View Session 17 in powerpoint slides [PPT 497.00
advertisement

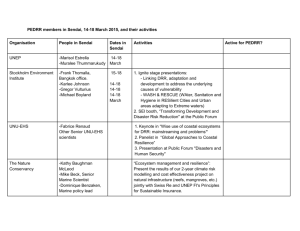
SESSION 17: DISASTER RISK REDUCTION AND EDUCATION Learning Objectives 1. Define DRR and its implications in relation to disaster management. 2. Understand priority actions identified under Hyogo Framework for Action, and particularly education-related 3. Understand why disaster risk reduction/mitigation are increasingly important. 4. Identify critical components of school safety. 5. Review DRR actions that MoE and education actors can support to be practically implemented at school, community and sector levels. Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) Disaster Risk Reduction: Seeks to minimise vulnerabilities and disaster risks throughout a society, to avoid (prevention) or to limit (mitigation and preparedness) the adverse impacts of hazards within the broad context of sustainable development Everyone is involved in DRR! Hyogo Framework for Action The Hyogo Framework for Action (2005-2015) - represents five goals and priorities for action on Disaster Risk Reduction over the next 10 years. 1. Ensure that disaster risk reduction is a national and a local priority with a strong institutional basis for implementation 2. Identify, assess and monitor disaster risks and enhance early warning 3. Use knowledge, innovation and education to build a culture of safety and resilience at all levels 4. Reduce the underlying risk factors 5. Strengthen disaster preparedness for effective response at all levels Why DRR? • Disasters are increasing in frequency and impact • The poorest of society are most affected • Children are proportionally the most vulnerable when disaster strikes • Disasters make the poorest even poorer • DRR is more cost effective than relief and recovery in the long-term: $1 versus $4 Disaster Risk Reduction Activities • Emergency Preparedness • Livelihoods support (including cash transfers, insurance, vouchers) • Early Warning Systems • Inclusion of DRR in Education curricula • Increasing awareness of DRR at all levels • Designing DRR materials for communities and schools • Building cyclone-resistant schools and hospitals School Safety The critical components of school safety are: 1. To save lives and prevent injuries 2. To prevent interruption of education 3. To develop resilient society able to reduce the social, economic, and cultural impacts of recurring hazards DRR and Education • Building a culture of resilience and safety through education • • Incorporation of DRR in national school curricula Teacher training on DRR • Training on school-level risk assessment Development of DRR resources and guidelines Building and retro-fitting school infrastructure to be disaster-resistant Strengthening disaster preparedness in education • • • Exercise: Design of DRR Education Activities In groups, focus on designing DRR interventions for each of the following levels: 1. For children and teachers at school level 2. For communities in disasterprone areas 3. For the Education Sector as a whole and wider government