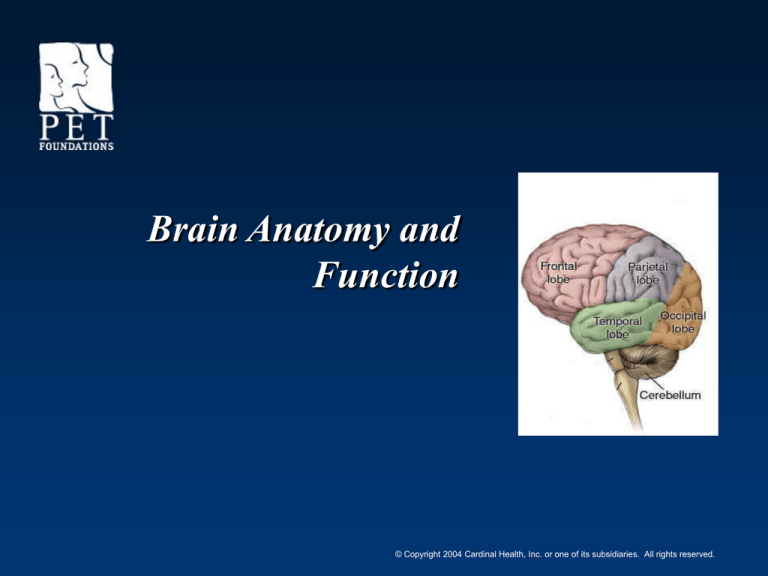
Brain Anatomy and
Function
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Anatomy of the Brain
• Separated into right
and left halves by the
Interhemispheric
Fissure
• The Central Sulcus
runs down &
forward
• The Lateral Fissure
runs backward & up
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Frontal and Temporal Lobes
Frontal
Temporal
• Thought
• Memory
• Voluntary
movement
• Auditory function
• Speech motor
• Covers 1/3rd of
area of the brain
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Parietal and Occipital Lobes
Parietal
• Sensation
• Touch
• Pressure
• Pain
Occipital
• Vision
• Visual
processes
• Reading
• Temperature
• Texture
• Position/spatial
orientation
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Medulla Oblongata,
Cerebellum, and Pons
Medulla
Oblongata
• Respiration
• Heart rate
• Continuous
with the
spinal cord
(2.5 cm)
Cerebellum
• Large Muscle
Coordination
• Balance
Walking,
Writing
Pons
• Relay between
the cerebral
hemispheres
and the
cerebellum
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Basal Ganglia and Thalamus
“The Brakes”
• Modifies movement
on a minute-tominute basis
• Inhibits Movement
• Coordination
• Cortical relay
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Limbic System
• Attention
• Sensory gateway
• Memory processing
• Rage
• Aggression
• Sexuality
• Appetite/Thirst
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
The Nerve Cell
Synaptic junction
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Neurotransmitters
• Serotonin – major – emotions,
judgment, eating and sleep
disorders (associated with
frontotemporal disorder)
• Glutamate/GABA - Widespread,
anxiety, sleep, (Valium targets this)
• Dopamine – memory, mood,
movement, Parkinson's Disease,
psychiatric problems
• Endorphins – relief of pain,
(Morphine targets this)
Lichtman, J., et al Washington University 2002
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Serotonin
Glutamate/GABA
Normal functions
Emotions
Judgment
Sleep
Normal functions
Imbalances
Imbalances
• Involved in most facets of
brain function
Depression
Memory disturbances
Suicidal behavior
Sleep disturbances
Anxiety
Anxiety
Impulsive behavior
Eating disorders
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Dopamine
Normal functions
Endorphins
Normal functions
Mood
•
Relieve pain
Movement
•
Induce euphoria
Memory
Imbalances
Movement disorders
Schizophrenia
Addiction
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Normal Aging Brain
• Brain weight and
volume decrease
• Grooves widen
• Surface smoothes
• Neurofibrillary tangles
increase
• Understanding
normal variation is
key to interpretation
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Brain Glucose Metabolism –
Normal
• Normal brain tissue actively metabolizes glucose
and its analogue (F-18 FDG)
• Glucose metabolism provides 95% of the energy
required for brain function
• FDG is irreversibly trapped within brain cells in
proportion to its use because it cannot be broken
down or stored unlike glucose
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
FDG-PET Normal Brain Metabolism
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
FDG-PET Abnormal Brain
Imaging
• Dementia
Memory loss
Cognitive Decline
• Epilepsy
Localization of a seizure focus
• Tumor Assessment
Radiation Necrosis vs Tumor
Grade
• Objective Imaging Diagnosis of Movement Disorders
Huntington’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Dementia Diagnosis:
Current Methods
• History and physical examination
Neurologist (Sens. = 50-80%)
Neuropsychologist / Neuropsychiatrist
• Neuropsychological testing
• MRI / CT
• Blood testing
• Functional Neuroimaging (SPECT/ PET/MR)
• Sens.=80-90%
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Summary
• Normal Brain Anatomy
• Normal Brain Function
• Current PET Brain Applications:
Diagnosis of Dementia
Seizure Localization
Tumor Assessment
Objective Imaging Diagnosis of Movement
Disorders (not CMS approved)
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Contributors
• Rebecca Trunnell Hyman
• Coordinator of PET Services
• Clinical PET of West County - Creve
Coeur, MO
• Kevin L. Berger, M.D.
• Assistant Professor of Radiology
• Director of PET Imaging
• Michigan State University – East
Lansing, MI
© Copyright 2004 Cardinal Health, Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.











![Cardinal[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005802263_1-db88c762ad48b407ee404d5f72cbf3ca-300x300.png)