Areas of Rectangles
advertisement

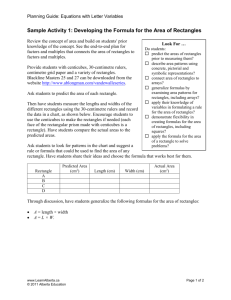
Areas of Rectangles Lesson 11.1 Geometry Honors Objectives: 1. Understand the areas postulate. 2. Know and use the formula for the area of rectangle. Lesson Focus The concept of the area of a geometric figure is introduced in this lesson. Three postulates are stated that give basic information about the area of a square, areas of congruent figures, and additional areas. The formula for the area of a rectangle is proved as a theorem. Areas of Rectangles Postulate The area of a square is the square to the length of a side. A = s2 Areas of Rectangles Area Congruence Postulate If two figures are congruent, then the have the same area. Areas of Rectangles Area Addition Postulate The area of a region is the sum of the areas of its nonoverlapping parts. Areas of Rectangles Theorem The area of a rectangle equals the product of its base and height. A = bh Areas of Rectangles Classify each statement as True or False. 1. If two figures have the same area, then they must be congruent. 2. If two figures have the same perimeter, then they must have the same area. 3. If two figures are congruent, then they must have the same area. 4. Every square is a rectangle. 5. Every rectangle is a square. 6. The base of a rectangle. Areas of Rectangles Classify each statement as true or false. 1. If two figures have the same area, then they must be congruent. False 2. If two figures have the same perimeter, then they must have the same area. False 3. If two figures are congruent, then they must have the same area. True 4. Every square is a rectangle. True 5. Every rectangle is a square. False 6. The base of a rectangle. True Written Exercises Problem Set 11.1, p.427: # 2 - 20 (even); Handout 11-1