Enlightenment in Europe
advertisement

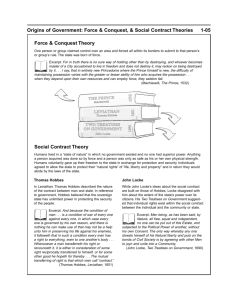
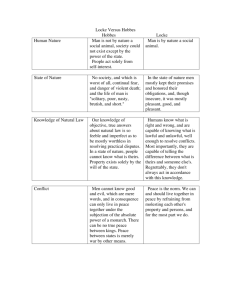
Enlightenment in Europe Mr. Porter Chapter 6 Section 2 Enlightenment • A new intellectual movement that stressed reason and thought and the power of individuals to solve problems. AKA- The Age of Reason Thomas Hobbes & John Locke Hobbes Locke • Both English Political Thinkers during the 1600’s. • Hobbes felt after the English Civil War that humans were naturally selfish & wicked. • To keep law and order people created government or a ruler. • Social Contract- an agreement by which people define and limit their individual rights, thus creating an organized society or government. Thomas Hobbes & John Locke Hobbes Locke • Hobbes felt that the best government was absolute monarchy. • Locke had a different view in which people could learn from life experiences to improve themselves. • All people born free and equal . • All people have 3 Natural Rights (Life, Liberty & Property) Thomas Hobbes & John Locke Hobbes Locke • If the government failed, then the people had the right to overthrow the government. • Idea of government by popular consent. Paris, France • Philosophes- one of a group of social thinkers in France during this time period. • Five Concepts from their beliefs • 1. Reason • 2. Nature • 3. Happiness • 4. Progress • 5. Liberty Francois Marie Arouet (Voltaire) • Published over 70 books and targeted the clergy, aristocracy and government. • His ability to write was his deadly weapon. • He fought for tolerance, reason, freedom of religious belief and freedom of speech. • His defense of Liberty was quoted as “I do not agree with a word you say but will defend to the death your right to say it.” Baron de Montesquieu • He looked at the British form of government as the best one of the time. • Published On the Spirit of Laws (1748) with a focus of separation of powers. • Idea of Checks and Balances • Where to we see Checks and Balances today? Jean Jacques Rousseau • He argued that civilization corrupted people’s natural goodness. • A good government was one that was created by the people and guided by society, a true democracy. • People give up some of their freedom for a common good. • 1762 wrote the Social Contract • All people were equal and titles of nobility should be abolished • His ideas inspired many leaders of the French Revolution. Cesare Bonesana Beccaria • Italian philosophe who put his attention towards the justice system. • Abuse of Justice • Torturing of witnesses and suspects • Irregular trials • He felt people accused of a crime should receive a speedy trial without torture. • Punishment should be based on the seriousness of the crime. • No capital punishment Women of the Enlightenment • Women were seen as a role of wife and mother. • Late 1600’s women writers began to express their beliefs on the rights of women. • By the 1700’s Mary Wollstonecraft argued against Rousseau that women should be educated to be virtuous and useful. • Wollstonecraft pushed for women to enter medicine and politics. Legacy of the Enlightenment • New ideas, beliefs, theories that challenged the church and state as well as the different social classes. • New Scientific discoveries • Began to question the church • Rise of individualism