7s. Business Process Analysis
advertisement

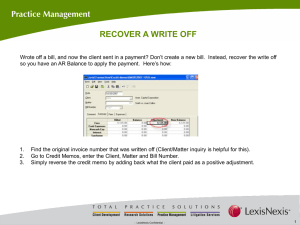
Business (trade) Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation Outline 1. What is Business Process Analysis and Why it is Required? 2. Examples of output from BPA Studies in WP3 2 What is a Business (trade) Process and it’s Analysis? A Business Process is a collection of related and structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product. Example - Obtaining a fumigation certificate for rice export - Applying and Issuing Process for a Certificate of Origin - Customs Clearance Process at the Border Point 3 What is.. ..a Business Process Analysis? An analysis and modelling of business processes for improvement, simplification and automation Example - Documenting existing practice in an administration/company - Describing a “Standard Procedure” - Identifying quantitative indicators (time, cost, docs) - Recommending ‘to-be’ situation or TF measures 4 Supply Chain Complexity Source : Complex Networked Supply Chain [Harwick, 1999 Trade Movement – 3 Kinds of Flow Seller (Exporter) Physical Goods Buyer (Importer) Payment Information/Documents Wholesalers Cargo Insurance Post-Harvesters Farmers Banks Exporters Importers Traders Consumers Freight Forwarders Customs Other-Government-Agencies Traders Ship Agent Transport-Operators Terminal-Operator Carriers Why conduct a Business Process Analysis? Business Process Analysis is a practical study to understand attributes of business processes, and their relationships Who involved Procedures and Documents required Related Rules and Regulations Some quantitative indicators 7 What are benefits of Business Process Analysis? 8 Use Case Diagram of Rice 3)Export from Myanmar Ship 3.2) Arrange overseas shipping Bank Customs department 3.3) Arrange pre-inspection and fumigation 1) Buy 1.1 Sales contract 3.4) Declare CusDec 2 ICD Shipping line 3.5) Collect empty container from ICD and deliver it to warehouse Importer 2) Pay Exporter (or representative) 2.1) Make advance payment Importer’s bank 3.1) Obtain Export License Directorate of Trade, MOC Transporter 3.6) Stuff containers at warehouse 3.7) Deliver to port of departure for Customs examination Exporter’s bank Customs broker Port 3.8) Examine commodity 3.9) Handle and load the goods onto the vessel SAD 3.10 ) Prepare required shipping documents for buyer 3rd party inspector 3.11) Deliver shipping documents to buyer FDA Courrier Transporter Port terminal 3rd party inspector Exporter (or representative) Customs department at the port Shipping Agency Department (SAD) 3.8.1Request for examination 3.8.1 Request for delivery 3.8.2 Receive request to send the loaded Container to Customs yard 3.8.2 Receive the request for fumigation 3.8.2 Receive port challen, SI, and 103 challen 3.8.1 Request for fumigation 3.8.1 Submit 103 slip, shipping instructions, & Port Challen 3.8.2 Receive request 3.8.3 Register case file 3.8.4 Reviews case file 3.8.5 Order to the port Customs examination team 3.8.3 Check the container against 103 challen 3.8.6 Examine the goods Found incorrect Found correct 3.8.7 Fumigate the containers after Customs examination 3.8.8 Allow shipment 3.8.9 Allow to load cargo 3.8.6 Check with loading list and prepare mate receipt Time-procedure Chart for Importing Animal Feed to Lao PDR 1. Check demand of import for animal feed by Livestock and Fishery Division, Customs and Trade Division 2 2. Certify of farm’s animal feed demand for importing 5 3. Declare of import documents to custom office at the border point for approval 3 4. Pay import tax, fee and custom to treasury office 2 5. Inspect of import goods by custom inspector at the checked point 1 6. Inspect of import goods by Agriculture Quarantine officers at the checked point 1 7. Trucks transport all goods to destination places 1 8. Pay to the export representative 2 TOTAL 17 Documents Required for Jute Bag Exports to India from Bangladesh Sl. Procedures Docs Reqd. Details Documents List 1 Receive order from the buyer, set the trade terms and finalize sales contract 6 Proforma Invoice, Commercial Invoice, Export License, Offer Letter, Sales Contract, Copy of TT 2 Contract inland transport agency 1 Transport Invoice 3 Prepare export documents 10 Proforma Invoice, Commercial Invoice, Certificate of Origin, SAPTA Certificate, Phytosanitary Certificate, Packing List, Export License, Sales Contract. Transport Invoice, Copy of TT 4 Transport to port of departure Nil 5 Obtain customs declaration from the customs authority at the land port (mainly by the C&F agent) 14 Proforma Invoice, Commercial Invoice, Certificate of Origin, SAPTA Certificate, Phytosanitary Certificate, Packing List, Export License, Sales Contract. Transport Invoice, Copy of TT, Export Form, VAT and Source Tax Chalan, Bill of Entry 6 Customs inspection and clearance 16 Proforma Invoice, Commercial Invoice, Certificate of Origin, SAPTA Certificate, Phytosanitary Certificate, Packing List, Export License, Sales Contract, Transport Invoice, Copy of TT. “C” Form, Out Pass 7 Border checkpoints 16 Proforma Invoice, Commercial Invoice, Certificate of Origin, SAPTA Certificate, Phytosanitary Certificate, Packing List, Export License, Sales Contract. Transport Invoice, Copy of TT, “C” Form, Out Pass None Economic impact of bottlenecks in business processes of cross border trade Each additional day of delay (e.g. because of trade logistics procedures) reduces trade by at least 1% Source: Simeon Djankov, Caroline Freund, and Cong S. Pham. (2007). Trading on Time. Washington, D.C.: World Bank. “Direct and Indirect Cost from import/exportrelated procedures and required documents is about 1-15% of product cost.” Source: OECD. (2003). Quantitative Assessment of the Benefits of Trade Facilitation. Paris: OECD Publications 13