Introduction to Database System

Introduction to Database System
Chapter 2:
Database Architecture
Adisak Intana
Lecturer
Table Contents
Database system environment
Database system architecture
Data independence
Database users
Data dictionary
Advantages and disavantages of database system
Introduction to Database System
2
Table Contents
Database system environment
Database system architecture
Data independence
Database users
Data dictionary
Advantages and disavantages of database system
Introduction to Database System
3
File System
A computerized data processing environment which is composed of four major parts :
Hardware
The computer hardware : CPU, mainmemory, and I/O devices
Software
– Application programs
Data is in a collection of independent files
Users
– Naive users
– Application programers
Introduction to Database System
4
File Processing System Environment
Application programs
Operating system
Files
Introduction to Database System
5
Database system
A computerized data processing environment which is composed of four major parts :
Hardware
The computer and the secondary storage devices
Software
Data is in a collection of related files in the form of database
Users
Introduction to Database System
6
Database processing system environment
Application program
DBMS
Operating system
Database
Introduction to Database System
7
Database processing using DBMS
Empl oyee
Custo mer
Produ ct data data
Database
DB
MS
Introduction to Database System
Staff recruitmen t system orders system
Sales accounting system
Departm ent1
Departm ent2
Departm ent3
8
Database
A shared collection of interrelated data.
A collection of data stored in a standardized format and designed to be shared by multiple users.
A collection of persistent related data of interest of a specific enterprize.
Database contains information about a particular enterprise.
Introduction to Database System
9
Units of data
File
Record
Field
Student file :
Student ID
4702777
4702888
Name
Amporn
Sasin
Introduction to Database System
Sex
F
M
Database
Age
18
19
10
Units of data
Physical level
Unit of data used by the hardware of computers.
– Bit
– Byte
– Word
Introduction to Database System
11
Units of data
Logical level
–
Unit of data used or viewed by the users.
Field
–
–
Record
File
– Database
Introduction to Database System
12
Units of data database file record field byte bit
Introduction to Database System
Student and teacher files
Listing of all students in student file
4720777, Amporn, F, 18
Amporn
01001011 (letter K in ASCII)
0 or 1
13
Database management system
(DBMS)
A collection of programs that enables users to modify and extract information from a database.
A suite of programs which typically manage large structured sets of persistent data and offering ad hoc query facilities to many users.
Introduction to Database System
14
Database users
Users in database environment are people whose jobs involve the day-to-day use of large database.
Users are differentiated by the way they expect to interact with the database management system.
– Naive users
Invoke and use the application programs that have been written for specific tasks.
Introduction to Database System
15
Table Contents
Database system environment
Database system architecture
Data independence
Database users
Data dictionary
Advantages and disavantages of database system
Introduction to Database System
16
User1
User work area
Simplified view of database system
User2
User work area
User3
User work area
User4
User work area
Externalal level
Logical database
Physical database
Introduction to Database System
Logical level
Physical level
17
External level
เป็นสถาปัตยกรรมข้อมูลระดับนอกสุด
ใกล้ชิดกับผู้ใช ้ฐานข้อมูลมากที่สุด
เพราะเป็นระดับที่กล่าวถึงมุมมอง
ข้อมูลของผู้ใช ้แต่ละคน (user view)
ผู้ที่เกี่ยวข้องคือ user ที่ใช ้ฐานข้อมูล
Introduction to Database System
18
Logical level
เป็นสถาปัตยกรรมข้อมูลระดับที่อยู่
ระหว่าง Internal กับ External ท า
หน้าที่ถ่ายทอดรูปแบบของ
Physical Level ให้อยู่ในรูปแบบที่
สามารถเข้าใจได้ง่าย (Logical
Structure) ผู้ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับข้อมูล
ในระดับนี้คือ DBA
Introduction to Database System
19
Physical level
เป็นสถาปัตยกรรมฐานข้อมูลระดับในสุด ซึ่ง
อธิบายโครงสร ้างของการจัดเก็บข้อมูลใน
เชิงกายภาพ (Physical Structure) ผู้ที่
เกี่ยวข้องกับระดับนี้คือ DBA และ System
Administrator
Introduction to Database System
20
Example
สถาปัตยกรรมระบบฐานข้อมูลทั้ง 3 ระดับ สามารถ
อธิบายได้โดยใช ้ ฐานข้อมูลระบบงานสินค้าคงคลัง
(northwind) ดังนี้
Physical Level
–
–
–
ฐานข้อมูล Northwind เก็บอยู่ในไฟล ์ที่ชื่อว่า northwind.mdb ซึ่งเป็นไฟล ์ของโปรแกรม MS Access
ท างานอยู่บนระบบปฏิบัติการ MS Windows 95/98
เก็บอยู่ใน directory c:\program files\microsoft office\samples บน Hard Disk ณ ต าแหน่ง Sector
84A6, Track 15, Cylinder 8 เป็นต้น
21
Example
External Level ฐานข้อมูล Northwind แบ่งให้
พนักงานแผนกต่าง ๆ มองเห็นได้ต่างกัน ดังนี้คือ
–
–
–
พนักงานฝ่ายขาย มองเห็นข้อมูลในCaregories, Orders,
Order Details, Products, Categories
พนักงานฝ่ายบุคคล มองเห็นข้อมูลใน Employees, Orders
ผู้จัดการทั่วไป (GM) มองเห็นข้อมูลทั้งหมด
Introduction to Database System
22
Example
Logical Level ฐานข้อมูล Northwind ประกอบด้วย
–
Tables คือ Categories, Customers, Employees, Order
Details, Orders, Products, Shippers และ Suppliers
–
Queries คือ Category Sales for 1995, Current Product
List, Employee Sales by Country,
Introduction to Database System
23
Simplified view of database system
DBA(s)/Programmers/Naive users
Programs/Query Language
Programs/Query Processor
Programs to access stored data
Users’ database
Data dictionary
Introduction to Database System
24
Table Contents
Database system environment
Database system architecture
Database users
Data independence
Data dictionary
Advantages and disavantages of database system
Introduction to Database System
25
Database users
–
–
Application programmers
Write application programs and interact DBMS through database language.
Database administrator
Introduction to Database System
26
Database administrator
Responsible for all the activities of the database system environment.
Must have a good understanding of the enterprise’s information resources and needs.
Introduction to Database System
27
Database administrator
Database administrator's duties include :
– Define the schema
– Define storage structure and access method
– Modify schema and physical organization
– Granting user authority to access the database
– Specifying integrity constraints
– Acting as liaison with users
– Monitoring performance and responding to changes in requirements
Introduction to Database System
28
Table Contents
Database system environment
Database system architecture
Database users
Data independence
Data dictionary
Advantages and disavantages of database system
Introduction to Database System
29
Database independence
The ability to change the description of a database structure at one level of the database system architecture without having to change the description at the next higher level database structure.
Introduction to Database System
30
Table Contents
Database system environment
Database system architecture
Database users
Data independence
Data dictionary
Advantages and disavantages of database system
Introduction to Database System
31
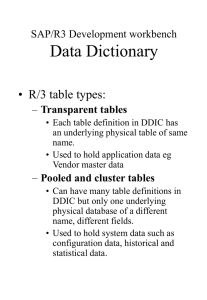
Data dictionary
The data dictionary or system catalog contains metadata
Metadata means
“ data about the data
”
This metadata is the definitions of the structure, data type, integrity constraints, etc. of the database and other objects in the DBMS rather than the users’ raw data.
Introduction to Database System
32
Data dictionary
The data dictionary can be regarded as a database in its own right, but it is the system database rather than user database.
The data in the data dictionary should be integrated into a database with the same structure as the user database.
It should certainly be possible to query the data dictionary just like the users’ database.
Introduction to Database System
33
Example Data dictionary
Introduction to Database System
34
Example Data in Database
Introduction to Database System
35
Table Contents
Database system environment
Database system architecture
Database users
Data independence
Data dictionary
Advantages and disavantages of database system
Introduction to Database System
36
Advantages of database approach
Providing a solution to basic data storage and retrieval.
Providing flexibility and availability of up-tominute information.
Reducing data redundancy.
Obtaining data consistency.
Sharing of data.
Introduction to Database System
37
Advantages of database approach
(continue)
Standard can be enforced.
Ad hoc queries are possible.
Ease of application programs development.
Reduce application program development time.
Uniform security, privacy, and integrity can be applied.
Obtaining data independence.
Introduction to Database System
38
Disadvantages of database approach
High cost
–
–
–
Conversion from file processing to
DBMS
More sophisticated hardware and software
Higher operating costs (personnel)
Complexity of DBMS administration
Vulnerability to failure
Difficulty of recovering & securing data assets
Introduction to Database System
39