Bactiquant Water Rapid Onsite Screening for Assessing Legionella

Bactiquant Water
Rapid Onsite Screening for Assessing
Legionella Risk
Presented by Lisa Rogers
“Legionellosis emerged because of human alteration of the environment, since
Legionella species are found in aquatic environments, and thrive in warm water and warm, damp places, such as cooling towers”
Legionella and the prevention of legionellosis, WHO 2007
World Wide
• Since 1976, 35 outbreaks reported 2-800 cases
– 11 in NA (US/CA)
– 14 in AUS/NZ
– 10 in Europe
• Sources
– 13 Cooling towers
– 5 each, Spas/hot tub, DHW, AC, and 4 unknowns
– Misc include potting mix, fountain, industrial systems
Year
2012
2012
2012 Scotland
2012 Chicago , Illinois
SW of Edinburgh
JW Marriott Hotel
2012 Auckland, NZ Unknown
2012 Stoke-on-Trent , UK Warehouse, Fenton
2012 Pittsburgh, PA VA Hospital
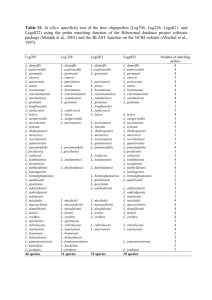
2013
City
Québec City,
Canada
Calp , Spain
Queensland , AUS
Location
Lower Québec City
Cause
Possibly cooling towers
AR Diamante Beach Hotel
Possibly solar water heating system for spa and DHW
Wesley Hospital
Possibly
Hot tub unknown cooling towers
Decorative Lobby Fountain
Water Source and/or AC
18
99
10
11
19
22
NYD, probably hot water system. 2
Cases
Fatality rate
180 7 %
17%
3%
30%
9%
5%
27%
50%
2013 Memphis , TN 24-Hour Fitness NYD probably pool or spa.
3 0%
2013 Milwaukee , WI Not yet determined Not yet determined, ongoing 20
2013 Reynoldsburg, OH
Wesley Ridge Retirement
Comm
2013 Warstein , Germany Warsteiner Brewery
Potable water system, ongoing 44
Air conditioning, ongoing 165
2013 Florence, AL Glenwood Nursing Home
Unknown, still under investigation.
13
Concerns
• CDC estimates 8,000 to 18,000 people are hospitalized each year in the U.S. Mortality rate is approximately 15%
• Legionella bacteria are found naturally in the environment
• French study found that L. pneumophila can travel airborne at least 6 km from its source
• Norway study found high velocity, large drift & high humidity in air scrubber… spread probably for >10 km
• WHO estimates the cost savings to implement preventive plans is $1-3M USD per life saved. (1200 x 1M= $1.2B)
Ideal Water Conditions
• Temperatures between 20° and 50°C (68° - 122°F)
• Optimal growth range is stagnant water 35° - 46°C [95° - 115°F]
• pH between 5.0 and 8.5
• Available iron and copper
• Sediment/scaling promote growth of commensal microflora
• Other micro-organisms including algae, flavobacteria, and Pseudomonas, which supply essential nutrients for growth of Legionella or harbor the organism (amoebae, protozoa)
• Low biocide concentrations
Water Sampling Guidelines
Table III:7-1. COLONY FORMING UNITS (CFU) OF LEGIONELLA PER MILLILITER
Action Cooling Tower Domestic Water Humidifier
1
2
100
1,000
10
100
1
10
Action 1: Prompt cleaning and/or biocide treatment of the system.
Action 2: Immediate cleaning and/or biocide treatment. Take prompt steps to prevent employee exposure.
Source : OSHA, 1999
CDC recently testified that there is no safe level !
Current Sampling Strategy
Culture Plate Analysis
• 3-5 days for HPC
• 7-10 days for Legionella
• Planktonic, highly variable, overloading, background interferences
PCR
• fast but expensive
How BQW can help
Rapid test can be performed in 15-30 mins
Easy Sampling and
Analysis
EPA ETV verified methodology
Enzyme substrate
Bacteria-enzyme
Fluorescent compound released
+
Principle Method
Why is Bactiquant Technology interesting ?
• Culture-independent technique
• Quantification of a naturally occuring hydrolase enzyme activity present in bacteria
• High specificity to bacteria, little background interference
• Use of fluorescence technology = high sensitivity
• Concentration Step = increased sensitivity and significant reduction in detection time
Laboratory Comparison BQW
10000000
1000000
100000
10000
1000
100
10
1
1 10 100 1000 10000
BactiQuant analysis result (fu/ml)
100000 1000000
EPA ETV Report Excerpt
Table 2: Linearity: BQ Value vs Concentration
Test
Organism
Concentration
Range
(CFU/mL)
Range of
Average BQ values
Lake Water
Indigenous
Bacteria
Lake Water
Indigenous
Bacteria without 1:5 dilution
3.7 x 10 2 to 6.0 x 10 3
3.7 x 10 2 x 10 3 to 3.0
1542 to
15607
1542 to
11106
P. aeruginosa
ATCC 27853
8.7 x 10 2 to 8.0 x 10 3
868 to 7655
Source Battelle / US EPA -2011
Slope
2.38
3.55
0.95
Yintercept
Coefficient of
Determination
(R 2 )
2243
739
-136
0.9138
0.9689
0.9923
Test Iteration
1
2
3
4
5
Average
Standard deviation
RSD (%)
Source Battelle / US EPA -2011
8.0 x 10 3
CFU/mL
11392
12332
11376
11513
11614
11645
396
3.4
EPA ETV Study Excerpt
High reproducibility
Adjusted Fluorescence (fu)
4.7 x 10 3
CFU/mL
2.1 x 10
CFU/mL
3 8.7 x 10 2
CFU/mL
6128
6074
6012
2799
2710
2559
1249
1247
1297
6508
6256
6196
2768
2945
2756
1437
1375
1321
196
3.2
140
5.1
83
6.3
EPA ETV Report Excerpt
Table 3. Bactiquant®-test Repeatability and Inter-Assay Reproducibility
Test Iteration
Average
BQV Fluorescence (flu)
Indigenous Bacteria from Lake
Water
(3.7 x 10 2 CFU/mL)
Analyst 1 Analyst 2
P. aeruginosa
(4.7 x 10
Analyst 1
3
ATCC 27853
CFU/mL)
Analyst 2
2363 2225 6888 6691
Standard deviation
RSD (%)
RPD (%)
152
6.4
6.0
57
2.6
333
4.8
2.9
93
1.4
Table 3 summarizes the repeatability and inter-assay reproducibility results for Bactiquant ® -test using two bacterial cultures in water. Two different people analyzed 4 samples of each culture, using different fluorometers .
CASE STUDIES
7
6
5
4
BQ value 1000
3
1
2
BQ value 100
BQ value 10
BQ
Legionella pneumophila serotype 2-14
0
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 51 53 55 57 59 61 63 65 67 69
Critical care facility, Courtesy of Clinical Microbiology Institute, Viborg Hospital, Denmark
2006.
X-axis Sample No. (1-70)
Y-axis Log10(adjusted fluorescence) and Log10(cfu) Legionella pneumophila serotype 2-14
Australia Case Study
• Wesley Hospital, Queensland: 2 cases, 1 death
• 5 Building, 560 bed facility
• Heat Treatment for 2 weeks @ 70C ( 158F)
• Over 3000 samples collected BQ, Legionella,
HPC
• 13 days to reopen, 29 days fully operational
• BQ used to screen, verify cleaning efficacy and validate post treatment
Comparison between Pre-Treatment (Blue), and Post Treatement samples collected on the 26/9 (Red) and the 30/9 (Green)
4500
4000
3500
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
104 110 114 135 226 226 Dirty 237A 237B
Room Number
285 315 316 609 L6 Endo Int
2
Pre-Treatement
Post Treatement (26/9)
Post Treatement (30/9)
1200
1000
800
600
400
1600
1400
Mains water 1
Mains water 2
200
0
25.09 11:00 26.09 12:00 26.09 13:00 26.09 14:30 26.09 16:00 26.09 17:00 26.09 18:30 30.09 12:00 30.09 13:30 30.09 14:30 30.09 16:30 30.09 18:00
Sample
“CETEC made use of the Bactiquant® water technology for the rapid screening of total bacterial loading within the potable water network. This technology allowed CETEC in under an hour to obtain results superior to plate count for the network. The ability to obtain rapid results as compared to 4 to 10 day timeframe for conventional methods presented significant time, logistical and financial savings.”
Excerpt from: The Australian Hospital Engineer, September 2013
New Studies
The Danish Health
Institute has started a two year project now with multiple sites looking at pre-screening as well as post treatment efficacy.
Hopefully, some results from that study will be forthcoming later this year.
Pros and Cons
• Rapid onsite testing aids in identifying hotspots
• Validate the efficacy of cleaning methods
• Monitor for changes in system quickly
• HPC nor BQW a perfect predictor of Legionella
• Not a substitute for direct Legionella analysis
Do you have any questions?
THANK YOU FOR LISTENING!
Lisa Rogers
Lrogers@mycometer.com
813-831-6511 www.mycometer.com