Aristotle`s Classification of Motion

Aristotle’s Classification of Motion
• Greek scientist
(Born 384 BCE)
• Classified motion into two categories
– Natural motion
– Unnatural motion
• Natural motion occurs without force.
• Unnatural motion required a force.
Aristotle’s Classification of Motion
• Aristotle believed that
– The speed at which an object falls is directly related to the mass of an object.
– Motion continues so long as there is only an applied motion (force) to an object. Removing the motion (force) stops the object.
• Aristotle’s ideas lasted almost 2000 years…
• It would take a man named Galileo to start the wheels of change in this field of knowledge called physics.
Galileo’s Concept of Inertia
• Galileo Galilei was an Italian scientist
(1564-1642 CE).
• Believed in experimentation
• Blew away
Aristotle’s notions of motion
Galileo’s Concept of Inertia
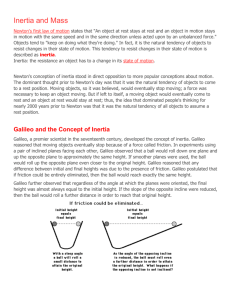
• Galileo found that
– Except for the effects of friction , objects fall at the same rate… regardless of size.
– Force is required to start an object moving, but not to keep it moving.
Galileo’s Concept of Inertia
• The tendency of things is to remain as they are…
– If moving, they tend to keep moving.
– If at rest, they tend to stay at rest.
• This is called inertia .
• Another inertia definition: The ability of an object to resist motion...
Concept Check
A ball rolling on a pool table slowly comes to a stop.
• How would Aristotle explain this behavior?
• How would Galileo explain it?
• How would you explain it?
Galileo Formulates Speed &
Velocity
• Until Galileo motion was described as either fast or slow.
• Galileo measured speed by considering distance and the time it took to cover it.
Speed =
Galileo Formulates Speed &
Velocity
• Velocity differs from speed in that we also know the direction of the moving object.
• Velocity is both speed and direction
(therefore, it is a “ vector quantity ”).
• Constant speed doesn’t mean constant velocity… the opposite is true though.
Concept Check
• What is the average speed of cheetah that sprints 100m in
4s?
• The speedometer on a bicycle moving east reads 50 km/h. It passes another bicycle moving west at 50 km/h. Do both bikes have the same speed? Do they have the same velocity?
• “She moves at a constant speed in a constant direction.”
Say the same sentence in fewer words.
Motion is Relative
• Everything is always moving!
• Our speed relative to the sun is 30 km/s.
• Discussing motion always involves a reference point.
Assignment
• History of Motion Questions &
Speed Worksheet
– Answer in complete sentences
– Use your own sheet of paper