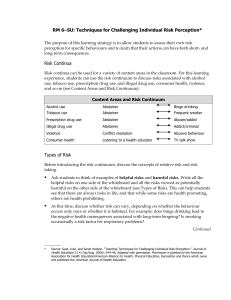
Risk-taking Behaviour
Behavior that has a potential negative
consequence.
Potential risk to the individual’s psychological or
physical health and wellbeing.
Is this risky behaviour?
Is this risky behaviour?
Is this risky behaviour?
Is this risky behaviour?
Is this risky behaviour?
ACTIVITY 1.
Rick-taking game.
Create groups of 4
Take turns in placing negative risk-taking
behaviours in order between most risky to least
risky
Discuss findings as a class
Doesn’t have to Negative!
Sometime we engage in risky behaviour which
can have positive effects on health.
Taking a risk to start something new can give us
more confidence and self esteem.
Starting apprenticeship
Wearing ‘daring’ new
fashion
Positive Risk-taking
behaviour
Still risky because there is still the potential for
negative health consequences.
Question:
What are the possible negative health
consequences from starting a new
apprenticeship or wearing daring new
fashion?
Costs of risky behaviours
Social cost- embarrassment or failure
Physical cost- accident or injury
Emotional cost- fear or sadness
Gullone & Moore (2000)
Four types of risk-taking behaviour:
1. Thrill-seeking
2. Reckless
3. Rebellious
4. Anti-social
Thrill-seeking
Socially acceptable
Challenging
Experimental
Eg. Bungee Jumping
Reckless
Higher chance of not
being socially acceptable
Dangerous
Negative social and
health outcomes
Eg. Unprotected sex
Rebellious
Acceptable for adults but
not for youths.
Acting out
Attention seeking
Eg. Underage drinking
Anti-social
Unacceptable for adults
and youths
Deviant behaviours
Eg. Bullying
Activity 2.
In your workbooks, analyse your four highest
ranking risk factors.
You need to explain what kind of risk factor they
are
You need to explain what the social cost of each
of the behaviours are
Trends in adolescent risktaking behaviours
Gullone and Moore found that adolescents are
more likely to engage in thrill-seeking risks.
Male youths tend to engage in more risk-taking
behaviours.
Female youths tend to judge behaviours as more
risky than males youths.
Factors in risk-taking
behaviour
Peer pressure
Mental health
Age,
Family background
Sex,
Culture
Personality type
Percieved risk
However…..
Psychologists have no complete explanation as
to why youths engage in risk taking.
Psychologists have no exact solution for youth
risk-taking behaviour.
Activity 3.
Write about a time when you have engaged in a
risk-taking activity.
What kind of risk taking activity was it?
What was the cost of the behaviour?
What influenced you to do this activity?