Earth’s outer layers are divided into a number of _______________ plates. Each plate contains ________ oceanic crust, often carrying some ___________ continental crust on top of it. The plates move because of very slow ______________ currents in the underlying solid mantle. Most major volcanic eruptions and _____________ happen at plate boundaries. This movement means that Britain has experienced various climates during its history and __________ for this is found in the different rocks that make up the country. Triassic Carboniferous Word bank: convection, dense, evidence, tectonic, earthquakes, lighter In the 1950s a group of scientists showed that it was possible to track the position of a slowly drifting country by studying (magnetic/atomic) particles in the rock. Some sediments from volcanic lava contain the mineral (magnetstone/magnetite). This mineral gets its name from the magnetic properties of its (crystals/fossils). Magnetite in lava can be magnetised in a fixed direction once the rock has (cooled/warmed) enough. The magnetism lines up in the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field at the time the rock was formed. By measuring the angle at which crystals are magnetised in rocks, scientists work out the (longitude/latitude) at which the rock was originally formed. C: Salt: sources and uses Salt can be used to preserve food and to add flavour to it. It can also be used to treat icy roads in winter and as a source of chemicals such as chlorine. ______ _______ is extracted from the sea by evaporating the water (e.g. east coast of Essex), ______ ________ is obtained by mining it from underground salt mines (e.g. in North Yorkshire and Cheshire). Salt used for the chemical industry in Britain is obtained by ____________ _____________ . Impurities like clay do not dissolve and so stay underground. The salt dissolves and is carried to the surface in solution. It is called brine. The crystals are separated from any remaining brine by filtering or using a centrifuge. Salt crystals are recovered from brine by evaporating the water. 1 Water is pumped into the rock. Subsidence Large scale pumping to extract brine in Cheshire in the 1870s eventually created large underground holes. This led to widespread subsidence resulting in buildings collapsing. Nowadays, holes in the rock are separated by pillars of rock to help prevent subsidence. (label the Peak District and Cheshire) Permian Carboniferous 310 MYA 220 MYA 280 MYA 350 MYA Sea water formed shallow salt marshes. Rock formed as the water evaporated. Peak district Formed as dead swamp plants formed peat and were compressed. Cheshire Sand and small pebbles were deposited in layers, which were compacted. Peak district Formed as dead animals and plants sank to the bottom of the sea and formed fossils. Peak district D: Salt in food Sodium from salt is an essential part of the diet. In your body it is found in __________ , ________ and _________ . The main sources of salt in the diet are __________ , ____________ and some dairy products such as cheese. Health experts think that people eat too much salt. They think that eating too much salt can raise people’s ___________ pressure and can therefore increase the risk of ____________ ____________ . Shabana: The research does not support a general recommendation to reduce sodium intake. Angie: There is conclusive evidence that moderate sodium reduction lowers blood pressure. Joseph: Cutting salt in the diet may be worthwhile for older people with high blood pressure. For people whose blood pressure is normal, the evidence is not strong enough to justify a general reduction in salt levels. Some people challenge the theory that reducing salt intake brings health benefits to all. Who is stating a health benefit of reducing salt intake? ______________ Who suggests the group of people who might benefit from reducing their levels? ______________ C3 Chemicals in our lives: Risks and Benefits (2) E: Alkalis and their uses Traditional alkalis were needed to _______________________________ ___________________________________________________________ One of the first pure chemicals made in Britain was alum. This was used for dyeing cloth. Alum was made on the North East coast of Britain, where rocks in the cliffs were rich in aluminium compounds. F: Chemicals from salt – the foul way 1. 2. 3. (Label Runcorn by the river Mersey) (label the North East coast of Britain) 4. 1 Rock was roasted in fires for many months The solution was boiled to evaporate most of the water. Alkali was added to neutralise the acids. The solution was allowed to cool in wooden casks and alum crystals formed. The resulting soluble chemicals were put into lead pans. Rock was put into pits of water and allowed to settle. Alkalis and their reactions – alkalis can neutralise acids Alkaline hydroxide + acid salt + water Alkaline carbonate + acid salt + carbon dioxide + water What products are formed during these reactions? 1. Calcium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid ____________________________________________ 2. Potassium hydroxide + sulfuric acid ____________________________________________ 3. Sodium carbonate + nitric acid ____________________________________________ G: Benefits and risks of water treatment Water that is contaminated by __________ can sometimes carry fatal diseases such as ________ , typhoid, dysentery and gastroenteritis. Waterborne infections cause 1.7 million deaths per year. Those who die are mainly __________ in developing countries. Chlorination of drinking water in Britain became common in the early twentieth century. Benefits Chlorination is used to __________________________ _____________________________________________ Using the graph, describe what happened to the numbers of deaths from typhoid fever in the USA following water chlorination. _____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ . Another advantage of treating water with chlorine is __ ____________________________________________ . Risks Why are some scientists concerned about chlorination? ______________________________________ How are trihalomethanes (THMs) formed? _________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ What are the suspicions about THMs? _____________________________________________________ Is there any evidence for this? ___________________________________________________________ How can the levels of THMs be limited? ___________________________________________________ Across: 3. The chemical produced when hydrogen chloride is oxidised (8) 4. The name of the gas given off during the Leblanc process (8,8,) 5. Hydrogen chloride dissolved in water produces hydrochloric acid. What happens to wildlife in rivers polluted with this acid? (4) 6. Alkalis were used in which industry in France in the 1700s? (5) 7. The laws passed by the Government to reduce the pollution produced by the chemical industry (6,4) 8. The inventor of the process used to make the alkali sodium carbonate from limestone and salt (7) 5. 6. 7. 8. Down: 1.The gas that smells of rotten eggs (8,7) 2. Chlorine is used to do what to paper and textiles? (6) H: Chemicals from salt – a better way Brine is a mixture of sodium chloride ( ) in water ( ). So there are just four elements in brine, which can be rearranged to make chlorine ( ) , sodium hydroxide ( ), and hydrogen ( ) .The chemical changes happen when an electric current flows through the solution. The process is called ______________________ . The equipment is designed with a porous membrane to keep the two main products, chlorine and sodium hydroxide, separate because they react with each other when they mix. Environmental impact of electrolysis Manufacturing chemicals from salt by electrolysis needs a lot of energy. How is most of this energy (electricity) produced? ________________________________________________________________________________ The industry is moving towards producing the electricity from renewable sources such as? ________________________________________________________________________________ Until recently the most common system for the electrolysis of brine used mercury as one of the metals in contact with the solution. What is the problem with using mercury? ________________________________________________________________________________ C3 Chemicals in our lives: Risks and Benefits (3) I: Protecting health and the environment Synthetic Chemicals in plastics and pesticides Amount of chemical in human blood Amount of chemical needed to be harmful Risk < 1 part per billion The likelihood of a hazard causing harm Can cause cancer Something that is likely to cause harm REACH (Registration, evaluation and authorisation of chemicals) was introduced in the EU in 2007 to collect information about the hazards of chemicals to assess risks. The responsibility for control and safety of chemicals is with the companies who make them or use the. J: Stages in the life of PVC PVC is a synthetic polymer that is strong, easy to mould and quite cheap. It is also hardwearing, durable and can be used to make a wide variety of products. The stages in the life of PVC products include production, use, and disposal. Label the statements P, U or D. Used as window frames Pipes are used underground to carry drinking water. Man made Hazard Large doses A LCA involves collecting data about each stage of the life of a product. An assessment of this kind can show, for example, what materials should be used to make different products. Label the statements below C (cradle) U (use) or G (grave). What is the problem with plasticisers? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Materials used to make the product. Shabana: There is evidence linking plasticisers with health problems such as cancer and infertility. Water and chemicals needed to maintain the product. Energy and water used in processing and manufacturing. Who above would support a ban on the use of plasticisers? __________________________ If there is no conclusive evidence that DEHP can cause harm, why do they have this opinion? ______________ Alternatives to using DEHP in medical equipment are expensive and not always available but the risk of not treating a patient is greater than the very small risk of from exposure to the plasticiser. Used as gutters L: From cradle to grave Plastic will not rot because it is not _______________ . Oil and products from oil, like plastic, are very valuable. They lose value as they are used and end up as waste. This is not ___________ because the materials cannot be used again. ____________ and reusing materials slow down the rate at which we use up natural resources that are not renewable. What are the most common plasticisers for PVC? ____________________________________________ Emily: PVC has been used for over 50 years and in that time , there has not been a single known case of anyone being harmed as a result of phthalates. Small molecules of vinyl chloride monomers are joined to make PVC polymers Recycling – waste ground into pellets, which can be reheated and moulded into new products K: Benefits and risks of plasticisers What are plasticisers? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ PVC sent to factories to be moulded under heat and pressure Energy recovery – polymer waste is burnt in incinerators and the energy used to produce electricity. Tipped into holes in the ground as landfill POPS (persistent organic pollutants) and pollutants There are some synthetic chemicals that everyone agrees are _________ even in very small amounts. These are chemicals that do not ________ _______ in the environment for a very long time. This means that they can spread around the world in air and water, and can ______________ in the fatty tissue of animals, which people then eat. Gurpal: The plasticiser DEHP has been shown to affect the development of the reproductive system and sperm in young male animals. These effects have not been found in human babies, but it has not been possible to show that there is no risk. Combining chlorine and ethene Energy needed to dispose of the product. Energy needed to use the product. Raw materials obtained and processed to make useful materials. Space needed to dispose of it. Energy needed to maintain the product.