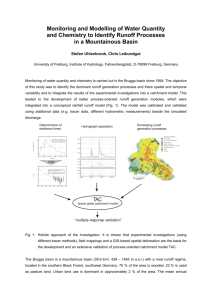
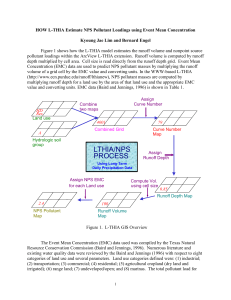
Effects of urbanization on the hydrologic cycle
advertisement

Jon Luevano Urbanization Growth and development of cities Large population density Highly industrialized Comparing city to city Size (area) Population density Percentage of urban coverage Hydrological impacts Key Hydrological Impacts Urban runoff hydrology River channelization Climatic changes Water quality Snow melt Urban Runoff Hydrology Impermeable surfaces change surface runoff patterns Lower percolation rates Higher overland flow rates Reduction in peak discharge time/size ○ Cherkauer (1975) ○ Rose and Peters (2001) Problems Potential for flooding Pollution River Channelization Human intervention on flow body of water Resource management Navigation and resource/power production Flood control Controlling runoff paths Increase discharge rates Problems Biological Vast increase in stream flow ○ Simon and Senturk (1977) Water Quality Sources for pollution Higher surface runoff Higher concentrations of contaminants ○ Davis (2001) ○ Gromaire-Mertz (1999) Focus Pinpoint and reduce use of specific sources of contamination Water treatment methods Snow Melt Surface water created from melting snow Factors Air temperature Solar radiation at surface ○ Ferguson (1999) Urban snow melt Timing/intensity of melt ○ Semandi-Davis (1998) ○ Jones (1997) Climatic Changes Climatic factors control hydrologic cycle Rural vs. Urban Warmer temperatures ○ Heat island effect Evaporation rates ○ Lowry (1967) Precipitation rates ○ Atkinson (1979) Concluding Remarks Importance of urban water management Keys Control of urban runoff pathways and exposure Limit contamination Improve treatment processes Increase knowledge and awareness References Atkinson, B.W. (1979) Urban influences on precipitation in London. In: G.E. Hollis (ed.) Man’s influence on the hydrological cycle in the United Kingdom. Geobooks, Norwich, pp. 123-133. Bengtsson, L., Westerstrom, G. (2009) Urban snowmelt and runoff in northern Sweden. Hydrological Science Journal 37:263-275. Cech, T. (2005). Principles of water resources: history, development, management and policy. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Cherkauer, D.S. (1975) Urbanization’s impact on water quality during a flood in small watersheds. Water Resources Bulletin 11:987-998. Chin, A., and Gregory, K.J. (2004) Managing urban river channel adjustments. Geomorphology 69:28-45. D’Arcy, B.J., Usman, F., Griffiths, D. and Chatfield, P. (1998) Initiatives to tackle diffuse pollution in the UK. Water Science and Technology 38:131-138. Davie, T., & Gerrard, J. (Eds.). (2008). Fundamentals of Hydrology (2nd ed.) New York, NY: Routledge. Davis, A.P., Ni, S.B. (2001) Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources, Chemospheren44:997-1009. Egodawatta, P., Miguntanna, N.S., Goonetilleke, A. (2012) Impact of roof surface runoff on urban water quality. Water Science & Techology 66(7):1527-1533. Ferguson, R.I. (1999) Snowmelt runoff models. Progress in Physical Geography 23:205-228. Gromaire-Mertz, M.C., Garnaud, S., Gonzalez, A. and Chebbo, G. (1999) Characterization of urban runoff pollution is Paris. Water Science and Technology 39:1-8. Jones, J.A.A. (1997) Global hydrology: processes, resources andenvironmental management. Longman, Harlow. Krein, A. and Schorer, M. (2000) Road runoff pollution by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and its contribution to river sediments. Water Research 34:4110-4115. Lee, J.H., and Bang, K.W. (2000) Characterization of urban stormwater runoff. Water Research 34:1773-1780. Lowry, W.P. (1967) The climate of cities. Scientific American 217(2):20. Rose, S. and Peters, N.E. (2001) Effects of urbanization on streamflow in the Atlantic area (Georgis, USA): a comparative hydrological approach. Hydrological Processes 15:1441-1457. Semandi-Davies, A. (1998) Modeling snowmelt induced waste water inflows. Nordic Hydrology 29:285-302. Simons, D.B. and Santurk, F. (1977) Sediment transport technology. Water resources punlications, Fort Collins, Colo. Weng, Q. (2012) Modiling urban growth effects on surface runoff with the integration of remote sensing and GIS. Environmental Management 28:737748.