Jason Adsit
advertisement

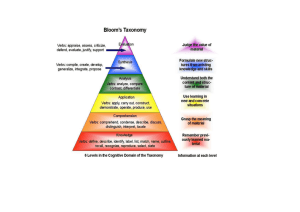
ASSESSING STUDENT LEARNING Jason Adsit – University at Buffalo Some Trends and Topics Internal and external pressures to develop a “culture of assessment” in higher education Shift from a focus on teaching to a focus on student learning Assessment: A Simple Definition Ewell (2001): The methods that an institution or program employs to gather evidence about student learning. Assessment: A Common Definition The process of collecting and analyzing information from multiple sources in order to develop a better understanding of what students know, believe, and are able to do as a result of their educational experiences. The Assessment Process (Suskie, 2009) Establishing clear, well-formulated learning outcomes Ensuring that students have sufficient opportunities to achieve the learning outcomes (through coursework, projects, examinations, etc.) The Assessment Process (Suskie, 2009) Systematically gathering and analyzing evidence and results to determine how well the students have achieved the expected outcomes Using the results to better understand and improve the teaching-learning process DEVELOPING LEARNING OUTCOMES Jason Adsit Background & Overview Goals, Objectives, and Outcomes: What’s the difference? What is a learning outcome? Why are learning outcomes important? What are the core elements of a learning outcome? Outcomes At the end of this session, participants will be able to… …identify the core elements of learning outcomes …explain how learning outcomes connect instruction and assessment …classify the different types of learning outcomes using Bloom’s Taxonomy …analyze the core components of learning outcome statements Why are learning outcomes important? Help foster curricular coherence by connecting classroom activities and assessment Guide instructional planning – content, delivery, and activities/assignments Guide the learner – set priorities and performance expectations Guide evaluation – establish a framework (and set of benchmarks) for assessing learning WHAT IS A LEARNING OUTCOME? Clarifying the muddle of terms… What is a learning objective? Goals Aims Standards Objectives Performance Criteria Benchmarks Measures Etc., etc. What is a learning outcome? General Specific What is a learning outcome? Goal Outcome What is a learning outcome? Clarifying the terminology: University School Program/Major Course Unit/Lesson LEARNING OUTCOMES: A DEFINITION What is a learning outcome? Goal A statement of the intended general aims of an instructional unit, course, or program Global, general Not necessarily measureable Outcome A statement that describes what the learner is expected to know and be able to do as a result of engaging in a learning activity Specific, targeted Measurable Core elements of a learning outcome Learning outcome: A statement (in specific and measureable terms) that describes what the learner will know and be able to do as a result of engaging in a learning activity Core elements of a learning outcome Learning outcome: A statement (in specific and measureable terms) that describes what the learner will know and be able to do as a result of engaging in a learning activity Core elements of a learning outcome Learning outcome: A statement … Outcome = Conditions + Performance + Criteria Conditions Given ‘x’ … Without ‘y’ … Performance …the learner will (verb)… Criteria/Standards Accuracy/Quality Quantity Time Constraints Goals vs. Outcomes Goal 1 At the end of the workshop, participants will understand the role and importance of learning objectives Outcome 1.1 Given a list of ten (10) statements, participants will be able to identify how each statement corresponds to Bloom’s taxonomy of cognitive behavior. Participants who correctly identify nine (9) or more statements will demonstrate sufficient knowledge of the topic Core elements of a learning outcome Learning outcome: A statement (in specific and measureable terms) … Measurable vs. Non-Measurable Terms Non-Measurable Measurable Appreciate Identify Be familiar with Compare Understand Justify Believe Demonstrate Core elements of a learning outcome Learning outcome: A statement (in specific and measureable terms) that describes what the learner will know and be able to do … Come to think of it, what is it that we want the learner to know and be able to do? Classifying Outcomes Bloom (1956) – Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (“Bloom’s Taxonomy”) Cognitive Domain – intellectual thinking or skills Psychomotor Domain – physical skills or the performance of actions Affective Domain – attitudes and values Learning outcome domains “Knowledge, skills, and dispositions” Cognitive Domain (Bloom, 1956) Level/Stage Definition – X is the ability to… Knowledge recall of previously-learned material Comprehension grasp the meaning of the knowledge being learned Application use learning materials in a new way – or for new situations Analysis break material down into its parts so that its organizational structure may be understood Synthesis combine previous experiences with new material to form new structures Evaluation judge the value of material for a given purpose Cognitive Domain (Bloom, 1956) Level/Domain Definition – X is the ability to… Sample Learning Outcome Verbs Knowledge recall of previously-learned material Define, repeat, recall, list, record, outline, specify, state, label, match Comprehension grasp the meaning of the knowledge being learned Identify, explain, recognize, discuss, review, summarize Application use learning materials in a new way – or for new situations Apply, illustrate, show, translate, interpret, employ, use Analysis break material down into its parts so that its organizational structure may be understood Analyze, categorize, inspect, examine, calculate, classify, organize Synthesis combine previous experiences with new material to form new structures Formulate, arrange, assemble, create, organize, manage, predict Evaluation judge the value of material for a given purpose Evaluate, judge, appraise, estimate, compare, assess Core elements of learning outcomes Example: At the end of this statistics lesson, students will be know about the concepts of mean, median, and mode How would you turn this into a learning outcome? What changes might you make to the outcome to assess higher levels of learning (from Bloom’s taxonomy)? Core elements of learning outcomes Example: At the end of this class, students will understand and appreciate the role of the pharmacist in the community How would you turn this into a learning outcome? What changes might you make to the outcome to assess higher levels of learning (from Bloom’s taxonomy)? Core elements of learning outcomes Example: At the end of this unit, students will know about the causes of poverty in Africa How would you turn this into a learning outcome? What changes might you make to the outcome to assess higher levels of learning (from Bloom’s taxonomy)? Core elements of learning outcomes Learning outcome: A statement (in specific and measureable terms) that describes what the learner will know and be able to do as a result of engaging in a learning activity Learning Activities Reverse-engineering your instruction: Identify the learning outcomes Identify the appropriate learning activities – and tailor them to the outcomes Identify the appropriate assessments of student learning Thanks!