- Dr Mamdooh A Abdelmottlep
advertisement

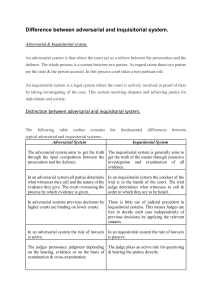
Substantive Law and Procedural Law in the Four Legal Traditions Richard H. Ward Dean & Director College of Criminal Justice Sam Houston State University Table 5.1 The Adjudicatory Process Adversarial Systems Inquisitorial System Who plays the role of the accuser? Role of accuser moves from the individual to the state in an evolutionary continuation of private vengeance The state as accuser replaces the individual in a developmental substitution for private vengeance How is truth determined? Truth is said to arise from competition between opposing sides, so the emphasis is on the trial phase Truth is said to arise from a continuing investigation, so the emphasis is on the screening process Where does power lie? Power is shared by the prosecutor, defense, judge, and jury, so the judge exerts influence indirectly in the role of referee Power is concentrated more in the judge, so the judge exerts influence directly in the role of investigator What level of cooperation is expected of the defendant? Defendant is neither expected nor required to cooperate with the investigation or court officials Defendant is expected, but not required, to cooperate with investigation (including court) officials Contrasting Adversarial and Inquisitorial Processes The inquisitorial systems emphasize the screening phase of the criminal process with the idea that a careful investigation will determine factual guilt. The adversarial system emphasize the trial phase, where the idea that complex rules of evidence to produce substantive results will ensure the defendant a fair trial Contrasting Adversarial and Inquisitorial Processes The adversarial systems are much more likely to restrict the involvement of the judiciary in both the investigatory and adjudicatory process. The direct involvement of the judge in inquisitorial system contrasts with his or her more indirect involvement in adversarial systems Contrasting Adversarial and Inquisitorial Processes Because the inquisitorial system assumes that all involved persons are seeking the truth, the defendant is expected (though not required) to be cooperative. That cooperation includes supplying information to investigators and answering questions at trial. The adversarial systems, on the other hand, neither expect nor require the defendant to assist investigators. The burden of proof is on the prosecutor, who assumes that the defendant will maintain silence. Contrasting Adversarial and Inquisitorial Processes The role of the judge in adversarial proceedings is primarily one of referee. The attorneys develop and present their respective cases, and then a jury decides between the two versions of the fact. The court in an inquisitorial system is another investigator with the added power of being able to decide the case. The judges ask most of the questions and develop the facts, while the attorneys exist more to argue the interpretation that the court should give those facts (see Ingraham, 1987, p. 121). Fig. 5.1 Flowchart for Achieving Rechtsstaat Substantive and administrative procedures are established to hold the nation’s government to the fundamental principles Those values are reduced to written form The supremacy of certain fundamental values is recognized Figure 5.2 Models for Accomplishing Judicial Review in Common and Civil Traditions Diffuse Concentrated A country’s entire judiciary has the duty of constitutional control with the potential inconsistency of decisions being lessened through stare decisis or a structural equivalent. A specific government entity rules on the constitutionality of laws, and problems of inconsistent decision are accordingly minimal. Mixed A specific government entity reviews the constitutionality of laws, and all courts in the country have the power to ignore laws they deem unconstitutional Supremacy Clause US Constitution - Article 6, section 2 This Constitution, and the Laws of the United States which shall be made in pursuance thereof; and all Treaties made, or which shall be made, under the Authority of the United States, shall be the supreme Law of the Land; and the Judges in every State shall be bound thereby, any Thing in the Constitution or Laws of any State to the Contrary notwithstanding