Stress Management
advertisement

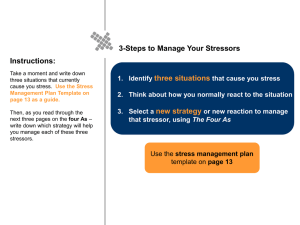
Stress Management Objectives O Define stress, adaptation, O Discuss the physical, O O O O O stressor, homeostasis, lack of oriented behaviors and defense and coping mechanisms. 2. List factors influencing the response to stressors. 3. Compare and contrast the Local Adaptation Syndrome with the General Adaptation Syndrome. Describe the psychological response to a stressor. O O O O psychological developmental results of prolonged stress. List behavioral, physical and emotional indicators of stress. Discuss the role of the nurse in the management of stress. Identify the role of the nurse in relieving stress. Describe stress management techniques that can benefit nurses themselves. Stress and Stressor O Stress - physiological or psychological tension that threatens homeostasis or a person’s psychological equilibrium. O Stressor – any event, situation, or other stimulus encountered in a person’s external or internal environment that necessitates change or adaptation by the person. Physiologic Homeostasis O Local Adaptation System (LAS)—involves only one specific body part O Reflex pain response O Inflammatory response O General Adaptation Syndrome—biochemical model of stress (Hans Selye) O Alarm reaction O Stage of resistance O Stage of exhaustion Psychological Homeostasis O Love and belonging needs O Safety and security needs O Self-esteem needs Question Tell whether the following statement is true or false. The inflammatory response is a response of the central nervous system to pain. A. True B. False Answer Answer: B. False The reflex pain response is a response of the central nervous system to pain. A Balance is Achieved (Homeostasis) Defense Mechanisms and Coping Mechanisms O are unconscious psychological strategies brought into play by various entities to cope with reality and to maintain self-image. O are commonly termed coping strategies or coping skills. Unconscious or non conscious strategies (e.g, defense mechanisms). Defense Mechanisms O Compensation O Denial O Displacement O Introjection O Projection O Rationalization Defense Mechanisms (cont.) O Reaction formation O Regression O Repression O Sublimation O Undoing Question Which defense mechanism listed below is portrayed in the following scenario? After throwing his lunch tray on the floor, a patient complains to the nurse manager about the quality of the food he is being fed during his hospital stay. A. Denial B. Displacement C. Rationalization D. Reaction formation Answer Answer: C. Rationalization Rationale: In rationalization, a person tries to give a logical or socially acceptable explanation for questionable behavior. A person in denial refuses to acknowledge the presence of a condition that is disturbing. Displacement refers to a person transferring an emotional reaction from one person to another. Reaction formation occurs when a person develops conscious attitudes or behaviors opposite to what he desires to do. Coping Mechanisms O Crying, laughing, sleeping, cursing O Physical activity, exercise O Smoking, drinking O Lack of eye contact, withdrawal O Limiting relationships to those with similar values and interests Factors Affecting Response to Stressor Personal Characteristics 1. Ability to cope with stress - support system - perception of stressor - previous experience 2. Practices /norms of peer group 3. Social environment 4. Available resources Nature of Stressor O Intensity O Scope O Duration O Number and nature of stressor An Imbalance Occurs During a Stressful Event General Adaptation Syndrome and Local Adaptation Syndrome O O GAS – response by whole body - how the body reacts to a stressor, real imagined, a stimulus that causes stress. or LAS - the localized response of a tissue, organ, or system that occurs as a reaction to stress Alarm Reaction O Person perceives stressor, defense mechanisms activated O Fight-or-flight response O Hormone levels rise, body prepares to react O Shock and counter-shock phases Stage of Resistance O Body attempts to adapt to stressor O Vital signs, hormone levels, and energy production return to normal O Body regains homeostasis or adaptive mechanisms fail Stage of Exhaustion O Results when adaptive mechanisms are exhausted O Body either rests and mobilizes its defenses to return to normal or dies The General Adaptation Syndrome Diagram of the GAS Model Emotional Responses to Stress O Mind–body interaction O Coping/defense mechanisms O Anxiety (most common) O Mild O Moderate O Severe O Panic Question Tell whether the following statement is true or false. Mild anxiety narrows a person’s perceptual fields so that the focus is on immediate concerns, with inattention to other communications and details. A. True B. False Answer Answer: B. False Moderate anxiety narrows a person’s perceptual fields so that the focus is on immediate concerns, with inattention to other communications and details. Psychological Response to Stress O Psychological adaptive behaviors (coping mechanisms) are directed at stress management O O 1. Task-oriented behaviors – use direct problem- solving technique 2. Ego-defense mechanisms – indirect methods of coping May be: Constructive – accept challenge to resolve stress Destructive – do not help with coping Types of Task-Oriented Behavior O Attack behavior – action to remove/overcome stressor O Withdrawal behavior – physical or emotional removal from stressor O Compromise behavior – change usual method of operating , substitute goals, omit satisfaction of needs Ego-defense mechanisms O Unconscious behaviors that offer psychological protection from stressor Examples: compensation conversion denial displacement identification regression projection rationalization Adaptation to Acute and Chronic Illness O General tasks—for example, maintaining self-esteem and personal relationships O Illness-related tasks—for example, handling pain and disability Effects of Long-Term Stress O Affects physical status O Increases risk for disease or injury O Compromises recovery and return to normal function O Is associated with specific diseases Family Stressors O Changes in family structure and roles O Anger and feelings of helplessness and guilt O Loss of control over normal routines O Concern for future financial stability Factors Affecting Stress and Adaptation O Sources of stress O Types of stressors experienced O Personal factors Categories of Stress O Developmental stress O Occurs when person progresses through stages of growth and development O Situational stress O Does not occur in predictable patterns Question Tell whether the following statement is true or false. An example of situational stress is the stress related to a marriage or divorce. A. True B. False Answer Answer: A. True An example of situational stress is the stress related to a marriage or divorce. Types of Stressors O Physiologic O Chemical agents, physical agents, infectious agents, nutritional imbalances, hypoxia, genetic or immune disorders O Psychosocial O Includes real and perceived threats Stressful Activities in Nursing Profession O Assuming responsibilities for which one O O O O is not prepared Working with unqualified personnel Working in environment in which supervisors are not supportive Caring for patient in cardiac arrest or dying person Experiencing conflict with peers Teaching Healthy ADLs O Exercise O Rest and sleep O Nutrition O Use of support systems O Use of stress management techniques O Time Management O Problem-Solving Process Stress Management Techniques O Relaxation O Meditation O Anticipatory guidance O Guided imagery O Biofeedback O Crisis intervention Question Tell whether the following statement is true or false. In the stress management technique known as anticipatory guidance, a person creates a mental image, concentrates on the image, and becomes less responsive to stimuli. A. True B. False Answer Answer: B. False In the stress management technique known as guided imagery, a person creates a mental image, concentrates on the image, and becomes less responsive to stimuli. Crisis Intervention O Identify the problem O List alternatives O Choose from alternatives O Implement the plan O Evaluate the outcome Evaluating the Plan of Care O Patient verbalizes causes and effects of O O O O stress and anxiety. Patient identifies and uses sources of support. Patient uses problem solving to find solution to stressors. Patient practices healthy lifestyle habits and anxiety-reducing techniques. Patient verbalizes decrease in anxiety and increase in comfort.