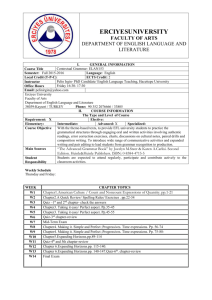
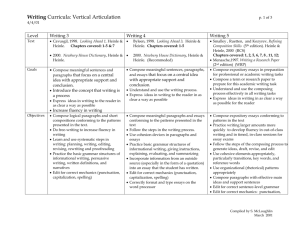
Project work.
advertisement

Alternative assessment Project work Alternative assessment The primary goal of alternative assessment is “to gather evidence about how students are approaching, processing, and completing ‘real-life’ tasks in a particular domain’’ (Garcia & Pearson as cited in Huerta-Macias,2002, p.339) Characteristics of Alternative Assessment Integrate assessment and learning activities. Indicate and highlight successful performance and positive traits. Consider students' needs, interests, and learning styles. Alternative Assessment Options Self- and peerassessment Cooperative test construction Dialogue journals Portfolios Projects Features of Project Work Focus on content learning rather than specific language forms Student-centeredness, as opposed to teacher centeredness Cooperative rather than competitive Authentic integration of skills and processing of info from varied sources Project work culminates in an end product (a stage performance, an oral presentation, etc. (Based on F. Stoller, 2002, p.110 ) Project Stages Classroom planning Real world/carrying out the project Agree on a theme Determine the final project Gathering, analyzing the information Reviewing and monitoring the work (discussion and feedback sessions) Returning to the classroom & presenting final product What about the teacher’s role? To suggest topics for the project. To prepare students for the language demands. To act as a counsellor and consultant Project Types: Collection projects Informational projects Orientation projects Social welfare projects Read more about types of projects and their products in in Teaching English as a second or foreign Language Ed. M. CelceMurcia pp. 339-340 Some project tips: Staff portrait gallery Tourist broadsheets Street interviews on a specific topic Czech/world cuisine in English Twinned towns School Exchange projects ‘Playing’ the role of a museum guide Staging a play for junior students, etc. Suggested reading Eyring, J. (2001).Experiential and negotiated language learning. In M. Celce-Murcia (Ed.), Teaching English as a second or foreign Language (pp.333-344). Heinle & Heinle. Fried-Booth, D.L. (1990). Project work. Oxford University Press. Stoller, F. (2002). Project work: A Means to Promote Language and Content. In J. Richards & W. Renandya (Eds.), Methodology in language teaching: An anthology of current practice (pp. 107-119). Cambridge University Press.