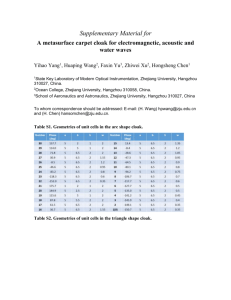
Invis Cloa_higher_f
advertisement

Harry: Invisible Man Is invisibility possible? ?Invisibility? How it works A digital video camera captures the scene. A computer processes the captured image. A projector receives the enhanced image and shines an projected image toward the person wearing the cloak. The cloak acts like a movie screen, reflecting light directly back. Is this any use? Camera Tripod? Bad points Good points •Only works in 2D •Results that work •Shows some reflection •Possible improvements •Not very dynamic! •Inexpensive •Bit of a cheat really!! What is Light? An electromagnetic wave, made up of different wavelengths. See for yourselves!! How does light interact with objects? Natural form of invisibility is an object which neither reflects nor absorbs light (it allows light to pass through it). Absorption - Occurs when electrons absorb light energy Reflection - Occurs strongly in smooth, conducting metals with free electrons Transmission - Occurs strongly when there are large enough gaps between atoms for the light to pass. Does invisibility exist in nature? Secret of the sky practical •Pour water into tank •Shine the flashlight beam through the tank as shown in the diagram. •Hold white paper in the two places shown on the diagram and record what light you see. •Add a pinch of powdered milk and then stir. Repeat the previous step. So why is the sky red/orange at sunset? Are there any invisible materials? Crystals Highly organised “crystaline” structure Exist in crystal planes which light can travel between Man made transparent solids Glass Plastics Boiled Sweets! How do we make glass transparent? Glass is made from sand! Heat to a liquid Made from sand (silica) Glass has strong/rigid bonds like a solid but… An irregular particle structure like a liquid thus allows light to pass Cool to glass Can we use this to make Harry invisible? Not without killing him!! A different approach Can we bend light? Yes - Refraction!! Air Glass When light passes through a material it slows as it has to pass trillions of atoms. The denser the material the “slower” it goes. How does this work? Disappearing bottle Why do the stars twinkle? Everyday examples of Refraction!! Do we need any special materials? Yes! Metamaterials! Metamaterials have properties not found in nature including NEGATIVE refractive index. Metamaterials contain tiny implants which can control the refractive index at every point in a material. This would enable light to meander and bend in a path around an object Cylindrical Cloak 1 mm 2006 a metamaterial made at Durham, North Carolina and Imperial College made an object invisible to microwave radiation. Fiberglass rings patterned with copper elements. The internal structures embedded in the metamaterial must be smaller than the wavelength of the radiation. This device works in the microwave spectrum. http://Duke University cloak Funded by the Pentagon’s Defence Advanced Research Projects Agency [DARPA]. The material properties vary from point to point and in a very specific way. This gives a subtle gradient in the electromagnetic properties of the cloak. Problem The internal structures embedded in the metamaterial must be smaller than the wavelength of the radiation. Wavelength of visible light 380nm (purple) to 780nm (red) We need structures 10s of nms in size How big is a nanometer? 1 m = 1 meter 0.01 m = 1 centimeter 0.001 m = 1 millimeter 0.000001 m = 1 micrometer . 0.000000001 m = 1 nanometer . There are approximately five atoms to 1 nanometer! 50 nanometers 20,000 per 1 mm!!! Is this possible? American news YES!! 2007 California Institute of Technology Is this any use? Claims to work for red light (780 nm) Good points Bad points •The practical data agrees with the theory •Only works in 2D •Large step towards an invisible cloak •Only works for one wavelength (the easiest one too!) David Smith Duke University “A true invisibility cloak IS possible within the laws of physics. With good research it should be a matter of time” Steps to success Invisibility for all wavelengths in 3D (Unclear solution based upon layers) Invisibility for all wavelengths in 2D (Requires complex stacking of wafers) Invisibility for one wavelength in 2D (Requires sophisticated patterns to bend light smoothly) Differences compared with Harry’s cloak This would be a rigid, most likely cylindrical, device. Need flexible metamaterials. Seeing out of any such device would be a problem. A spy hole would mean floating eyes. What are the uses for an invisibility cloak? Hiding Eyesores Police Army Spy on people Stealing Fashion Philosophical View on Invisibility Plato Greek philosopher Born 424 BC, Athens Ring of Gyges Morality is a social construct . The use of invisibility removes this construct and the temptation to steal and kill at will becomes irresistible.