Chapter 3 Plate Tectonics Theory & Evolution
advertisement

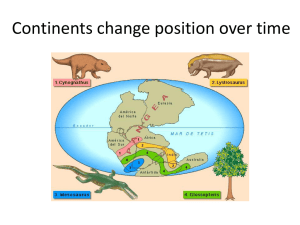
Chapter 3 Plate Tectonics Theory & Evolution Assignment 1 – Summary of Why? • Class results: 35 enrolled students • 22 Seniors • 33 Non Science majors • • • • 7 Fear/Hate math Interests (80% - say need Q GE) to finish or other Alt. E w/ Algae Most “Love the Oceans/Water” want to learn more OUTLINE • • • • • A Theory of Earth Historical Development of Plate Tectonics Earth’s layers Study of Plate Motions Summary of Plate Driving Forces A Theory of Earth • What is the Theory of Plate Tectonics? – Earth crust divided into plates, move independently • In response to? – HEAT FLOW thru crust What is continental drift? The coming together or drifting apart of Continents on the face of earth OUTLINE • • • • • A Theory of Earth Historical Development of Plate Tectonics Earth’s layers Study of Plate Motions Summary of Plate Driving Forces ~1900 MOST Scientists considered Earth to be rigid, Stagnant . . . Wegener’s idea hinted that: Crust (continents) floated in molten fluid • Idea: – Earth’s rigid crust underlain by weak plastic interior. . . RECALL (HOT-molten fluid) ((HOT)) 5500*C 6600*C Using Wegener’s idea – Arthur Holmes (1928) proposes: Mantle convection - serves as driving mechanism for continental drift • What is Mantle convection? – Materials rising from mantle – spread out sideways (laterally) and pulls continents w/ it. Continents move Hot air/liquid rises. . . crust Think of Boiling Pasta MANTLE 1960s New Technolgies • Sonar of ocean shows: – Mid ocean ridges (mtn ranges) Warmcool cool Warm cool cool Warm cool Warm cool cool Heat flow= Greater at Mtn. Ridges At odds w/ idea Of Static earth. . .. With Pangea/Mantle Convection idea Seafloor Spreading concept emerges. . . Dietz/Hess (1960s) What is the idea of Seafloor Spreading? Earth’s crusts being driven apart (laterally) by convection currents. . . Submersibles confirm Mid ocean ridge lateral movement Plate Tectonics/ Seafloor Spreading Submersibles confirm Awesome Biological discoveries – mid ocean Ridges (hydrothermal vents) lateral movement 1970s http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XotF9fzo4Vo&NR=1 2003 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AlHJqA8YkoI Seafloor Spreading Direct evidence was lacking., . . Paleomagnetism (study of magnetic properties in rocks) RECALL + - - (Iron) Over (geologic time-100 Mya) Poles reverse (Polar Reversal) + + + How does this help confirm the theory of continental drift? Curie Point – at certain temp. magnetic properties (elements) of rock solidify Align with earth’s current magnetic field. . . Can determine Position of the “Poles” when the Rock formed. . . Very Old Older Old Vine-Matthews-Morley Hypothesis Using Magnetometer Discovered “Zebra stripes” Indicating polar reversals in seafloor and age distances From mid Ocean Ridge Mid ocean Ridge (Mtn) Where is the seafloor oldest & youngest above? New Newest Plate Tectonics confirmed -What’s really going on. . Mid ocean ridge SeaFloor spreading -makes new ocean crust (basalt) Subduction- removes ocean crust. . .(melts forms coast Mtns) zone •Earth’s layers shifting “Lithospheric plates” That move atop “plastic” . . .Asthenosphere Lithosphere: Oceanic Crust vs Continental Crust • What is their composition? • Which is more dense/why? Granite/quartz (less dense~ 2.7 g cm-3) Mostly Silica/less minerals Mid ocean ridge Basalt (more dense~ 3 g cm-3) Lots of minerals/Iron, nickel etc OUTLINE • • • • • A Theory of Earth Historical Development of Plate Tectonics Earth’s layers Study of Plate Motions Summary of Plate Driving Forces The Major Plates both continental and oceanic How many plates are recognized by the Geophysicists? = 14 (see above) GPS now tracks Plate Movements (via Mtn tops etc.) all moving in diff. directions Types of Plate Boundaries • What are the three types? 1. Peru/Chile trench 2. 3. Convergent boundary (oceanic crust vs oceanic crust) e.g. Marianna Trench • both Forms Mariana Is. 1 crust Subducts Marianna Convergent boundary (oceanic crust vs continental crust) e.g. Peru/Chile & the Andes Mtns Formation of Andes Mtns S. America Plate Melting of Subducted oceanic crust Nasca Plate Convergent boundary (continental crust vs continental crust) e.g. the Himalayas Mtns Mt. Everest http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xL6sKtG2UVs How can Rigid plates can move about a sphere? • Because of the existence of . . . – Transform Faults Relieves built up tension in spreading plates. . Transform Boundaries (faults) -offsets the stress of expanding plates Mid ocean ridge Transform Boundaries (faults) -offsets the stress of expanding plates Hot Spots & Mantle Plumes • What are hotspots? – Stationary locations in the asthenosphere where magma breaks through Diamond Head Hawaii http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hOCfb9ox_90 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GrONBPEgxTc&feature=related e.g. Hawaiian Islands Or Tahiti (Bora bora) Hot Spots (Literally) Tahiti Opening and Closing of Ocean Basins (over geologic time) • The Wilson Cycle – Seafloor spreading Formation of an Ocean Basin e.g. the Atlantic (stable crust) (formation of . . .. . .Mid Ocean ridge) rains fill in etc. Opening and Closing of Ocean Basins (over geologic time) Closing of an Ocean Basin e.g. N. Pacific ~ Eventually Ocean Seafloor age N. Pacific basin eventually swallowed Old New OUTLINE • • • • • A Theory of Earth Historical Development of Plate Tectonics Earth’s layers Study of Plate Motions Summary of Plate Driving Forces Plate Driving Forces (i.e. the “forces” that “move” the “plates”) • What are the two major Models? 1) Convection model Convection currents w/i asthenosphere drive plate motions Magma rises b/c hot Less/dense Magma Sinks b/c cool/dense 2) Ridge-Push, Slab-Pull Model (plain) (plain) hot New crust cooler old crust Major Concepts END on a Nice Note: Tahiti –Bora Bora GPS now tracks Plate Movements (via Mtn tops etc.)