The Universal Problem Solving Process
advertisement

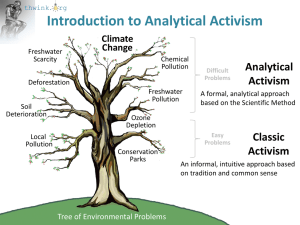
A Story of Two Processes It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness…. The Question Why, despite over 30 years of prodigious effort, has the human system failed to solve the environmental sustainability problem? Difficult social problems historically take a long time to solve: Women’s suffrage problem Slavery problem Divine right of kings problem Racial discrimination problem The dangers of smoking tobacco The recurring war in Europe problem The Question Why, despite over 30 years of prodigious effort, has the human system failed to solve the environmental sustainability problem? Kyoto Protocol Brundtland Report UN Earth Summit Silent Spring Limits to Growth The Question Why, despite over 30 years of prodigious effort, has the human system failed to solve the environmental sustainability problem? “The growth rate of emissions was 3.5% per year for the period of 2000-2007, an almost four fold increase from 0.9% per year in 19901999. The actual emissions growth rate for 2000-2007 exceeded the highest forecast growth rates for the decade 2000-2010 in the emissions scenarios of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Special Report on Emissions Scenarios (IPCC-SRES). This makes current trends in emissions higher than the worst case IPCC-SRES scenario.” (Source: www.globalcarbonproject.org/carbonbudget/07/index.htm .) “Modern environmentalism is no longer capable of dealing with the world's most serious ecological crisis.” (Source: Shellenberger, Michael and Nordhaus, Ted. 2004. The Death of Environmentalism.) The Question Why, despite over 30 years of prodigious effort, has the human system failed to solve the environmental sustainability problem? A Possible Answer The field been using the wrong problem solving process. Examples of the right process: Scientific Method Project management processes like CPM and PERT The Toyota Production System The Capability Maturity Model, for software development Countless training and problem solving processes What process are problem solvers currently using to solve the sustainability problem? As we use the term, an activist is anyone actively working to change the behavior of a social system. The Process of Classic Activism problem symptoms causes causes Step 1. Identify the problem to be solved proper practices are not being followed causes A. The proper practices are not yet known can be solved by Step 2. Find the proper practices causes causes B. People don’t know about the proper practices or why they should practice them C. People don’t want to follow the proper practices, even though they are fully aware of them and why they should logically follow them can be solved by can be solved by Step 3. Tell people the truth about the problem and the proper practices Step 4. Exhort, inspire and bargain with people to get them to support the proper practices Environmental Problems (1) Examples of Classic Activism Outcomes (1) The 11 problems are from the Scientific Committee on Problems of the Environment study (SCOPE), whose results were summarized in the UNEP’s Global Environment Outlook 2000 on page 339. The problems are sorted in order of decreasing importance. These are approximately the top 11 components of the global environmental sustainability problem. Solution Success 1. Climate change Low 2. Freshwater scarcity Low 3. Deforestation and desertification Low 4. Freshwater pollution Medium 5. Loss of biodiversity 6. Air pollution (excluding climate chg) Low Medium 7. Soil deterioration Low 8. Ecosystem functioning Low 9. Chemical pollution 10. Stratospheric ozone depletion Medium High 11. Natural resource depletion Low Non-environmental Problems Women’s suffrage High Slavery High Urban decay Medium Racial, gender, age, etc. discrimination Medium The dangers of smoking tobacco Medium The obesity epidemic Low Does Classic Activism have a flaw? (Break to examine the tool of simulation modeling to answer the question) Causal Loop Diagram of Classic Activism Does Classic Activism have a flaw? We hypothesize that Classic Activism contains these two critical flaws: 1. It doesn’t consider systemic change resistance. 2. It’s intuitive instead of analytical, so it tends to not find true root causes and the high leverage points needed to resolve them. Can we develop a better process that lacks these flaws? The System Improvement Process (SIP) What quality gate must a better process pass? The Six Principles 1. A complex system problem can be proactively, reliably, and fully solved only by resolving its root causes. 2. In problems where problem solvers are in the minority or lack governance of the system, root causes can be efficiently resolved only by pushing on their related high leverage points . 3. If analysis finds the correct root causes and high leverage points, solution implementation will be relatively easy. 4. The more difficult the problem, the more mature the process used to solve it must be. 5. Difficult problems are best decomposed into smaller subproblems, each designed to be an order of magnitude easier to solve. 6. Understanding complex social system behavior correctly and deeply requires modeling. Are these the right principles? The four main steps of solving each subproblem SIP The five substeps of system understanding The three subproblems of the main problem The System Improvement Process (SIP) 1. Problem Definition A. Change Resistance B. Proper Coupling C. Model Drift 2. System Understanding A Find the immediate cause of the problem symptoms in terms of the system's dominant feedback loops. ANALYSIS B Find the root cause of why they are dominant. C Find the low leverage points and symptomatic solutions. D Find the feedback loops that should be dominant to resolve the root causes. E Find the high leverage points to make those loops go dominant. Spend about 80% of your time here. The problem solving battle is won or lost in this step, so take the time to get it right. 3. Solution Convergence 4. Implementation Analysis Results of SIP 1. Problem Definition Summary of results of executing SIP on the global environmental sustainability problem A. Change Resistance 2. System Understanding ANALYSIS This is where we’ve spent about 90% of our time. 3. Solution Convergence B. Proper Coupling C. Model Drift Root cause of successful Root cause of improper change resistance is high coupling is mutually exclusive deception effectiveness. goals between corporate life form and Homo sapiens. Root cause of excessive model drift is quality of political decision making is too low. You Can’t Fool All of the Corporate Benevolence People All the Time loop loop needs to go dominant. needs to go dominant. The Race to the Top among Politicians loop needs to go dominant. HLP is general ability to detect manipulative deception. HLP is rules of the game for corporate life form. HLP is quality of the process of political decision making. Six solution elements Corporation 2.0 Politician decision ratings Not ready for Not ready for implementation Not ready for implementation 4. Implementation implementation Actual Results of Classic Activism Done by 1. Problem The Definition Limits to Growth 2. System Understanding A ANALYSIS B C D E 3. Solution Convergence 4. Implementation Actual progress on the global environmental sustainability problem using Classic Activism A. Change Resistance ? ? ? ? ? ? ? B. Proper Coupling Dominant loops causing symptoms found by World3 model. ? ? ? ? ? ? C. Model Drift ? ? ? ? ? ? ? How can we accelerate a change from Classic Activism The Old and New Paradigms to a process that’s capable of solving the sustainability problem? Classic Activism System Improvement Process An intuitive approach An analytical approach If that doesn’t work, exhort, Tell the people the inspire and Find the truth about the bargain with proper problem and the people to get practices proper practices them to support the proper practices Pushing on low leverage points Success on easy problems Failure on difficult problems Decompose the problem into 3 Use 4 main Execute the system subproblems: steps for understanding step using the 5 substeps A. Change Resistance each B. Proper Coupling subproblem and simulation modeling C. Model Drift Pushing on high leverage points Success on easy problems Success on difficult problems