Verbals and Verbal Phrases
advertisement
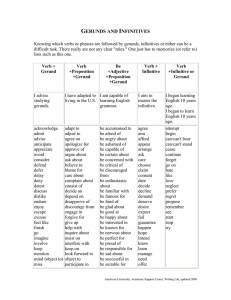
Verbals and Verbal Phrases ELA8C1f—The student analyzes the structure of a sentence (basic sentence parts). What is a VERBAL? A verb acting like another part of speech 3 types: infinitives, gerunds, and participles Infinitives to + a verb Can be used as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb in a sentence Examples: I like to read before I go to sleep. Most people like to watch comedies on TV. To succeed in school, you must work hard. Infinitives vs. Prepositional Phrases Be aware that the word TO does not always mean you have an infinitive. If TO is not followed by a verb, it is NOT an infinitive. I like to shop at the mall. Let’s go to the mall. Which sentence contains an infinitive and which sentence contains a prepositional phrase? Why? Gerunds A verb acting like a noun Always ends in –ing Can be used as subjects, direct objects and indirect objects, objects of prepositions, and predicate nominatives. Gerunds continued Examples Swimming is my favorite sport. Do you like riding horses? Many students like playing basketball in PE. Gerund or not? The dog, carrying its bone in its mouth, ran around the house. Carrying is NOT a gerund; not used as a noun Smiling is an indication that a person is happy. Smiling is a gerund; it is used as a noun (subject of the the sentence) Participles A verb acting like an adjective Often ends in –ing or –ed but occasionally ends in another way Examples Smiling, the teacher collected homework from her students. I like ice skating on frozen ponds. Barking dogs can be a nuisance. The burnt popcorn made the entire house smell. Participial Phrases A participial phrase is a participle and all of its objects or modifiers Examples Rounding third base, the runner charged toward home plate. The pitcher, losing control, has overthrown the ball. Especially pleased, the crowd cheered loudly. Hints Participles and participial phrases are almost always near the noun or pronoun they modify. Participles and participial phrases can usually be taken out of a sentence and the sentence will still make sense. The skilled catcher trapped the wild pitch in his mitt. The catcher trapped the wild pitch in his mitt.