Phylum Annelida
advertisement

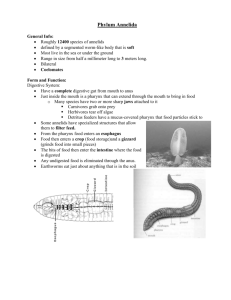
Phylum Annelida Leech Earthworm The Segmented Worms Nereis Are There Many Kinds of Annelids?? • 15,000 species of annelids can be divided into three major groups Polychaeta Oligocheata Hirudinea What Are Annelids? General Characteristics • Bilateral symmetry • Definate anterior / posterior ends • Distinguishable dorsal / ventral side • True tissue / organ level of organization • Segmented bodies • The distinguishing feature of all annelids » Annelida = “little rings” • Range in size • < 1mm up to 3 meters!! » Eg. giant Australian earthworm The Internal Structure of Annelids • Complete digestive tract – Several specialized regions • Circulatory system – Closed vessels – Blood containing hemoglobin • Nervous system – Brain-like structure • Reproductive structures – Ovaries and testes All Annelids Are Coelomates . . . • They have a true body cavity – Coelom is lined with mesoderm cell layer • “Tube-within-a-tube” body plan – Outside tube • Body wall – Inside tube • Digestive tract Annelids are the simplest animals to have a true coelom! What happens to the “stuff” annelids eat?!? • Specialized regions aid in digesting the organic matter in soils ingested – CROP • Temporarily stores food – GIZZARD • Thick walled organ which grinds food Nereis . . . The Hunter • Marine Sandworm – Found at tide level • Carnivorous – Feeds on small animals • Distinct anterior segment – Prostomium • 2 short tentacles + 2 palps • 2 pairs of small eyes – Peristomium • 4 pairs of tentacles surrounding mouth Figure 32-14, Pg. 698 Tentacles Palps How does the pharynx work?? • The pharynx is extended out of the mouth • Pointed claw-like jaws capture prey Pharynx Jaw • Pharynx pulls food back through mouth • Food moves into intestine where digestion begins These Guys Can Move! Parapodia • Nereis have structures allowing them to swim AND creep over sand – Parapodia • Paddle-like extensions – Setae Setae • Bristle-like structures Reproduction in Annelids • Oligochaeta & Hurudinea – Hermaphrodites • Cross-fertilization – Internal fertilization • Polycheata – Separate sexes – External fertilization » Gametes are released through excretory organs » Free-swimming larva Earthworms Create a Cocoon! Clitellum : sperm are stored temporarily until a mucus cocoon is created to protect the fertilized eggs! Leeches: the ecto-parasite! • Feed on the blood of their prey • Hirudin » Enzyme which prevents blood clotting • The jaws break through the host’s skin • Blade-like jaws make incision Two Evolutionary Innovations • The presence of a true coelom – Provides support » Acts as a hydrostatic skeleton – Room for organ development – Advancements in locomotion » Not the dance!!!! . . . Motility!!! • Segmentation of the body – Specialization of body regions » Feeding and sensory input, motility – Modification of various segments for different functions Worms today. . . Mollusks tomorrow! Until then . . . Be kind to your neighborly annelid . . . You may depend on one someday!