Medical History
advertisement

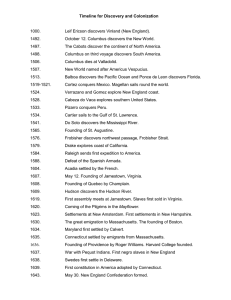
History of Medicine Dark & Middle Ages (400 AD – 1400 AD) Custodial care with treatment by bleeding, herbs, & prayer o Widespread tuberculosis and syphilis Punctuated by epidemics o Bubonic plague o Smallpox o Diphtheria Renaissance (1350-1650 AD) Building of Universities around common Libraries built from texts translated from Arabic back into Latin. Universities organized around seminaries and medical schools. Re-emergence of science and the importance of publishing along with the invention of the printing press The debate over dissection Continuing epidemics 16th & 17th Centuries (1500-1700 AD) Human anatomy accurately described by Leonardo da Vinci Body circulation first described by William Harvey Microscope invented by Antoine van Leeuwenhoek th 18 Century (1700-1800 AD) Change in medical teaching to include observation of patients and autopsies in addition to lectures and labs with dissections. Autopsies led to better understanding of causes of disease. Stethoscope invented by Laennec Joseph Priestly discovers oxygen and its role in respiration Edward Jenner discovers vaccination as a method of prevention for smallpox th 19 Century (1800-1900 AD) Connection between disease of childbed fever and dirty hands established Microorganisms linked to disease by Louis Pasteur, and the pasteurization process was introduced Joseph Lister applied carbolic acid to kill germs in wounds – first antiseptic First sterile or asepsis environment for surgery developed by Ernst von Bergmann Robert Koch, the father of microbiology, discovers many disease causing organisms and furthers the need for cleanliness and sanitation in preventing the spread of contagious disease 1895 -- x-rays discovered by Wilhelm Roentgen, important diagnostic tool Paul Ehrlich uses chemicals as medicines and discovers that chemicals are effective on some microorganisms but not others. Sigmund Freud, father of modern psychology and psychiatry, established the connection between mind and body and established the presence of psychosomatic illness 20th Century (1900-2000 AD) Sulfa compounds discovered to effectively kill many bacterias. Alexander Fleming found penicillin to work better. Virus discovered Jonas Salk and Albert Sabin develop a new but opposite methods of vaccination and effective immunizations for polio. These methods lead to immunizations for other diseases Watson & Crick discover the molecular structure of DNA which opens the field for identification and treatment of inherited illnesses