Software Presentation
advertisement
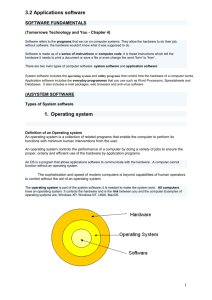
Software custom-written, off-the-shelf, generic, system, applications, utility, integrated 13/04/2015 1 Learning Objectives Define the different types of software. Describe the purpose of each of the software types giving common examples of applications for each type. Discuss the relative advantages and disadvantages of using off-the-shelf and bespoke software packages. 13/04/2015 2 APPLICATION SOFTWARE SYSTEM SOFTWARE HARDWARE 13/04/2015 3 Difference between Hardware and Software Hardware: Comprises the physical parts of the computer system that are hard to touch. Software: 13/04/2015 Makes a computer do something and are written to run on the hardware. 4 Watch a computer booting up or logging onto a network. • What is happening? • How is it happening? • How does the computer know what to do? 13/04/2015 5 • What is software? • How is it related to hardware? Without software a computer system could not function! 13/04/2015 6 Software • Software is the general term used to describe all the changeable programs, routines or procedures that run on a computer. • Software makes a computer do something and are written to run on the hardware. 13/04/2015 7 Software • What types of software have you encountered? What were their functions? • What were their software names and product names? (They are different!) • The difference between generic and product names is like the difference between a 'car' and a make of car e.g. 'Fiat‘ or ‘Dacia’. 13/04/2015 8 Systems software • Performs tasks needed to run the computer system / hardware • They help the computer run smoothly. • Helps the user to control and make best use of the computer hardware. • Allows the user to carry out different tasks with different programs rather than one specific task with one program. 13/04/2015 9 There are 2 main types of software Software System Software / Operating System Collection of system programs that: Applications Software Carries out some task/s for the user allowing the user to produce something useful. • Control and manage the activities of the computer system hardware • Manage applications. • Provide an interface between user and hardware. 13/04/2015 10 Applications Software Software that can be made to do many different tasks. Off-the-shelf Generic Software / General Purpose Excel, Word, PowerPoint etc.. 13/04/2015 Custom-Written / Bespoke Special Purpose Integrated Software Packages Individual Programs Prewritten ready to buy Software written to the specification of a particular organisation or customer. Microsoft Office Software to perform a specific task e.g. payroll, accounts, stock control, fill in forms A number of different pieces of software that can share / merge data. e.g. 1. A graph from a spreadsheet can be placed in a report. 2. Common screen design / toolbars / icons makes it simpler for people to learn. 11 Advantages of off-the-shelf packages Immediately available, bespoke software takes time to write. Many users who share the development costs, making it a cheaper alternative. Thoroughly tested and so fewer bugs (due to the number and variety of users). More likely to be compatible with other applications packages. More likely that there are well established training courses in the software. User groups often available. 13/04/2015 12 Advantages of Bespoke Packages / Custom Written Software Will be tailored to the exact needs of the user. Perhaps no off-the-shelf software fulfils the system requirements as the application is a one off. There is a potential to work with the developers to expand the marketplace for the new software. Will not contain extra routines that will never be used. 13/04/2015 13 Applications for which Common Packages are not appropriate Where the use is so specialised that the software will need to be written (or at least tailored) for that particular use. E.g. Many uses of control software. Robots used on production lines tend to be one-off machines, designed for that particular purpose, consequently, the software that would drive them would, similarly, be one-off. A stock control system in a warehouse would have standard modules, but would have other sections which would be for that warehousing system alone. How different from the standard design is the system for which we want the software? The further away from the standard, the more difficult it is to use standard software, and the more likelihood there is that the system will require software written specially for it. 13/04/2015 14 Used to control communication between computer and peripherals by converting OS commands into instructions that the peripheral will understand. Supplied with a new peripheral and needs to be installed it can be used. Part of OS To protect files from attack by virus Format Reduces size of files without loss of detail by Deletes the contents of a disk, divides the surface of storage media into tracks and sectors and, produces an index before being used. Deleting Files 13/04/2015 Designed to carry out “housework” and common tasks. Anti virus software File Compression Hardware Drivers Program (Hard-Drive) Utilities replacing all common letter combinations by single characters and deleting redundant data so that less storage space required and faster transmission. Library / File-handling Search Sort Copy / Backup Defragment To keep files sensibly arranged on the hard drive To manage the files that are stored on a computer system (Organising) New Folders & Moving files 15 Plenary What are the different types of software? What are they used for and can you give examples? What are the relative advantages and disadvantages of using off-the-shelf and bespoke software packages? 13/04/2015 16