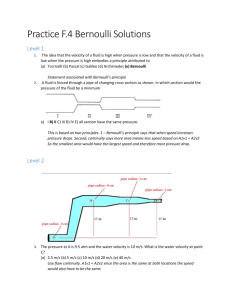
Bernoulli`s Principle
advertisement

Bernoulli’s Principle Natalie O’Neal Vickie Rincones Emily Perkins Brittany Schultz Tenneille Duke Introduction • Subject: Science • Objective: To discover Bernoulli’s Principle • Materials: Hair dryer, ping pong balls, balloons, straws, and coke cans • Methods: Notes and experiments • Grade: 8th grade • Age: 13 & 14 year olds • Languages: 2 - English and Spanish Strategies • Sheltered Instruction • Scaffolding by repetition of vocabulary • Cooperative learning by working in groups • Students learn through: Kinesthetics by performing experiments Auditory learning by listening to lecture Visual learning by seeing realia and watching video Bernoulli’s Principle • What are we learning today? – Bernoulli’s Principle • Why are we learning about it? – To understand pressure systems and apply them to real life examples • How are we going to learn? – We will learn through note-taking and handson experiments. • What should we know before we begin? – Key Terms: Speed, Velocity Who is Bernoulli? • 18th century Swiss scientist • Studied fluid flow in pipes *Fluid = any liquid Vocabulary • Speed = Rapidez - how fast something moves Formula: Distance / Time • Velocity = Velocidad – speed of an object and its direction of motion • Air Pressure = Presión de Atmosférica – the force exerted by air on any surface in contact with it • Lift = Ascender – raise from a lower position to a higher position *Exerted = pushed Bernoulli’s Principle • Textbook Definition: When the speed of a fluid increases, internal pressure in the fluid decreases. • Our Definition: When speed increases, pressure decreases. *Increase = to go higher *Pressure = a type of force *Decrease = to go lower High Pressure/Low Pressure • High Pressure always travels to Low Pressure areas. Experiments • Video Link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ctJyu5ete6Y • Hair dryer demonstration • Coke can demonstration Additional Examples • 1. Umbrella – The curved part of an umbrella causes air moving across it to have a higher velocity (similar to an airplane’s wing). – On a windy day, the higher velocity creates much lower pressure on the top of the umbrella. – The high pressure under the umbrella pushes up to the lower pressure, causing the umbrella to turn inside out. Additional Examples • 2. Faucet and ball – The moving water creates low pressure because of the increased velocity. – The high pressure around the stream pushes the ball towards the low pressure, causing it to touch the water stream. Additional Examples • 3. Perfume Sprayer – When you squeeze the bulb, air rushes across the open end of the tube to create low pressure. – Higher pressure on the liquid pushes it up and it is carried away by the stream of air. Additional Examples • 4. Insects – Insects increase their lift by flapping their wings forward and backward, not up and down. – The tilt of their wings provide an angle to create low pressure and lift. Additional Examples • 5. Shower curtain – When taking a shower, the moving water creates low pressure inside the shower. – High pressure outside the shower moves towards the low pressure, causing the shower curtain to swing against your legs.