Excretory System
advertisement

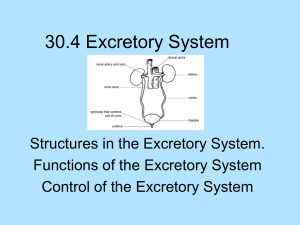
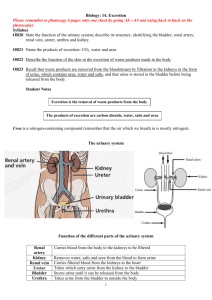
Excretory System Osmoregulation & Excretion Osmoregulation is important in homeostasis. Hyperosmotic Hyposmotic Isoosmotic Excretion helps in maintaining ionic & PH balance. The excretory system of all vertebrates have tubules specialized in excretion called nephrons. Excretion Simple organisms e.g Paramecium contractile vacuole Invertebrate animals e.g earthworm metanephridia grasshoper malphighian tubules N.B: Vertebrates have a backbone or a spinal column a.k.a vertebral column (e.g mammals,reptiles, amphibians, birds, sharks etc) Invertebrates do not have a backbone or spine a.k.a vertebral column (e.g insects, worms,snails, crabs) The human Excretory System Kidney & Urinary System Functions: 1- Maitain water content 2- Eliminate toxins & unwanted byproducts (ammonia) 3-Maintain proper body PH. Questions-Activity Q1. Describe 2 main functions of the kidney. Answer: -Elimination of wastes, regulation of PH and water balance Q2. what deamination and why is it important? Removal of amino group from an organic compound is deamination. It is important because many humans consume high protein diets which means the liver needs to convert these proteins into carbohydrates through deamination. Q3. How does formation of urea prevent poisoning? Answer: Because deamination creates a byproduct ammonia which is poisonous. 2 molecules of ammonia combine with a carbon dioxide to form urea which is 100 000x less toxic than ammonia. Animals can store urea for short time in their body, which permits controlled excretion in their urine. Q4. Fish are able to excrete ammonia continuously from their gills. Explain why birds & mammals cannot continuously remove toxic waste. The waste product is urine in humans and birds instead of ammonia. Urine would have to be excreted from body continuously with makes it difficult for land animals to survive because fluids would have to be continuously replaced in order to maintain homeostasis. Kidney & Urinary System When a.a are deaminated in liver it releases ammonia. Mammals convert ammonia to urea (2 ammonia+ 1 CO2) Goes into blood to kidney to be eliminated as urine. Kidney ureter urinary bladder urethra Nephrons Blood is filtered by the kidney at a rate of 1.2 l/min Urine formation depends on 3 things: 1- Filtration 2- Reabsorption 3- Secretion Kidney Urine Formation Activity Pg.450-452 Nephron Questions- Activity 1- Why is it beneficial to have two kidneys rather than one? 2- Explain the function of a nephron 3- Athletes undergo random urine testing for drugs. Describe the pathway of substances such as drugs through the urinary system from the time they enter glomerulus to the time they excrete urine.