Implementation and Assessment of Teaching Methodology
advertisement

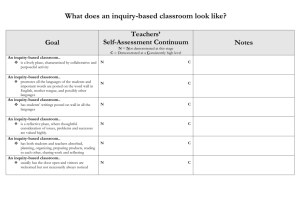
ENGINEERING AND DESIGN: Implementation and Assessment of Teaching Methodologies to Empower Student Learning What pedagogies empower student learning? How do we assess learning? May 14, 2014 Daniela Pusca, Ph.D., P.Eng. Jacqueline Stagner, Ph.D., P.Eng. Concerns at the beginning of the course: • How to make the first year course exciting • How to communicate what engineers actually do • How to develop an understanding of the design processes • How to assess the students’ learning Challenges for The First Year Engineering Students Not familiar with the design process used within engineering May also not recognize the real problem to be solved and what are the limitations in achieving a solution Not familiar with the various aspects of project management Learning Outcomes and the Graduate Attributes Ability to design solutions for openended engineering problems and to design systems and components. Communication skills Teamwork and leadership skills Ability to to identify, formulate, and analyze engineering problems GRADUATE ATTRIBUTES Ability to create, select, apply, and adapt modern engineering tools Learning Outcomes No. Learning Outcome Code 2a Learning Outcome 1 Classify a given problem, and the type of solution sought. 2 3 4 Problem Analysis Determine primary objectives and key constraints. Identify existing solution processes that can be applied to solve a problem. Extract engineering requirements from relevant engineering Codes and Standards. Apply formal idea generation tools to develop a diverse set of candidate engineering design solutions. 2b 2b 4a Use models to generate a diverse set of candidate engineering design solutions. 4b Apply formal multi-criteria decision making tools to select candidate engineering design solutions for further development. Refine a conceptual design into a detailed design. Use of Engineering Tools Create engineering designs: Use of CAD tools. Individual and Team Work Complete a successful project. Illustrate concepts in graphical form. Communication Skills Relate ideas in a multi-modal manner – visually, textually and orally. 4c 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Design Learning Outcomes from the University of Toronto attribute tables posted on the EGAD website, http://egad.engineering.queensu.ca/?page_id=1207 4b 4d 5a 6c 7a 7b Evaluation Methods Method of Evaluation Related Learning Outcomes Mid-Term Exam Learning Outcome 11 Drafting Portfolio: Class Sketches, Laboratory assignments (individual) Design Portfolio (group) Progress Tests I Learning Outcomes 4, 9, 10, 11, and 12 Progress Tests II Learning Outcome 11 Progress Tests III Learning Outcome 11 Progress Tests IV Learning Outcome 9 Oral Presentation Learning Outcome 12 Learning Outcomes 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, and 12 Learning Outcome 11 Methods of Instruction Qualitative Data ISSUES Initial Course Design New Course Design Yes No 1.2.1 Case-based teaching Yes Yes 1.2.2 Inquiry-based learning No Yes 1.2.3 Discovery learning No Yes 1.2.4 Problem/project-based learning Yes Yes 1.0 Course Design 1.1 Traditional teaching methods 1.2 Inductive teaching methods The multitude of approaches that may be used were mapped against what we want students to learn (desired attributes). Methods of Instruction More student-centered, activity-based teaching and learning Inductive teaching methods How it was implemented Students study cases that reflect all of 1.2.1 Case-based teaching the teaching points the instructor wishes to convey. 1.2.2 Inquiry-based Exercises/applications solved during learning lecture time (answer = desired learning) Applications during lecture time: 1.2.3 Discovery learning examination and analysis of given models to discover design concepts 1.2.4 Problem/projectInvolves assignments that call for based learning students to design a product 1.2.1 Case-Based Teaching Students study cases involving scenarios likely to be encountered in professional practice. Example: For each case, be able to IDENTIFY the techniques used to develop concepts • Teflon (Design by accident) • So What’s wrong with Our Toaster? (Checklisting) • Jokes for Trash (Inversion) Source: Engineering by Design author Gerard Voland, Publisher: Prentice Hall, 2004 1.2.2 Inquiry-Based Learning Students are presented with: • a question to be answered / interpreted Accomplish the desired learning in the process of responding to that challenge Example: Circular sweep The desired learning: • an axis of rotation has to be defined • location of the axis relative to the profile can greatly affect the resulting sweep • angular displacements other than 360 degrees can be specified Inquiry-Based Learning Cont’d Example: Circular sweep Challenge: Match the objects with the profiles Source: Introduction to Graphics Communications for Engineers (4th edition), by Gary R. Bertoline, McGraw-Hill Higher Education Inquiry-Based Learning Cont’d Example: Circular sweep Challenge: Match the objects with the profiles Source: Introduction to Graphics Communications for Engineers (4th edition), by Gary R. Bertoline, McGraw-Hill Higher Education 1.2.3 Discovery Learning Learning takes place not through instruction, but through examination and analysis. Example: Visualization by surfaces The desired learning: • to read 2D engineering drawings, • to develop mental 3D images of the objects • to improve the ability to visualize multiview drawings Discovery Learning Cont’d Example: Visualizing 3D objects Challenge: Match the given surface letter from a pictorial drawing with the corresponding surface from the multiview drawing Source: Introduction to Graphics Communications for Engineers (4th edition), by Gary R. Bertoline, McGraw-Hill Higher Education Discovery Learning Cont’d Example: Visualizing 3D objects Challenge: Match the given surface letter from a pictorial drawing with the corresponding surface from the multiview drawing Source: Introduction to Graphics Communications for Engineers (4th edition), by Gary R. Bertoline, McGraw-Hill Higher Education 1.2.3 Problem/Project-Based Learning Project-based learning Problem-based learning •Involves assignments that call for students to design a product •Involves assignments that call for students to design a product •The culmination of the project is a written and oral report summarizing what was done to achieve the final design • The solution process is more important than the final design. • Students apply previously acquired knowledge • Students have not previously received formal instruction in the necessary background material A directed project-based learning approach Implementation Analysis Needs assessment ENGINEERING DESIGN PROCESS Abstraction and synthesis Problem formulation Activity Characteristics: Students work in groups and develop team, leadership, and task completion skills Apply what they were taught during the first part of the lectures: visualisation techniques sketching isometric drawing orthographic projection Students brainstorm different solutions for the design problems Present their ideas through a variety of communication techniques visual written oral Instructor’s role Student-centred teaching Provides the necessary skills for project management and graphical communication of the design solution Promotes positive attitude and group effort Acts as project manager GA’s Role Form the project (design) groups (5-6 students) Guide the students Provide feedback Assist the students to access resources needed to solve the problem/situation Open-Ended Design Projects Assigned: • • • • • • • Aluminum can crusher Toothpaste dispenser Ball return Wheelchair vehicle lift Sports wheelchair Multipurpose ladder for home use Multipurpose study desk Communication Assignments Requirements for each design team: a notebook three milestone reports the final report oral presentation Feedback from Students Regarding PBL • Two questionnaires were delivered in order to assess the new course design from students’ perspective. • Linear scale used: 1=not useful, 2=useful, 3=extremely useful Communication practicesresults based on post-course questionnaire Project managementresults for post-course questionnaire Conclusions Regarding PBL Good aspects associated with the course design Issues that must be improved: • Interactions with TAs • Interactions with team members Positive feedback in regard with communication practices - no average score below 2 Today, the concerns still are: • How to make the first year course exciting • How to better communicate what engineers do • How to develop a better understanding of the design processes • How to assess the students learning Goal Adventurous Exciting Rigorous Creative Demanding