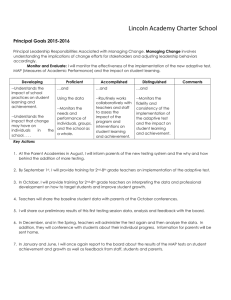
Project method - www.muthupandi.co.in
advertisement

Project method Introduction School is a community in miniature and the project method aims at providing community life activities on a small scale in the school. The project method is the pragmatic educational philosophy of John Dewey, the noted American Philosopher-cum-educator. The pragmatic educational philosophy lays great strees on providing differend kinds of rich experience to the children. This method was developed by William Head Kilpatrick of the university of Columbia. Introduction This project method is the expression of the widespread dissatisfaction against the bookish method which makes children passive in which children are drilled and spooned with information which mostly unconnected with the real life. Definitions A Project is a bit of real life that has been imported into the school. ----------- By Ballard A Project is a Whole purposeful activity proceeding in a social environment. ----------- By William Project is a unit of educative work in which the most pupils are made responsible for planning and purposing. ---------- By Parker A project is a problematic act carried to completion in its natural setting. ----------- By Stevenson Characteristics of a Project Method A project is a purposeful activity A Project is a Real Life activity Project is a activity in a natural setting A project is a problem-centred activity A project is an activity in a social setting A project is a whole-hearted activity A project is an activity which results in positive result A project is a comparative activity A project is an activity which provide an integrated view of a subject A project is a new way of teaching the child to live A project is an activity through which solution of a problem is found out by the pupil Main Principles of a Project Method The principle of Purpos The Principle of activity Experience is the best teacher. What is real must be experienced. The children learn new fact through their experience The Principle of Reality Children are active by nature. They love activity. The curiosity nature of the child makes him active in nature. So such activities should be provided to them to learn by doing. The Principle of Experience Knowledge of pupose is a great stimulus which motivates the child to realiize his goal. The child must know why we are doing such things in variouse situations Life is real and education to be meaningful and must be real. So real life situations should be provided. The Principle of Freedom The Principle of Utility Different Types of Projects The Producer Type The Consumer Type Where the objective is to obtain either direct or vicarious experience such as reading and listening. The Problem Type In which the emphasis is directed towards the actual construction of a material object or article In which the chief purpose is to solve a problem involving the intellectual processes, such as determiing the density of a certain liquid The Drill Type Where the objective is to attain a certain degree of skill in a reaction. Essentials of Good Projects Timely Usefulness Interesting Challenging Economical Rich in Experience Co-operativeness Various Steps in a Projects 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Providing a situation Choosing and purposing Planning Executing Recording Evaluating