Unit 4-6_URBAN GOVERNANCE
advertisement

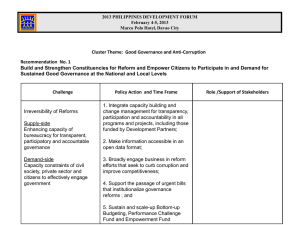
UNITS 4-6 URBAN GOVERNANCE 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 1 Unit 4: Actors (Stakeholders) in Settlement Growth and Management 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 2 The Settlement Planning Arena A High-stakes Game Berke, Godschalk and Kaiser (2006) describe settlement planning and management as a “high-stakes game”. What do the authors mean by that? Multiplicity of interests/values and stakeholders There are narrow interests vs. public interests 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 3 The Settlement Planning Arena The Game Players: Who are the “game players” in the settlement planning and management arena? 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 4 The Settlement Planning Arena The Game Players: Government (political leaders + technocrats) Land owners (traditional authorities, families, individuals, etc) Businesses (estate developers, industrial and commercial entities, etc) Citizens/residents, etc, etc What are the interests of these different players (actors/stakeholders)? 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 5 The Settlement Planning Arena Competition and Cooperation Why would you describe the settlement planning process as a game of “competition and cooperation”? 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 6 The Settlement Planning Arena The Role of the Planner What is the role of the planner in the game? Does he have one role? Why would you say the planner is One of the game players? A rule setter? A neutral mediator? 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 7 Units 5-6: Urban Management in the Context of Decentralization and Local Governance in Ghana 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 8 Decentralization What is Decentralization? Transfer of political, administrative, planning and fiscal authority and responsibilities from central government to local government units 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 9 Decentralization What is the Rationale for Decentralization? Failure of centralized systems to deliver efficiently Decentralization has the potential to ensure a more equitable distribution of resources It is part of the good governance/ democratization agenda It is supposed to engender popular participation in decision-making 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 10 Overview of Ghana’s Decentralization Policy Some Key Features: Re-demarcation of administrative jurisdictions (districts) Establishment of Metropolitan, Municipal and District Assemblies Establishment of sub-district structures 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 11 Overview of Ghana’s Decentralization Policy Some Key Features (cont.): Restructuring of resource allocation and resource sharing b/n central and local govts E.g. District Assemblies Common Fund Land rates and minerals royalties Grants and transfers External credits 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 12 Overview of Ghana’s Decentralization Policy Some Key Features (cont.): Participation of Non-State Actors business entities NGOs CBOs Other CSOs MLGRD responsible for implementing the decentralisation policy 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 13 Overview of Ghana’s Decentralization Policy Main Components of Ghana’s Decentralization Policy Political decentralisation Administrative Decentralisation Decentralized Development Planning Fiscal decentralization 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 14 A. Political Decentralisation Re-demarcation of the country into districts Establishment and empowerment of the RCCs, MMDAs & the Sub-District Structures to perform various functions Establishment of the MMDAs as legislative, administrative, planning, service delivery, budgeting and rating authorities Sub-district structures to facilitate resource mobilization and popular participation 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 15 B. Administrative Decentralisation Restructuring of ministerial institutions and transferring defined functions, powers and resources to local govts Integration of sectorial programmes, resources and assets into the Assembly system Restructuring of 22 depts into 16, 13 and 11 depts under the Metropolitan, Municipal and District Assemblies respectively Passage of a Local Govt Service Act to bring all employees of the MMDAs into the public service. 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 16 C. Decentralised Development Planning A bottom-up, integrated and participatory development planning system. Planning at district, sub-district and sectorial levels coordinated by the DPCU RPCUs responsible for harmonising and synchronising district plans based on national policy framework and guidelines issued by NDPC Development of service centres and rational, efficient and sustainable settlement and land use patterns 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 17 D. Fiscal Decentralisation Meant to enhance the Assemblies’ access to resources Creation of DACF , allocated based on a formula prepared by the Administrator of DACF and approved by Parliament Establishment of ‘MPs Common Fund’ 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 18 D. Fiscal Decentralisation Ceding of income tax payable by informal sector operators, vehicle operators, and betting, entertainment and advertising companies to the MMDAs. IGF sources of the MMDAs: user fees, rates (basic and property), licenses, investment incomes, loans/overdrafts, etc Submission of MMDA budget to the RCCs for harmonization, co-ordination and collation and approval of by Min. of Finance 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 19 The New Local Gov’t System . 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 20 Functions of DAs Three Broad Functions: Deliberative Function Legislative Function Executive Function 86 Specific Functions See handout 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 21 Challenges of the New Local Gov’t & Planning Systems Has Ghana’s New Local Government/ Decentralized Planning System worked as expected? If no, what are the challenges/ problems associated with it? 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 22 Challenges of the New Local Gov’t & Planning Systems Excessive control by central government Lack of coordination and integration of planning activities by various departments/ agencies Emphasis on socio-economic development planning and marginalization of physical planning Sub-standard, disjointed and atomistic land use plans prepared by quacks contracted by customary land owners 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 23 Challenges of the New Local Gov’t & Planning Systems Non-enforcement of planning schemes and standards: Lack of political will Low capacity of DAs Corruption among some public officials Abuse of re-zoning provisions General disregard for planning and orderly development, etc 4/13/2015 Urban Governance 24