Force
advertisement

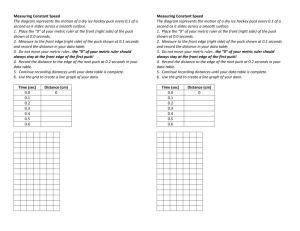
Forces and Motion Scientists construct explanation of phenomena (something that happens) by analyzing a situation, applying ideas and evaluating an explanation. The analysis is good when the interaction is correctly described and the energy diagram (or force diagram) is correct. Source Water Decrease in Motion Energy Receiver Mechanical Energy Water and String Increase in Thermal Energy What we know An ______ applied mechanical interaction occurs when two non-elastic (rigid or stiff) objects push or pull on each other. What we know A ______ friction mechanical interaction occurs when two surfaces rub against each other. What we know A ______ drag mechanical interaction occurs when an object moves through fluid like a gas or a liquid, and the fluid resists the object’s motion. What we know An _______ elastic mechanical interaction occurs when two objects push or pull on each other and at least one of them is stretchy. What we know During a mechanical interaction, mechanical energy is transferred from the source _____ to the receiver. ______. What we know 1. Interactions Ideas 2. Energy Ideas 3. Now we will layer FORCE ideas to explain those same changes in motion during an interaction . What we want to know How do forces affect motion? How does a constant forward force affect motion? How can an arrow be used to represent a force? Background Information Force: A force is a push or pull and has both strength and direction. This idea is represented by a force arrow. What Do You Think? An air puck glides on a cushion of air. The base of the puck has a stem with a small hole drilled down the center. An air-filled balloon fits over the stem. The air from the balloon makes an air cushion for the puck to float on. The air does not push the puck – it just creates a frictionless surface for the puck to glide on. Think about it What does the teacher do? What does the air puck do? Write about it While gliding on a cushion of air, does the puck – speed up – slow down – constant motion? Read about it Read the following thinking bubbles among four students who are trying to account for the puck’s motion as it glides on the cushion of air. The puck looks like it moves with constant speed, but is really slowing down because the hand is no longer pushing it. To keep it moving, you would have to keep pushing it. Write, in Your own Words, Why you Think the Puck had The motion That you Observed. The puck looks like it moves with constant speed, but is really slowing down a bit. Even if the air in the balloon never ran out, the puck would eventually stop because everything eventually slows down and stops. The puck keeps moving because the quick shove the teacher gave it stays with it even after the puck is no longer touching her hand. The puck keeps moving because nothing is stopping it. 1 2 3 4 What Do You Think? If you used a hair dryer to exert a constant force on a small ball, what kind of motion would the ball have? Will it speed up? Or move at a constant speed? Why? Predict and please answer these in your notebook For You To Do – Part A Ball and Hair Dryer: (teacher demo) 1. What kind of motion did the ball have? Did it speed up? Or move at a constant speed? 2. Is this what you predicted in the WDYT section? 3. Please answer in your notebook What Do You Think? Suppose you have a fan connected to a car. (When the fan blades whirl around, they push the air backwards. In return, the air pushes steadily forward on the fan unit and the car.) When the fan is on, the air provides a constant forward force on the car and fan unit. Would the car speed up or have a constant speed? Why? Predict and please answer in your notebook For You To Do – Part A Fan Car (teacher demo). 3. What kind of motion did the car have? Did it speed up? Or move at a constant speed? 4. Is this what you predicted in the WDYT section? Please write this in your notebook Low Friction Car (YOU do it) Now you come up with one or two different ways to exert a constant forward force on the car. This means that any pushing or pulling on the car needs to remain at constant strength. You wll use a low-friction car that has very little friction Between its moving parts. Think about it Describe how you will exert a constant forward force on the low-friction car. Exert a constant forward force on the Car and observe its motion. 6. What kind of motion did the car have? Did it speed up? Or move at a constant speed? 5.